Pride/Hughes/Kapoor Business, 10th Edition
... competition is the market situation in which there are many buyers and sellers of a product, and no single buyer or seller is powerful enough to affect the price of that product. All buyers and sellers together determine the price of a product through the forces of supply and demand. The supply is t ...
... competition is the market situation in which there are many buyers and sellers of a product, and no single buyer or seller is powerful enough to affect the price of that product. All buyers and sellers together determine the price of a product through the forces of supply and demand. The supply is t ...
monopoly - WordPress.com
... The government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce some good or servicepublic franchise, government license, patent, copyright. The costs of production make a single producer more efficient than a large number of producers- Natural Monopoly ...
... The government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce some good or servicepublic franchise, government license, patent, copyright. The costs of production make a single producer more efficient than a large number of producers- Natural Monopoly ...
Concepts For Micro Theory
... "moon" shaped tangency of budget line & indiff curve normal vs. inferior goods complementary vs. substitute goods derivation of demand curves ...
... "moon" shaped tangency of budget line & indiff curve normal vs. inferior goods complementary vs. substitute goods derivation of demand curves ...
Word Doc
... Monopoly causes in an inefficient allocation of resources by restricting output below what would be achieved by a competitive market. As a result, there is a deadweight loss in welfare. In addition, monopoly redistributes gains from consumers to producers by transferring some consumer surplus to pro ...
... Monopoly causes in an inefficient allocation of resources by restricting output below what would be achieved by a competitive market. As a result, there is a deadweight loss in welfare. In addition, monopoly redistributes gains from consumers to producers by transferring some consumer surplus to pro ...
Explain the difference between short-run and long-run
... Monopolistic Competition is a market structure featuring few large and many small firms, fairly low entry barriers similar goods and relatively high competition. Over the short-run, firms can usually gain some abnormal profit, but over the long run, other firms entering the market due to the low ent ...
... Monopolistic Competition is a market structure featuring few large and many small firms, fairly low entry barriers similar goods and relatively high competition. Over the short-run, firms can usually gain some abnormal profit, but over the long run, other firms entering the market due to the low ent ...
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy
... Managing a Monopoly • Market power permits you to price above MC • Is the sky the limit? • No. How much you sell depends on the price you set! ...
... Managing a Monopoly • Market power permits you to price above MC • Is the sky the limit? • No. How much you sell depends on the price you set! ...
HW 4 - Part II Cost and PC Markets-1
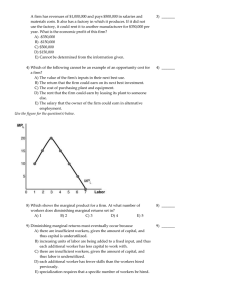
... B) A firm decides how many units to produce by comparing marginal revenue with marginal cost. C) As long as variable costs are covered, the firm will produce the number of units where MR equals MC. D) If price is below AVC, the firm will not produce any units. E) A firm in perfect competition has a ...
... B) A firm decides how many units to produce by comparing marginal revenue with marginal cost. C) As long as variable costs are covered, the firm will produce the number of units where MR equals MC. D) If price is below AVC, the firm will not produce any units. E) A firm in perfect competition has a ...
Chapter 18 The markets for the factors of production Factors of
... labor hour or machine hour), all other factors remaining constant. ...
... labor hour or machine hour), all other factors remaining constant. ...
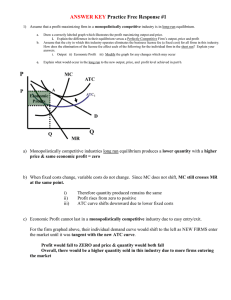
ANSWER KEY Practice Free Response
... a) Monopolistically competitive industries long run equilibrium produces a lower quantity with a higher price & same economic profit = zero ...
... a) Monopolistically competitive industries long run equilibrium produces a lower quantity with a higher price & same economic profit = zero ...
