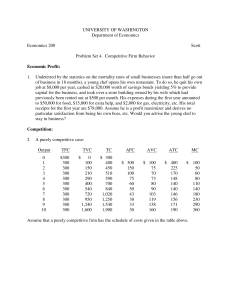
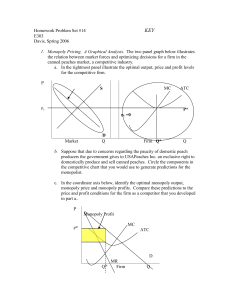
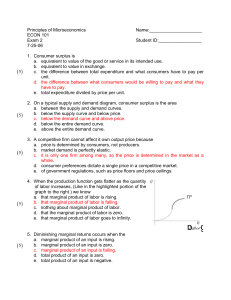
Answers to Extra Practice Quiz
... The value of total surplus in a perfectly competitive market is the sum of consumer plus producer surplus. In this example, CS = $500 and PS = $250. Total surplus is therefore equal to $750. 3. (1 point) In the class we have talked about how a firm profit maximizes by producing that level of output ...
... The value of total surplus in a perfectly competitive market is the sum of consumer plus producer surplus. In this example, CS = $500 and PS = $250. Total surplus is therefore equal to $750. 3. (1 point) In the class we have talked about how a firm profit maximizes by producing that level of output ...
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy
... • Short run profits leads to entry. • Entry increases market supply, drives down the market price, increases the market quantity. • Demand for individual firm’s product shifts down. • Firm reduces output to maximize profit. • Long run profits are zero. ...
... • Short run profits leads to entry. • Entry increases market supply, drives down the market price, increases the market quantity. • Demand for individual firm’s product shifts down. • Firm reduces output to maximize profit. • Long run profits are zero. ...
Pricing in Imperfectly Competitive Markets
... Switching and Search Costs • Once a consumer has experienced a product, there may be a cost associated with switching to a new product • There may also be a cost associated with finding out what products are available and at what price • In equilibrium, firms can have market power if these costs ar ...
... Switching and Search Costs • Once a consumer has experienced a product, there may be a cost associated with switching to a new product • There may also be a cost associated with finding out what products are available and at what price • In equilibrium, firms can have market power if these costs ar ...
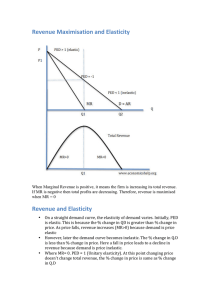
Revenue Maximisation and Elasticity Revenue
... Increase profit. Higher profit enables higher wages and more money for investment. Economies of Scale. In industries with high fixed costs, increased market sales leads to lower average costs enabling a f ...
... Increase profit. Higher profit enables higher wages and more money for investment. Economies of Scale. In industries with high fixed costs, increased market sales leads to lower average costs enabling a f ...
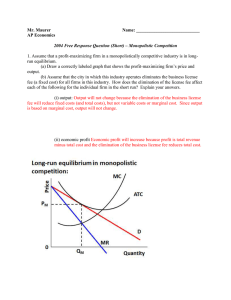
Mr. Maurer Name: AP Economics 2004 Free Response Question
... demand curve be price inelastic? Explain. No, the typical firm’s demand curve would be elastic at the profit-maximizing price because marginal revenue is positive in this portion of the demand curve, so total revenue increases as price decreases. (c) Given the information in part (a), what happens t ...
... demand curve be price inelastic? Explain. No, the typical firm’s demand curve would be elastic at the profit-maximizing price because marginal revenue is positive in this portion of the demand curve, so total revenue increases as price decreases. (c) Given the information in part (a), what happens t ...
ECON460: Answer Key to Problem Set 1
... d. Solve for the short-run perfectly competitive equilibrium levels of price and output in which there are two firms.What are profits of each firm in this short-run equilibrium? Answer: need to find the intersection of the industry demand curve and the 2-firm supply curve above: Q = 100 − p = 4p − 4 ...
... d. Solve for the short-run perfectly competitive equilibrium levels of price and output in which there are two firms.What are profits of each firm in this short-run equilibrium? Answer: need to find the intersection of the industry demand curve and the 2-firm supply curve above: Q = 100 − p = 4p − 4 ...
Document
... The fall in the marginal cost of production causes a favorable shift in supply and a lower price accompanied by greater output. ...
... The fall in the marginal cost of production causes a favorable shift in supply and a lower price accompanied by greater output. ...
Chpt 7 PP
... perfect competition? Because each unit sells for the same price, therefore each unit sold adds the price to total revenue ...
