Economics for Today 2nd edition Irvin B. Tucker
... is very small relative to the market as a whole, all the firms sell a homogeneous product, and firms are free to enter and exit the industry. ...
... is very small relative to the market as a whole, all the firms sell a homogeneous product, and firms are free to enter and exit the industry. ...
chapter outline - rci.rutgers.edu
... We know how to answer these questions. What about: ♦ “Why do airline pilots earn more than school bus drivers?” ♦ “Why is land on the Boardwalk in Atlantic City more expensive than land fifty miles southwest of Atlantic City?” We can use same tools to answer these questions. Factors of Production Wh ...
... We know how to answer these questions. What about: ♦ “Why do airline pilots earn more than school bus drivers?” ♦ “Why is land on the Boardwalk in Atlantic City more expensive than land fifty miles southwest of Atlantic City?” We can use same tools to answer these questions. Factors of Production Wh ...
ec101 microeconomics tutorial
... graphical analysis to identify the profit maximisation position of each. c) Why is it that cartels are often short-lived? Twenty “A firm under monopolistic competition has monopoly over its product but faces competition in the overall product range”. Discuss the above statement highlighting the exte ...
... graphical analysis to identify the profit maximisation position of each. c) Why is it that cartels are often short-lived? Twenty “A firm under monopolistic competition has monopoly over its product but faces competition in the overall product range”. Discuss the above statement highlighting the exte ...
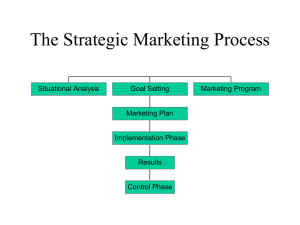
The Strategic Marketing Process
... Four market-product strategies: Alternative ways to expand marketing opportunities, using Coca-Cola Company products as examples Market Penetration ...
... Four market-product strategies: Alternative ways to expand marketing opportunities, using Coca-Cola Company products as examples Market Penetration ...
lec20 - People.vcu.edu
... Unless there are zero profits, the firms will undercut each other to get more sales. ...
... Unless there are zero profits, the firms will undercut each other to get more sales. ...
ECO2 REV3 – Answers
... 21. Price elasticity of oligopolies is greater than that of monopolistic competition. No, smaller. 22. How can monopolies go out of business? If demand for their product is too low or if the ATC > Price. 23. Perfectly competitive firms lower their prices in order to increase their sales. No, they a ...
... 21. Price elasticity of oligopolies is greater than that of monopolistic competition. No, smaller. 22. How can monopolies go out of business? If demand for their product is too low or if the ATC > Price. 23. Perfectly competitive firms lower their prices in order to increase their sales. No, they a ...
Marketing Strategy
... • Cost-leadership advantage – Low-cost producer – Experience curve – Need to obtain largest market share to have lowest cost per unit in industry – Ability to offer lower prices and more value to customers in competitive stages of product life cycle ...
... • Cost-leadership advantage – Low-cost producer – Experience curve – Need to obtain largest market share to have lowest cost per unit in industry – Ability to offer lower prices and more value to customers in competitive stages of product life cycle ...
Document
... profit? • To find the answer, “think at the margin.” If increase Q by one unit, revenue rises by MR, cost rises by MC. • If MR > MC, then increase Q to raise profit. ...
... profit? • To find the answer, “think at the margin.” If increase Q by one unit, revenue rises by MR, cost rises by MC. • If MR > MC, then increase Q to raise profit. ...
Market Structure: Perfect Competition
... FB 2400 Economics I Topics Market Structure Market Structure: Perfect Competition ...
... FB 2400 Economics I Topics Market Structure Market Structure: Perfect Competition ...
PDF format
... Which of the following is not an effect of an above-equilibrium price support on a farm product? a) the consumer will pay a higher price and consume less of the product b) the gross incomes or receipts of farmers will rise c) the consumer will pay a higher price and consume more of the product d) th ...
... Which of the following is not an effect of an above-equilibrium price support on a farm product? a) the consumer will pay a higher price and consume less of the product b) the gross incomes or receipts of farmers will rise c) the consumer will pay a higher price and consume more of the product d) th ...
Chapter 9
... from the original (Q-DQ) (inframarginal) units of output, the price reduction effect Price-taking firm faces a horizontal demand curve and is not subject to the price reduction effect ...
... from the original (Q-DQ) (inframarginal) units of output, the price reduction effect Price-taking firm faces a horizontal demand curve and is not subject to the price reduction effect ...
Marketing and society : social responsibility and marketing ethics
... and action as well as profit ...
... and action as well as profit ...
Econ 73-250A-F Spring 2001 Prof. Daniele Coen-Pirani MIDTERM EXAMINATION #2
... firm’s cost curve c(y), average cost curve AC(y), and marginal cost curve MC(y). Exercise #3. Short questions. To get full credit you should justify your answers. (a) [5 pts.] Show that, in the short run, if the price of the fixed factor is increased, profits will decrease. (b) [10 pts.] If pMP1 > w ...
... firm’s cost curve c(y), average cost curve AC(y), and marginal cost curve MC(y). Exercise #3. Short questions. To get full credit you should justify your answers. (a) [5 pts.] Show that, in the short run, if the price of the fixed factor is increased, profits will decrease. (b) [10 pts.] If pMP1 > w ...
market foreclosure
... prevent arbitrage. The simplest way to do this is to write no-resale contracts with its buyers, but these are not always enforceable or possible. • When arbitrage risks undermining a PD strategy, it may be desirable for the firm to vertically integrate with the downstream firms that face more elasti ...
... prevent arbitrage. The simplest way to do this is to write no-resale contracts with its buyers, but these are not always enforceable or possible. • When arbitrage risks undermining a PD strategy, it may be desirable for the firm to vertically integrate with the downstream firms that face more elasti ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... Given the total cost function C = 1000 + 100Q – 10Q2 +1/3Q2, find: a. The Marginal Cost function b. The slope of Marginal Cost function. c. The Output at which Marginal Cost is equal to Average Variable Cost. 12. State and prove Euler’s Theorem. 13. Given the Consumption function ...
... Given the total cost function C = 1000 + 100Q – 10Q2 +1/3Q2, find: a. The Marginal Cost function b. The slope of Marginal Cost function. c. The Output at which Marginal Cost is equal to Average Variable Cost. 12. State and prove Euler’s Theorem. 13. Given the Consumption function ...