* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 Supply
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Supply chain management wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
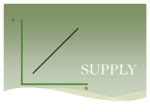
Chapter 5 Supply Supply: amount of a product that would be offered for sale at all possible prices Law of Supply: suppliers will offer more products at higher prices than at low Quantity Supplied: amount of a product that producers bring to market at any given price Supply Curve: graph showing the various quantities supplied at each and every price Market Supply Curve: graph that shows the Q of a product offered at various P by all firms that offer the product Change in Supply: situation in which suppliers offer different amounts of products for sale at all possible P (pg. 117) Break Even Point: total product a firm must sell to cover its costs Raw Materials: unprocessed natural products Subsidy: govt. payment to encourage or protect economic production Short Run: period of production that’s too short for any adjustments in production except for changes in L Long Run: period of prod. That’s long enough for adj. in all resources Supply Elasticity measure of the way Q S responds to changes in P Theory of Production: the relationship between factors of production and the output of G&S E-Commerce: electronic business or exchanges over the internet Fixed costs are minimal, reach more customers Fixed Cost: costs a business incurs even if nothing is produced Variable Cost: cost that changes when output changes Total Cost: sum of fixed and variable costs Total Revenue: # of units sold multiplied by avg. price per unit