... perfect competition? Because each unit sells for the same price, therefore each unit sold adds the price to total revenue ...
Profit Maximization
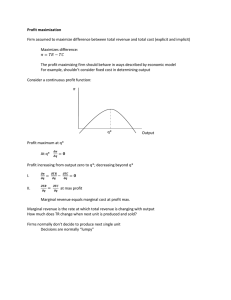
... Marginal revenue equals marginal cost at profit max. Marginal revenue is the rate at which total revenue is changing with output How much does TR change when next unit is produced and sold? Firms normally don’t decide to produce next single unit Decisions are normally “lumpy” ...
... Marginal revenue equals marginal cost at profit max. Marginal revenue is the rate at which total revenue is changing with output How much does TR change when next unit is produced and sold? Firms normally don’t decide to produce next single unit Decisions are normally “lumpy” ...
File
... A monopoly is a market structure in which there is only one producer/seller for a product. In other words, the single business is the industry. Entry into such a market is restricted due to high costs or other impediments, which may be economic, social or political. For instance, a government can c ...
... A monopoly is a market structure in which there is only one producer/seller for a product. In other words, the single business is the industry. Entry into such a market is restricted due to high costs or other impediments, which may be economic, social or political. For instance, a government can c ...
Chapter 1: Human Misery
... Market Structure Perfect Competition – Monopolistic Competition – Oligapoly ...
... Market Structure Perfect Competition – Monopolistic Competition – Oligapoly ...
Practice Problems
... (b) Suppose the equilibrium price in the desk lamp market is $ 50. How many table lamps should Edward produce, and how much profit will he make? (c) If next week the equilibrium price of desk lamps drops to $ 30, should Edward shut down? Explain. ...
... (b) Suppose the equilibrium price in the desk lamp market is $ 50. How many table lamps should Edward produce, and how much profit will he make? (c) If next week the equilibrium price of desk lamps drops to $ 30, should Edward shut down? Explain. ...
Monopolistic Competition
... behaves very much like a monopoly Key difference is the availability of substitutes ...
... behaves very much like a monopoly Key difference is the availability of substitutes ...
PrinciplesChapter7_2..
... Nearly 120 years ago Alfred Marshall defined the periods of production and sale – in the market period, output could not change (since it had already been produced and was sent to market). During the market period the price could change, but not output, if there were a sudden change in demand. In th ...
... Nearly 120 years ago Alfred Marshall defined the periods of production and sale – in the market period, output could not change (since it had already been produced and was sent to market). During the market period the price could change, but not output, if there were a sudden change in demand. In th ...
Industrial Economics
... c=5 and no fixed costs. She can charge different prices in the two markets. What is the profit maximazing combination of quantities for this monopolist? Q2. Suppose that a monopoly can produce any level of output it wishes at a constant marginal cost of $5 per unit. Assume that the monopoly sells it ...
... c=5 and no fixed costs. She can charge different prices in the two markets. What is the profit maximazing combination of quantities for this monopolist? Q2. Suppose that a monopoly can produce any level of output it wishes at a constant marginal cost of $5 per unit. Assume that the monopoly sells it ...
Problem 14 Key - people.vcu.edu
... b. Intuitively, why is marginal revenue more steeply sloped than demand (average revenue?) Reason for Steeper MR Slope:_To sell more units the firm must reduce the price on unit that would have sold at a higher price c. Identify the optimal level of output, price and profits for this firm. = 500 –Q ...
... b. Intuitively, why is marginal revenue more steeply sloped than demand (average revenue?) Reason for Steeper MR Slope:_To sell more units the firm must reduce the price on unit that would have sold at a higher price c. Identify the optimal level of output, price and profits for this firm. = 500 –Q ...
Solution
... c. variable cost divided by output. d. a cost a firm can write off of its taxes. e. so small it is not important in the firm’s decision-making process. ...
... c. variable cost divided by output. d. a cost a firm can write off of its taxes. e. so small it is not important in the firm’s decision-making process. ...
Unit 5: Factors Market
... Rent, Interest, and Profits Return to concept of scarce resources and how we pay for them. Land=rent Labor=wages Capital=interest Entrepreneurship= profit Again difference between economic profit and accounting profit Ratio of efficient use of factors vs. the output firm receives and price paid for ...
... Rent, Interest, and Profits Return to concept of scarce resources and how we pay for them. Land=rent Labor=wages Capital=interest Entrepreneurship= profit Again difference between economic profit and accounting profit Ratio of efficient use of factors vs. the output firm receives and price paid for ...