Verb
... particularly in questions or when the sentence begins with there. Examples: o Why are they falling asleep? o There are no excuses for such behavior! TIP! o The subject can come anywhere in a sentence. o Identify the subject correctly, and you’ll be okay! First locate the verb and then just ask yours ...
... particularly in questions or when the sentence begins with there. Examples: o Why are they falling asleep? o There are no excuses for such behavior! TIP! o The subject can come anywhere in a sentence. o Identify the subject correctly, and you’ll be okay! First locate the verb and then just ask yours ...
Grammar Notes - Paulding County Schools
... coordinating (cc): FANBOYS (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) subordinating (sc): start dependent clauses (and therefore must be followed by subject and verb) after, since, before, while, because, although, so that, if, when, whenever, as, even though, until, unless, as if, etc. correlative (co ...
... coordinating (cc): FANBOYS (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) subordinating (sc): start dependent clauses (and therefore must be followed by subject and verb) after, since, before, while, because, although, so that, if, when, whenever, as, even though, until, unless, as if, etc. correlative (co ...
Y4 Literacy Curriculum - Garswood Primary School
... Make appropriate choices of pronoun or noun within a Understand and use the connectives since, during, until, unless, also, thanks to this, as a result, sentence to avoid ambiguity and repetition to express time and cause Expand noun phrases using adjectives and prepositional phrases (the strict ...
... Make appropriate choices of pronoun or noun within a Understand and use the connectives since, during, until, unless, also, thanks to this, as a result, sentence to avoid ambiguity and repetition to express time and cause Expand noun phrases using adjectives and prepositional phrases (the strict ...
Example Of Subject Noun
... Subject is about what or who is spoken in a sentence or clause. The subject can be a person, animal, object, or an abstract concept. Each complete subject is basically constructed by one or more noun or pronoun with / without additional modifier (s) that can be either article (the, an, an), adjectiv ...
... Subject is about what or who is spoken in a sentence or clause. The subject can be a person, animal, object, or an abstract concept. Each complete subject is basically constructed by one or more noun or pronoun with / without additional modifier (s) that can be either article (the, an, an), adjectiv ...
Grammar Launch Organizer - The Liberty Common School
... • Know the following parts of speech and how they are used: nouns (for concrete nouns), pronouns (singular and plural), verbs: action verbs and auxiliary (helping) verbs, adjectives. Grade 4 • Identify subject and verb in a sentence and understand that they must agree. • Know the following parts of ...
... • Know the following parts of speech and how they are used: nouns (for concrete nouns), pronouns (singular and plural), verbs: action verbs and auxiliary (helping) verbs, adjectives. Grade 4 • Identify subject and verb in a sentence and understand that they must agree. • Know the following parts of ...
Example
... (To apologise for something bad. To inform something bad. This is used in more formal situations.) ...
... (To apologise for something bad. To inform something bad. This is used in more formal situations.) ...
Beni Culturali e Spettacolo
... extremely, fairly, highly, quite, slightly, totally, utterly. In informal use, the word pretty is often used as an ...
... extremely, fairly, highly, quite, slightly, totally, utterly. In informal use, the word pretty is often used as an ...
Complements
... of verbs. A direct object is a noun or pronoun that tells who or what receives the action of a verb. A sentence with an direct object may also have an indirect object, a noun or pronoun that tells to or for whom or what the action of the verb is done. (An indirect object never follows a preposition. ...
... of verbs. A direct object is a noun or pronoun that tells who or what receives the action of a verb. A sentence with an direct object may also have an indirect object, a noun or pronoun that tells to or for whom or what the action of the verb is done. (An indirect object never follows a preposition. ...
Clauses - North Pocono School District
... Modify nouns and pronouns Answer the questions which one? ...
... Modify nouns and pronouns Answer the questions which one? ...
13 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement
... Think for a moment about the verbs, walk, run, eat, sleep, try, study, and work. Now, give these verbs the subject “I.” I walk; I run; I eat; the pronoun “I” is the only word that can be a first person subject; likewise, the word “you” is the only word that can be a second person subject. The presen ...
... Think for a moment about the verbs, walk, run, eat, sleep, try, study, and work. Now, give these verbs the subject “I.” I walk; I run; I eat; the pronoun “I” is the only word that can be a first person subject; likewise, the word “you” is the only word that can be a second person subject. The presen ...
unit i (part of speech)
... An adverb is a word that changes or qualifies the meaning of a verb, adjective, other adverb, clause, sentence or any other word or phrase, except that it does not include the adjectives and determiners that directly modify nouns. Adverbs are traditionally regarded as one of the parts of speech. Adv ...
... An adverb is a word that changes or qualifies the meaning of a verb, adjective, other adverb, clause, sentence or any other word or phrase, except that it does not include the adjectives and determiners that directly modify nouns. Adverbs are traditionally regarded as one of the parts of speech. Adv ...
Shurley English Level 4 Student Textbook
... 1. If there is only a main verb in a sentence, the tense is determined by the main verb and will be either present tense or past tense. 2. If there is a helping verb with a main verb, the tense of both verbs is determined by the helping verb, not the main verb. If there is more than one helping verb ...
... 1. If there is only a main verb in a sentence, the tense is determined by the main verb and will be either present tense or past tense. 2. If there is a helping verb with a main verb, the tense of both verbs is determined by the helping verb, not the main verb. If there is more than one helping verb ...
