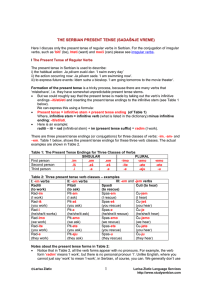
the serbian present tense (sadašnje vreme)
... verbs, such as ‘biti’ (be), hteti (want) and moći (can) please see irregular verbs. I The Present Tense of Regular Verbs The present tense in Serbian is used to describe: i) the habitual action: Ja plivam svaki dan. ‘I swim every day’ ii) the action occurring now: Ja plivam sada. ‘I am swimming now’ ...
... verbs, such as ‘biti’ (be), hteti (want) and moći (can) please see irregular verbs. I The Present Tense of Regular Verbs The present tense in Serbian is used to describe: i) the habitual action: Ja plivam svaki dan. ‘I swim every day’ ii) the action occurring now: Ja plivam sada. ‘I am swimming now’ ...
4th Grade Language Curriculum
... Prepositional Phrase - A prepositional phase (a group of two or more words) begins with a preposition and ends with a noun or pronoun (usually something you can see). It may end with an abstract noun (with much happiness), but usually ends with a concrete noun (with my dad). A phrase doesn t express ...
... Prepositional Phrase - A prepositional phase (a group of two or more words) begins with a preposition and ends with a noun or pronoun (usually something you can see). It may end with an abstract noun (with much happiness), but usually ends with a concrete noun (with my dad). A phrase doesn t express ...
Understanding Sentences
... Adverb clauses can be used in the same way that adverbs are used. They will answer “how,” “when,” “where,” “why,” or “how much” about a verb, adjective, or adverb. They are introduced by a subordinating conjunction—after, although, as, as if, as ____ as, because, before, if, in order that, since, s ...
... Adverb clauses can be used in the same way that adverbs are used. They will answer “how,” “when,” “where,” “why,” or “how much” about a verb, adjective, or adverb. They are introduced by a subordinating conjunction—after, although, as, as if, as ____ as, because, before, if, in order that, since, s ...
englishgrammarbook (1)
... A preposition usually indicates the temporal, spatial or logical relationship of its object to the rest of the sentence as in the following examples: The book is on the table. The book is beneath the table. The book is leaning against the table. The book is beside the table. She held the book over t ...
... A preposition usually indicates the temporal, spatial or logical relationship of its object to the rest of the sentence as in the following examples: The book is on the table. The book is beneath the table. The book is leaning against the table. The book is beside the table. She held the book over t ...
Phrases and Clauses
... Clauses can be joined with: 1. Coordinating conjunctions (join two independent clauses) - AKA “FANBOYS” for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so 2. Subordinating conjunctions (join dependent clause to independent clause) Some examples: - if, since, because, with, when, whether, while 3. Relative Pronouns - w ...
... Clauses can be joined with: 1. Coordinating conjunctions (join two independent clauses) - AKA “FANBOYS” for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so 2. Subordinating conjunctions (join dependent clause to independent clause) Some examples: - if, since, because, with, when, whether, while 3. Relative Pronouns - w ...
Grammar Review parts of speech
... Day One of the Grammar Review – The Essential Parts of Speech There are eight parts of speech, but we are going to focus on four key ones today. If you can understand the function of the noun, verb, adjective, and adverb, you will be more successful in the world of grammar. The Noun You all know tha ...
... Day One of the Grammar Review – The Essential Parts of Speech There are eight parts of speech, but we are going to focus on four key ones today. If you can understand the function of the noun, verb, adjective, and adverb, you will be more successful in the world of grammar. The Noun You all know tha ...
Noun: A noun is a person, place, thing, quality, or act
... Examples: pencil, girl, supermarket, happiness Verb: Verbs are action or existence words that tell what nouns do. Examples: to fly, to run, to be, jump, lived Adjective: An adjective describes a noun. Examples: hairy, crazy, wonderful Adverb: An adverb describes a verb, adjective, or adverb. It ofte ...