6Review questions 2
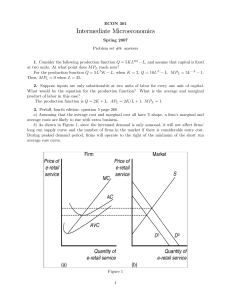
... b. Suppose that currently there are 90 firms active in this market. Compute the equilibrium price. c. Compute the price elasticity of the market demand at the equilibrium price. Is it elastic or inelastic? d. Write the equation for the residual demand for firm j. Assume that all firms other than j p ...
... b. Suppose that currently there are 90 firms active in this market. Compute the equilibrium price. c. Compute the price elasticity of the market demand at the equilibrium price. Is it elastic or inelastic? d. Write the equation for the residual demand for firm j. Assume that all firms other than j p ...
Lecture 19
... • The major market forms are: – Perfect competition, in which the market consists of a very large number of firms producing a homogeneous product. – Monopolistic competition, also called competitive market, where there are a large number of independent firms which have a very small proportion of the ...
... • The major market forms are: – Perfect competition, in which the market consists of a very large number of firms producing a homogeneous product. – Monopolistic competition, also called competitive market, where there are a large number of independent firms which have a very small proportion of the ...
Week 6 In-class Cost and PC Markets
... B) A firm decides how many units to produce by comparing marginal revenue with marginal cost. C) As long as variable costs are covered, the firm will produce the number of units where MR equals MC. D) If price is below AVC, the firm will not produce any units. E) A firm in perfect competition has a ...
... B) A firm decides how many units to produce by comparing marginal revenue with marginal cost. C) As long as variable costs are covered, the firm will produce the number of units where MR equals MC. D) If price is below AVC, the firm will not produce any units. E) A firm in perfect competition has a ...
Study guide 2005 1 st mid-term
... 1. (30 points) Assume that a retail clothing store is operating under conditions of monopolistic competition. First draw a diagram showing the firm when the industry is in long-run equilibrium. Then draw a diagram showing the impact of an increase in the demand for clothing on its output, price and ...
... 1. (30 points) Assume that a retail clothing store is operating under conditions of monopolistic competition. First draw a diagram showing the firm when the industry is in long-run equilibrium. Then draw a diagram showing the impact of an increase in the demand for clothing on its output, price and ...
EcN212EX3
... marginal revenue is less than marginal cost b. the wage rate is higher than the average total cost. c. total revenue exceeds total cost d. the value of marginal product of labor exceeds the wage rate ...
... marginal revenue is less than marginal cost b. the wage rate is higher than the average total cost. c. total revenue exceeds total cost d. the value of marginal product of labor exceeds the wage rate ...
Chapter 6: The Role of Profit
... The effects of profit-maximizing behavior on consumers in each market structure The short-run and long-run outcomes of profit-maximizing behavior natural monopolies and how governments regulate them ...
... The effects of profit-maximizing behavior on consumers in each market structure The short-run and long-run outcomes of profit-maximizing behavior natural monopolies and how governments regulate them ...
Chapter Summaries
... 2A market structure is a model of the producing and selling environments in which firms operate. The three characteristics that define market structure are the number of firms, the ease of entry, and whether the products are differentiated. §2.a ...
... 2A market structure is a model of the producing and selling environments in which firms operate. The three characteristics that define market structure are the number of firms, the ease of entry, and whether the products are differentiated. §2.a ...
Chapter 5 Supply
... Supply: amount of a product that would be offered for sale at all possible prices Law of Supply: suppliers will offer more products at higher prices than at low Quantity Supplied: amount of a product that producers bring to market at any given price Supply Curve: graph showing the various quantities ...
... Supply: amount of a product that would be offered for sale at all possible prices Law of Supply: suppliers will offer more products at higher prices than at low Quantity Supplied: amount of a product that producers bring to market at any given price Supply Curve: graph showing the various quantities ...