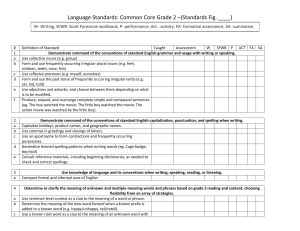
Language Standards: Common Core Grade 2 –(Standards Fig
... Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage with writing or speaking. Use collective nouns (e.g. group) Form and use frequently occurring irregular plural nouns (e.g. feet, children, teeth, mice, fish) Use reflexive pronouns (e.g. myself, ourselves) Form and use the ...
... Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage with writing or speaking. Use collective nouns (e.g. group) Form and use frequently occurring irregular plural nouns (e.g. feet, children, teeth, mice, fish) Use reflexive pronouns (e.g. myself, ourselves) Form and use the ...
Glossary of Writing Terms
... MCTC offers students a great education. Parts of Speech (verbs, nouns, pronouns, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections) – the categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences Prepositions – describes a relationship between other words in a ...
... MCTC offers students a great education. Parts of Speech (verbs, nouns, pronouns, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections) – the categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences Prepositions – describes a relationship between other words in a ...
porto - Humble ISD
... passive personal endings makes these verbs either active or passive. *There are a few stem vowel changes, such as in the Future tense of 1st and 2nd conjugations, ...
... passive personal endings makes these verbs either active or passive. *There are a few stem vowel changes, such as in the Future tense of 1st and 2nd conjugations, ...
Form and meaning in the sentence.
... 1. How and why we build sentences. Our mind builds sentences by combining words, in order to express meanings. Notice that the form of a word does not directly depend on its meaning: We say that the relationship between form and meaning is arbitrary. In other words there is nothing in table that mak ...
... 1. How and why we build sentences. Our mind builds sentences by combining words, in order to express meanings. Notice that the form of a word does not directly depend on its meaning: We say that the relationship between form and meaning is arbitrary. In other words there is nothing in table that mak ...
Nouns-les noms
... department, le tableau). Probably the easiest way to master the idea of gender is by learning nouns with their article: le, un for a masculine noun; la, une for a feminine noun. Plurals are most commonly formed by the addition of –s to the singular; there are however a number of other ways to indica ...
... department, le tableau). Probably the easiest way to master the idea of gender is by learning nouns with their article: le, un for a masculine noun; la, une for a feminine noun. Plurals are most commonly formed by the addition of –s to the singular; there are however a number of other ways to indica ...
Grammar & Mechanics
... Preposition- a word that links nouns, pronouns, and phrases and signals the beginning of a prepositional phrase. Up, on, upon, by, to, and down are some examples of prepositions. Prepositional Phrase Ex: by the barking dog Prepositional Phrase Ex: She quickly ran by the barking dog. ...
... Preposition- a word that links nouns, pronouns, and phrases and signals the beginning of a prepositional phrase. Up, on, upon, by, to, and down are some examples of prepositions. Prepositional Phrase Ex: by the barking dog Prepositional Phrase Ex: She quickly ran by the barking dog. ...
the parts of speech
... plan into action. [Putting their plan into action is the direct object of the verb avoid. Plan is the direct object of the gerund putting. ...
... plan into action. [Putting their plan into action is the direct object of the verb avoid. Plan is the direct object of the gerund putting. ...
Subject and Object Complements Notes
... o Completes the meaning of the direct object in a sentence o Found only after verbs such as appoint, call, consider, elect, label, make, name, or think. Ex: The President named her administrator of NASA. I consider her the best candidate for the job. ...
... o Completes the meaning of the direct object in a sentence o Found only after verbs such as appoint, call, consider, elect, label, make, name, or think. Ex: The President named her administrator of NASA. I consider her the best candidate for the job. ...
Subjects and Verbs Handout
... If you know that list is the subject, then you will choose is for the verb. Being able to identify the subject and verb correctly will also help you with commas and semicolons as you will see later. Definition. A Verb is a word that shows action (runs, hits, slides) or state of being (is, are, was, ...
... If you know that list is the subject, then you will choose is for the verb. Being able to identify the subject and verb correctly will also help you with commas and semicolons as you will see later. Definition. A Verb is a word that shows action (runs, hits, slides) or state of being (is, are, was, ...
Tema/Topic:______ Nombre/Clase/Fecha: - yo-amo
... Nombre/Clase/Fecha:__________________________ Words that are similar in English and in Spanish. ...
... Nombre/Clase/Fecha:__________________________ Words that are similar in English and in Spanish. ...
Unit 1: The Nuts and bolts of English Nouns
... Notice that verbs do not appear in a future form. There is no future verb for walk or any other verb in the English language. When we want to talk about a walk in the future, we often say, we will walk or we are going to walk. We will deal with future tense constructions in greater detail in the ...
... Notice that verbs do not appear in a future form. There is no future verb for walk or any other verb in the English language. When we want to talk about a walk in the future, we often say, we will walk or we are going to walk. We will deal with future tense constructions in greater detail in the ...
Chapter 5 Slides - USC Upstate: Faculty
... “Sometimes people are just trying to make their mark. Just like there are select words that only certain people you know say.” ...
... “Sometimes people are just trying to make their mark. Just like there are select words that only certain people you know say.” ...