... Examples: pencil, girl, supermarket, happiness Verb: Verbs are action or existence words that tell what nouns do. Examples: to fly, to run, to be, jump, lived Adjective: An adjective describes a noun. Examples: hairy, crazy, wonderful Adverb: An adverb describes a verb, adjective, or adverb. It ofte ...
Phrases and Clauses - CCSS7thGradeEnglishMaterials
... Clauses can be joined with: 1. Coordinating conjunctions (join two independent clauses) - AKA “FANBOYS” for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so 2. Subordinating conjunctions (join dependent clause to independent clause) Some examples: - if, since, because, with, when, whether, while 3. Relative Pronouns - w ...
... Clauses can be joined with: 1. Coordinating conjunctions (join two independent clauses) - AKA “FANBOYS” for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so 2. Subordinating conjunctions (join dependent clause to independent clause) Some examples: - if, since, because, with, when, whether, while 3. Relative Pronouns - w ...
sentence construction - Groton Public Schools
... 6. The damages (were, was) not serious, but the cost of repairs was over a thousand dollars. 7. My head (feel, feels) as if it is about to burst. 8. Joseph (have, has) two sisters, one brother, and several pets. 9. When a tree (fall, falls) in a forest and no one is present, does it make a sound? 10 ...
... 6. The damages (were, was) not serious, but the cost of repairs was over a thousand dollars. 7. My head (feel, feels) as if it is about to burst. 8. Joseph (have, has) two sisters, one brother, and several pets. 9. When a tree (fall, falls) in a forest and no one is present, does it make a sound? 10 ...
Dating archaicness in Indo- European languages: various issues
... valence augmented by a second or indirect object, or an opposition of speech-act participant vs. non-participant in indirect-object marking on the verb). 27. Active verbs have more morphological variation or make more morphological distinctions than inactive verbs. 28. The morphological category of ...
... valence augmented by a second or indirect object, or an opposition of speech-act participant vs. non-participant in indirect-object marking on the verb). 27. Active verbs have more morphological variation or make more morphological distinctions than inactive verbs. 28. The morphological category of ...
Communication Profile
... plural “s” irregular plural (child, children) first/second person subject pronoun (I, you, it) third person subject pronoun (he, she) plural subject pronoun (we, they) object pronoun (me, him, her, us, them) possessive pronoun (his, hers, ours, theirs reflexive pronoun (myself, yourself, itself) pre ...
... plural “s” irregular plural (child, children) first/second person subject pronoun (I, you, it) third person subject pronoun (he, she) plural subject pronoun (we, they) object pronoun (me, him, her, us, them) possessive pronoun (his, hers, ours, theirs reflexive pronoun (myself, yourself, itself) pre ...
9 LP 4 sub verb agree KEY
... Collective nouns need a plural verb when the group Statistics is not a required course for theater majors. acts as individuals. The audience arrive at the theater at different times. These statistics show that people prefer musicals to dramas. Indefinite Pronouns Indefinite pronouns such a ...
... Collective nouns need a plural verb when the group Statistics is not a required course for theater majors. acts as individuals. The audience arrive at the theater at different times. These statistics show that people prefer musicals to dramas. Indefinite Pronouns Indefinite pronouns such a ...
Useful First-Conjugation Verbs Ending in
... essi they (masculine), and esse they (feminine). In English, subject pronouns must be used with verbs. In Italian, however, the forms of the verb change to show who the subject is, and pronouns are used only for emphasis or contrast. Italian verbs are divided into three groups, called conjugations. ...
... essi they (masculine), and esse they (feminine). In English, subject pronouns must be used with verbs. In Italian, however, the forms of the verb change to show who the subject is, and pronouns are used only for emphasis or contrast. Italian verbs are divided into three groups, called conjugations. ...
simple and compound Tenses.
... We shall be limiting ourselves in this section to four simple tenses, whose salient features and equivalents in English are shown below. Compound Tensesare treated in a separate section. The tenses we will deal with here are the present, the imperfect, the future and the conditional present. The Pas ...
