Unit 1 Test: Study Guide PART I: Vocabulary PART II: Grammar and
... withhold self deliberately; refrain; desist Adjective deviating from normal; unusual; irregular Adjective sudden; unexpected; quickly changing AD (to, toward, or near) Part of Speech Definition Verb to change or modify so it’s suitable Adjective mentally or physically dependent on something Adjectiv ...
... withhold self deliberately; refrain; desist Adjective deviating from normal; unusual; irregular Adjective sudden; unexpected; quickly changing AD (to, toward, or near) Part of Speech Definition Verb to change or modify so it’s suitable Adjective mentally or physically dependent on something Adjectiv ...
8 Parts of Speech
... There are six kinds of pronouns: personal, demonstrative, indefinite, intensive, reflexive, and interrogative. ...
... There are six kinds of pronouns: personal, demonstrative, indefinite, intensive, reflexive, and interrogative. ...
Parts of Speech
... To + verb Can act like noun (I like to eat) Can act like adjective (It’s the best place ...
... To + verb Can act like noun (I like to eat) Can act like adjective (It’s the best place ...
Irregular Verbs
... A word which is used to describe a noun to indicate a quality or to determine or limit the noun. Examples of descriptive adjectives are inteligente (intelligent ), pequeño/-a (small). Most adjectives have both masculine and feminine, singular and plural forms: the “masculine” vowel is -o, and the “f ...
... A word which is used to describe a noun to indicate a quality or to determine or limit the noun. Examples of descriptive adjectives are inteligente (intelligent ), pequeño/-a (small). Most adjectives have both masculine and feminine, singular and plural forms: the “masculine” vowel is -o, and the “f ...
Parts of Speech
... He told me that my dog dashed in his backyard. I sprinted as fast as I could and I still lost! (action verbs) I am hungry. (linking verb) I was hoping we could go together. (helping verbs) ...
... He told me that my dog dashed in his backyard. I sprinted as fast as I could and I still lost! (action verbs) I am hungry. (linking verb) I was hoping we could go together. (helping verbs) ...
DAY 127 CAPITALIZATION
... to seem, to stop Sometimes, a catenative verb will have a direct object. Ex.— I managed to splice two wires together. Write a sentence using a catenative verb. to ...
... to seem, to stop Sometimes, a catenative verb will have a direct object. Ex.— I managed to splice two wires together. Write a sentence using a catenative verb. to ...
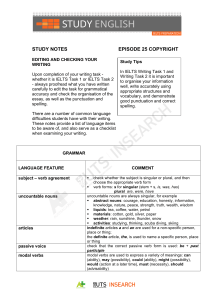
study notes epi - Australia Plus TV
... full stops used at the end of a sentence commas used correctly: • separate items in a list • when a subordinate clause begins the sentence • when sentences are joined by coordinating conjunctions and, or or but, a comma is unnecessary provided b ...
... full stops used at the end of a sentence commas used correctly: • separate items in a list • when a subordinate clause begins the sentence • when sentences are joined by coordinating conjunctions and, or or but, a comma is unnecessary provided b ...
Past participle (solved, run) - Unit Operations Lab @ Brigham Young
... • Aristotle taught that matter comprised earth, wind, fire, and water. (not comprises earth, wind, fire, and water – further note the use of comprise here). ...
... • Aristotle taught that matter comprised earth, wind, fire, and water. (not comprises earth, wind, fire, and water – further note the use of comprise here). ...
Parts of Speech - Flagstaff High School
... * 2. Think of an event in time * Ex: Before breakfast, during breakfast, after breakfast, between breakfast and lunch ...
... * 2. Think of an event in time * Ex: Before breakfast, during breakfast, after breakfast, between breakfast and lunch ...
Parts of Speech
... Relative pronouns: that, which, who, whom, whose Interrogative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which, that Demonstrative pronouns: this, that, these, those Indefinite pronouns: all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, both, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, few, many, neither, nobody, ...
... Relative pronouns: that, which, who, whom, whose Interrogative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which, that Demonstrative pronouns: this, that, these, those Indefinite pronouns: all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, both, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, few, many, neither, nobody, ...
Year 5 Parents Curriculum Presentation
... -These come before nouns or noun phrases A, an, the, this, that, these, those Prepositions - Link nouns or pronouns in a sentence. They usually indicate when or where something happens - About, above, across, after, under, behind, upon, over, between. ...
... -These come before nouns or noun phrases A, an, the, this, that, these, those Prepositions - Link nouns or pronouns in a sentence. They usually indicate when or where something happens - About, above, across, after, under, behind, upon, over, between. ...
Phrases - Huber Heights City Schools
... Verbal phrase- [NOT a verb phrase] = looks like a verb but does not act like a verb Participial phrase (present and past) = always serves as an adjective modifying nouns or pronouns Ex. = I saw two kittens playing happily. Thinking about the snow, Joe pulled on his cap. The very frightened cat ran u ...
