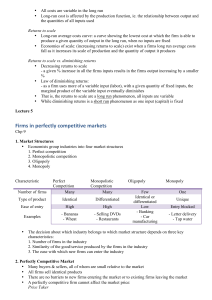
SECTION 11: Market Structures: Perfect Competition & Monopoly: Need to Know: PERFECT COMPETITION
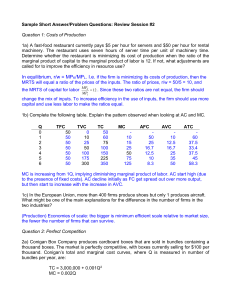
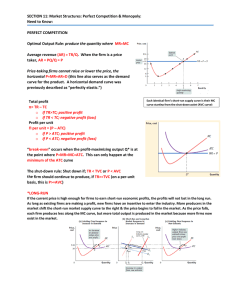
... “break‐even” occurs when the profit‐maximizing output Q* is at the point where P=MR=MC=ATC. This can only happen at the minimum of the ATC curve ...
... “break‐even” occurs when the profit‐maximizing output Q* is at the point where P=MR=MC=ATC. This can only happen at the minimum of the ATC curve ...
Perfect Competition
... 5. Revenue concepts and operating decisions for a Psetting firm 6. Monopolies and roles of government a. b. ...
... 5. Revenue concepts and operating decisions for a Psetting firm 6. Monopolies and roles of government a. b. ...
here - mrrobinson.org
... 3. New vs Old firms have no advantages over each other 4. Seller/Buyer informed about price ...
... 3. New vs Old firms have no advantages over each other 4. Seller/Buyer informed about price ...
Review Session #2
... 4c) Define a natural monopoly, explaining what the size of the market has to do with whether an industry is a natural monopoly. Suppose that a natural monopolist were required by law to charge its average cost. Draw a diagram, label the price charged, and the deadweight loss to society relative to m ...
... 4c) Define a natural monopoly, explaining what the size of the market has to do with whether an industry is a natural monopoly. Suppose that a natural monopolist were required by law to charge its average cost. Draw a diagram, label the price charged, and the deadweight loss to society relative to m ...
Principles of Microeconomics_CLEP Exam
... of economics that apply to the analysis of the behavior of individual consumers and businesses in the economy. Questions on this exam require candidates to apply analytical techniques to hypothetical as well as real-world situations and to analyze and evaluate economic decisions. Candidates are expe ...
... of economics that apply to the analysis of the behavior of individual consumers and businesses in the economy. Questions on this exam require candidates to apply analytical techniques to hypothetical as well as real-world situations and to analyze and evaluate economic decisions. Candidates are expe ...
Title Goes Here - Binus Repository
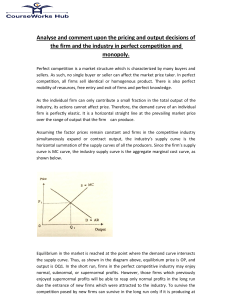
... Allocative efficiency (or efficiency) occurs when no possible reorganization of production can make anyone better off without making someone else worse off. Under condition all allocative efficiency, one person’s satisfaction or utility can be increased only by lowering someone else’s utility. ...
... Allocative efficiency (or efficiency) occurs when no possible reorganization of production can make anyone better off without making someone else worse off. Under condition all allocative efficiency, one person’s satisfaction or utility can be increased only by lowering someone else’s utility. ...
unit seven
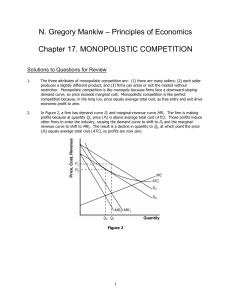
... • As new firms enter a monopolistically competitive industry, the demand curves of existing firms shift to the left, pushing MR with them. • In the long run, profits are eliminated. This occurs for a firm when its demand curve is just tangent to its average cost curve. ...
... • As new firms enter a monopolistically competitive industry, the demand curves of existing firms shift to the left, pushing MR with them. • In the long run, profits are eliminated. This occurs for a firm when its demand curve is just tangent to its average cost curve. ...
Problem Set 3
... a. If the demand in a particular market is Q = 14,000 - 100P, what is the competitive equilibrium price, total output of the picnic-table industry, and number of picnic table firms in this market? You may assume that picnic-table manufacturing is a competitive constant-cost industry. b. At this long ...
