* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Supply Powerpoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
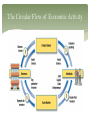
SUPPLY Objectives Explain that market supply is based on each seller’s cost and the number of sellers in the market; analyze the effect of factors that can change supply. Big Questions What is Supply? What causes a change in Supply? What is Supply? Supply is defined as the amount of a product that would be offered for sale at all possible prices that could prevail in the market. Law of Supply The basic law of supply is common sense: as prices rise, supply increases; as prices fall, supply decreases. The Supply Curve Supply curves are a lot like demand curves. Information about the amount of a specific good or service that a provider will supply at various prices is plotted on a graph like this. Price is on the vertical axis, Quantity is on the horizontal. Supply curves slope upward, reflecting the Law of Supply. Higher Price = Higher Quantity Change in Supply Factors that can cause a Change in Supply • Cost of Inputs • Government regulations • Productivity • The number of • Technology competitors • Taxes and subsidies • Expectations Cost of Inputs (Factors of Production) As production costs change, a producer’s willingness and ability to supply a product at a specific price will change. The Circular Flow of Economic Activity Cost of Inputs (Factors of Production) Land Labor Capital Entrepreneurship Cost of Inputs (Factors of Production) Increased production costs will decrease supply and shift the supply curve to the left. Cost of Inputs (Factors of Production) If a product becomes cheaper to produce, suppliers will offer more for sale at each market price. The supply curve shifts to the right. Productivity When management motivates its workers, or if workers decide to work more efficiently, productivity should increase. The result is more can be produced at every price. The supply curve shifts to the right. Happy workers = more productivy = increased supply Technology The introduction of a new machine, chemical, or industrial process can affect supply by lowering the cost of production or by increasing productivity. New technology = greater productivity = increased supply Technology New technologies do not always work as expected, of course. Equipment can break down and shift the curve to the left. Technology Fail = lower productivity = lower supply Taxes and Subsidies Firms view taxes as costs. If taxes increase, the cost of production goes up, supply decreases. Conversely, if taxes decrease, firms will supply more. A subsidy is a government payment to an individual, business, or other group to encourage or protect a certain type of economic activity. The government pays suppliers to guarantee a consistent supply. The subsidy lowers production costs and allows for greater supply. Expectations Expectations about the future price of a product can also affect the supply curve. If producers think the price of a product will go up, they may withhold some of the supply. Government Regulations When the government establishes new regulations, the cost of production can be affected, causing a change in supply. In general, Increased regulations = increased production costs = lower supply. Relaxed regulations = Greater supply. We can talk about externalities later. Number of Sellers A change in the number of suppliers causes the market supply curve to shift to the right or left. The larger the number of suppliers, the greater the market supply. Reverse is also true. Elasticity of Supply Supply elasticity is a measure of the way in which quantity supplied responds to a change in price. Determinants of Supply Elasticity Only Production considerations determine supply elasticity. If a firm can react quickly to higher or lower prices, then supply is likely to be elastic. If the firm takes longer to react, supply is inelastic. What is better for the firm?