... Verbal phrase- [NOT a verb phrase] = looks like a verb but does not act like a verb Participial phrase (present and past) = always serves as an adjective modifying nouns or pronouns Ex. = I saw two kittens playing happily. Thinking about the snow, Joe pulled on his cap. The very frightened cat ran u ...
key exercise p. 7
... 329.1: the determiner few is used with plural nouns; little is used before singular/uncountable nouns 68.1/356.1: we do not use the definite article before most when it means ‘the majority of’ 299.1: the to-infinitive should be used after the verb forget when it refers to the present or future (rath ...
... 329.1: the determiner few is used with plural nouns; little is used before singular/uncountable nouns 68.1/356.1: we do not use the definite article before most when it means ‘the majority of’ 299.1: the to-infinitive should be used after the verb forget when it refers to the present or future (rath ...
Subject-Verb Agreement
... A pronoun replaces a noun in a given sentence. There are various types of pronouns: subject (I, you, he, she, it, we, they), object pronouns (me, you, him, her, it, us, them), Possessive pronouns (mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, yours, theirs), Reflexive (myself, yourself, himself, herself, itsel ...
... A pronoun replaces a noun in a given sentence. There are various types of pronouns: subject (I, you, he, she, it, we, they), object pronouns (me, you, him, her, it, us, them), Possessive pronouns (mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, yours, theirs), Reflexive (myself, yourself, himself, herself, itsel ...
Grammar Blog 2 More Basics. The last blog said that a verb and its
... 1. Nouns can be described by one or more adjectives: e.g. a clever boy, a small red book, outstanding beauty. 2. Verbs can be described by one or more adverbs (usually ending in Cly). e.g. The door slammed loudly. He answered clearly and precisely. He runs fast.) 3. Adverbs can also describe adjecti ...
... 1. Nouns can be described by one or more adjectives: e.g. a clever boy, a small red book, outstanding beauty. 2. Verbs can be described by one or more adverbs (usually ending in Cly). e.g. The door slammed loudly. He answered clearly and precisely. He runs fast.) 3. Adverbs can also describe adjecti ...
ISE Checklist
... The presence of comparison words like "than," "like," and "as" also tends to indicate illogical comparisons A sentence with a list often has a parallelism issue Make sure to watch for redundancy: the use of different two words or phrases that have the same meaning ...
... The presence of comparison words like "than," "like," and "as" also tends to indicate illogical comparisons A sentence with a list often has a parallelism issue Make sure to watch for redundancy: the use of different two words or phrases that have the same meaning ...
here - The Thomas Adams School
... Comparative adjective – comparing two things: today is colder than yesterday Superlative adjective – comparing three or more things: today is the coldest day of the year so far. Comparative adjectives often use the suffix ‘er’ and superlative uses ‘est’, although there are many irregular forms that ...
... Comparative adjective – comparing two things: today is colder than yesterday Superlative adjective – comparing three or more things: today is the coldest day of the year so far. Comparative adjectives often use the suffix ‘er’ and superlative uses ‘est’, although there are many irregular forms that ...
wonderful world of phrases and clauses
... infinitives. If a “to” is followed by a noun, it is being used as a preposition. If it is followed by a verb, then it is an infinitive. ...
... infinitives. If a “to” is followed by a noun, it is being used as a preposition. If it is followed by a verb, then it is an infinitive. ...
daily grammar practice terms monday notes (parts of speech)
... 1. personal (1st person: pronouns having to do with “me”; 2nd person: pronouns having to do with “you”; 3rd person: pronouns having to do with everyone else) ...
... 1. personal (1st person: pronouns having to do with “me”; 2nd person: pronouns having to do with “you”; 3rd person: pronouns having to do with everyone else) ...
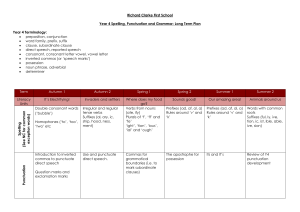
Year 4 SPAG Overview - Richard Clarke First School
... Noun phrases expanded by the addition of modifying adjectives, nouns and preposition phrases (e.g. the teacher expanded to: the strict maths ...
... Noun phrases expanded by the addition of modifying adjectives, nouns and preposition phrases (e.g. the teacher expanded to: the strict maths ...
THE QUESTIONS FOR FINAL EXAMINATION AT ROMANIAN
... 1. Impersonal Moods (Infinitive, Participle, Gerund and Supine); 2. Personal Moods (Indicative, Conjunctive, Conditional); 3. The Indicative Mood (Present, Past, Future Tense); 4. The Conjunctive Mood (Present, Past Tense); 5. The Conditional Mood (Present, Past); 6. Active Voice, Pasive Voice and R ...
... 1. Impersonal Moods (Infinitive, Participle, Gerund and Supine); 2. Personal Moods (Indicative, Conjunctive, Conditional); 3. The Indicative Mood (Present, Past, Future Tense); 4. The Conjunctive Mood (Present, Past Tense); 5. The Conditional Mood (Present, Past); 6. Active Voice, Pasive Voice and R ...