... a. If the demand in a particular market is Q = 14,000 - 100P, what is the competitive equilibrium price, total output of the picnic-table industry, and number of picnic table firms in this market? You may assume that picnic-table manufacturing is a competitive constant-cost industry. b. At this long ...
Lecture 08.1a
... – Factors that differentiate products are duplicated by competing firms. » drives price down and, » monopolistically competitive firm will make zero economic profit (i.e. a rate of return equal to the rate required to compensate debt and equity holders for the risk of investing in the firm). ...
... – Factors that differentiate products are duplicated by competing firms. » drives price down and, » monopolistically competitive firm will make zero economic profit (i.e. a rate of return equal to the rate required to compensate debt and equity holders for the risk of investing in the firm). ...
投影片 1
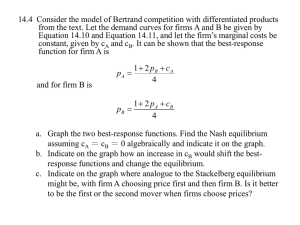
... might be, with firm A choosing price first and then firm B. Is it better to be the first or the second mover when firms choose prices? ...
... might be, with firm A choosing price first and then firm B. Is it better to be the first or the second mover when firms choose prices? ...
Aim: How do large firms maximize their profit based on competitive
... • That the number of suppliers be large (the second condition), means that they do not have the ability to collude. ...
... • That the number of suppliers be large (the second condition), means that they do not have the ability to collude. ...
Name
... They face a perfectly inelastic demand curve. Their marginal revenue curve rises as they produce increasing amounts of a product. They have a unique cost structure as compared to all other firms. If they are profit maximizing they will produce where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. e. There ma ...
... They face a perfectly inelastic demand curve. Their marginal revenue curve rises as they produce increasing amounts of a product. They have a unique cost structure as compared to all other firms. If they are profit maximizing they will produce where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. e. There ma ...
Final Exam Review Sheet
... 18. Finding consumer surplus, producer surplus, social surplus, and dead weight loss on a graph. 19. Impact of a unit tax on a supply and demand diagram. 20. Negative externality of production (pollution). 21. Calculating elasticity of supply and demand. 22. Maximize utility under a budget constrain ...
... 18. Finding consumer surplus, producer surplus, social surplus, and dead weight loss on a graph. 19. Impact of a unit tax on a supply and demand diagram. 20. Negative externality of production (pollution). 21. Calculating elasticity of supply and demand. 22. Maximize utility under a budget constrain ...
Homework Quiz 8
... higher prices in the short run, then an increase in production in the long run that would cause price to decline. d. lower prices in the short run because of higher sales, but higher prices in the long run as the inventory of beer is depleted. 6. The characteristics of perfect competition in the lon ...
... higher prices in the short run, then an increase in production in the long run that would cause price to decline. d. lower prices in the short run because of higher sales, but higher prices in the long run as the inventory of beer is depleted. 6. The characteristics of perfect competition in the lon ...
Quiz-5
... wages are not constant of competition of increasing returns to the variable input of diminishing returns to the variable input The market price increases as more output is produced and supplied to the market F. of principle of diminishing marginal utility ...
... wages are not constant of competition of increasing returns to the variable input of diminishing returns to the variable input The market price increases as more output is produced and supplied to the market F. of principle of diminishing marginal utility ...
Big test in prep for 3
... 9) Where is the shutdown point for a firm? If a firm cannot earn at least enough to cover all of its variable costs then in the short run it will shut down. This occurs at 'point B' where marginal cost is equal to minimum average variable cost. This is called the 'shut down point'. 10) Why is the M ...
... 9) Where is the shutdown point for a firm? If a firm cannot earn at least enough to cover all of its variable costs then in the short run it will shut down. This occurs at 'point B' where marginal cost is equal to minimum average variable cost. This is called the 'shut down point'. 10) Why is the M ...
Economies of Scale and International Trade,a
... to specialize in the production of only limited number of goods & services and to manufacture them in large quantities, partly for exports. Two types: (1)External economiescost per unit depends on the size of industry, not the size of the firm. (2) Internal economiescost per unit depends on the size ...
... to specialize in the production of only limited number of goods & services and to manufacture them in large quantities, partly for exports. Two types: (1)External economiescost per unit depends on the size of industry, not the size of the firm. (2) Internal economiescost per unit depends on the size ...