* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PES-Introduction
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Gasoline and diesel usage and pricing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Supply chain management wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
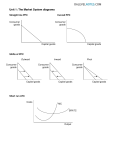
Price Elasticity of Supply – practice exercises 1. In each of the following cases, calculate the price elasticity of supply to 2 decimal places; decide whether this makes the supply of this product elastic or inelastic: a. The price of a product falls from 60p to 40p, causing supply to contract from 120 to 100 b. The product’s price is reduced from £45 to £40. As a result, supply falls from 6000 to 5000 c. The price of a product rises from £50 to £60, causing supply to extend from 100 to 200 d. A product’s price rises from £12 to £15 but supply remains unchanged at 2000 e. Supply extends from 900 to 1200 because of a rise in price from £10 to £11 2. Decide for each of these products whether supply is likely to be elastic or inelastic; list reasons for your decision: a) Pork b) Paper clips c) Fresh strawberries d) Neck ties e) Tinned pears f) Aeroplanes