... We shall be limiting ourselves in this section to four simple tenses, whose salient features and equivalents in English are shown below. Compound Tensesare treated in a separate section. The tenses we will deal with here are the present, the imperfect, the future and the conditional present. The Pas ...
Present, Past, and Future Tenses
... The present tense of the verb is the base form of the verb. When the subject is a singular noun or he, she, or it, you usually add s to the verb. ...
... The present tense of the verb is the base form of the verb. When the subject is a singular noun or he, she, or it, you usually add s to the verb. ...
Subject Verb Agreement reminders
... Like most pronouns, the relative pronouns who, which, and that have antecedents, nouns or pronouns to which they refer. Relative pronouns used as subjects of subordinate clauses take verbs that agree with their antecedents. Take a dress that travels well. Our ability to use language is one of the th ...
... Like most pronouns, the relative pronouns who, which, and that have antecedents, nouns or pronouns to which they refer. Relative pronouns used as subjects of subordinate clauses take verbs that agree with their antecedents. Take a dress that travels well. Our ability to use language is one of the th ...
Present, Past, and Future Tenses
... The present tense of the verb is the base form of the verb. When the subject is a singular noun or he, she, or it, you usually add s to the verb. ...
... The present tense of the verb is the base form of the verb. When the subject is a singular noun or he, she, or it, you usually add s to the verb. ...
Verb-Tenses
... The present tense of the verb is the base form of the verb. When the subject is a singular noun or he, she, or it, you usually add s to the verb. ...
... The present tense of the verb is the base form of the verb. When the subject is a singular noun or he, she, or it, you usually add s to the verb. ...
All About Gerunds, Participles, and Infinitives
... There are also helping verbs. • Helping verbs always help either an action verb or a linking verb. • I will play the piano. (will = helping verb, play = action verb) • I will be a teacher. (will = helping verb, be = linking verb) ...
... There are also helping verbs. • Helping verbs always help either an action verb or a linking verb. • I will play the piano. (will = helping verb, play = action verb) • I will be a teacher. (will = helping verb, be = linking verb) ...
Basic Sentences
... • A verb is a word used to describe an action, state, or occurrence. • The verb forms the main part of the predicate. • A predicate is the part of the sentence or clause that contains a verb. • In a sentence, the verb has to tell: 1) What is done to the subject. 2) What the subject does. 3) What the ...
... • A verb is a word used to describe an action, state, or occurrence. • The verb forms the main part of the predicate. • A predicate is the part of the sentence or clause that contains a verb. • In a sentence, the verb has to tell: 1) What is done to the subject. 2) What the subject does. 3) What the ...
Chapter 2
... When we want to say that something is not true or is not the case, we can use negative words, such as “not.” When we use be as a main verb, we simply put not after the form of be as in: 1. She is not a student. 2. They are not students. In case we don’t have an auxiliary verb or the verb is not “be” ...
... When we want to say that something is not true or is not the case, we can use negative words, such as “not.” When we use be as a main verb, we simply put not after the form of be as in: 1. She is not a student. 2. They are not students. In case we don’t have an auxiliary verb or the verb is not “be” ...
100305 Research Day 26
... 4. Infinitive phrases, which begin with an infinitive and include the object of the infinitive or other words that are acting as part of the phrase. 5. Appositive phrases, which are nouns or pronouns desctibing another noun or pronoun in the sentence. ...
... 4. Infinitive phrases, which begin with an infinitive and include the object of the infinitive or other words that are acting as part of the phrase. 5. Appositive phrases, which are nouns or pronouns desctibing another noun or pronoun in the sentence. ...
LEVEL: INTERMEDIATE Purpose clauses They are introduced by
... Word order: purpose clauses can have an initial (in more formal contexts) or final position (i.e. they can be used before or after the main clause), but those introduced with “so that” and “so as to” have a final position: 1) (In order) + to infinitive …, / subject + main verb…: In order to achieve ...
... Word order: purpose clauses can have an initial (in more formal contexts) or final position (i.e. they can be used before or after the main clause), but those introduced with “so that” and “so as to” have a final position: 1) (In order) + to infinitive …, / subject + main verb…: In order to achieve ...