Document
... declining, then new firms cannot compete on a cost basis. A monopoly hospital in a small town may have substantial economies of scale if it can meet demand with only 40-50 beds. ...
... declining, then new firms cannot compete on a cost basis. A monopoly hospital in a small town may have substantial economies of scale if it can meet demand with only 40-50 beds. ...
Chapter 5 Supply
... for example, are willing to keep their profits lower than they could be in order to avoid taking risks. Others would rather work less and take smaller profit. Also, laws and rules limit the pursuit of profits. They include laws that set maximum hours and minimum wages for workers, and workplace saf ...
... for example, are willing to keep their profits lower than they could be in order to avoid taking risks. Others would rather work less and take smaller profit. Also, laws and rules limit the pursuit of profits. They include laws that set maximum hours and minimum wages for workers, and workplace saf ...
Chapter 15 - Monopoly
... – Arises because a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market • At a smaller cost than could two or more firms ...
... – Arises because a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market • At a smaller cost than could two or more firms ...
Economic profit - Choose your book for Principles of Economics, by
... 2. How does the competitive firm’s price and quantity compare to the monopoly in panel b? • The monopoly’s price is $20 -- $5 less than the competitive firm’s price. • The monopoly’s output quantity is 10,000 - 6,000 greater than the competitive firm’s ...
... 2. How does the competitive firm’s price and quantity compare to the monopoly in panel b? • The monopoly’s price is $20 -- $5 less than the competitive firm’s price. • The monopoly’s output quantity is 10,000 - 6,000 greater than the competitive firm’s ...
Price discrimination Summary
... Notice that we have drawn the home demand curve as a steeper graph than the foreign one. This is usually the case since the firm’s demand is more likely to be inelastic at home due to fewer competitors. This is why price charged on the home market is higher than that charged abroad. However, margina ...
... Notice that we have drawn the home demand curve as a steeper graph than the foreign one. This is usually the case since the firm’s demand is more likely to be inelastic at home due to fewer competitors. This is why price charged on the home market is higher than that charged abroad. However, margina ...
Prices! - Doral Academy Preparatory
... problem when it temporarily controlled prices in WWII but it wasn’t as severe. – Even though rationing systems work to an extent people sometimes ignored the government to make some extra income on the side. • When this kind of thing happens it is referred to doing business on the black market. As m ...
... problem when it temporarily controlled prices in WWII but it wasn’t as severe. – Even though rationing systems work to an extent people sometimes ignored the government to make some extra income on the side. • When this kind of thing happens it is referred to doing business on the black market. As m ...
Supply
... What is Supply? • Supply is how much a firm is willing to sell at every given price, ceteris paribus • Thus, if all else remains the same and the price of a good goes up, what would you expect the response of a firm to be? – To produce more, since prices are going up, so will profits ...
... What is Supply? • Supply is how much a firm is willing to sell at every given price, ceteris paribus • Thus, if all else remains the same and the price of a good goes up, what would you expect the response of a firm to be? – To produce more, since prices are going up, so will profits ...
Chapter 2
... The key factor in communicating information about a brand and differentiating it from competitors is: ...
... The key factor in communicating information about a brand and differentiating it from competitors is: ...
review mon and after
... A) It is at the opposite end of the spectrum from a perfectly competitive firm. B) A monopoly has no rivals. C) A monopoly does not need to worry about other firms entering the industry. D) All of the above are true. ...
... A) It is at the opposite end of the spectrum from a perfectly competitive firm. B) A monopoly has no rivals. C) A monopoly does not need to worry about other firms entering the industry. D) All of the above are true. ...
Ch13 Review Ques ons
... 2) A compe..ve firm can sell all the output it wants without having any impact on market price. For each addi.onal unit sold, its revenue will rise by the market price. Hence, MR is the same ...
... 2) A compe..ve firm can sell all the output it wants without having any impact on market price. For each addi.onal unit sold, its revenue will rise by the market price. Hence, MR is the same ...
Understanding supply
... sell at all prices. Producers control supply-side of our economy. What is the difference between a supply schedule & a supply curve? Which way does the supply curve always slope? Why? The Law of Supply says as prices increase the quantity supplied increases. Do Supply Graphing Exercises, p. 73. ...
... sell at all prices. Producers control supply-side of our economy. What is the difference between a supply schedule & a supply curve? Which way does the supply curve always slope? Why? The Law of Supply says as prices increase the quantity supplied increases. Do Supply Graphing Exercises, p. 73. ...
File
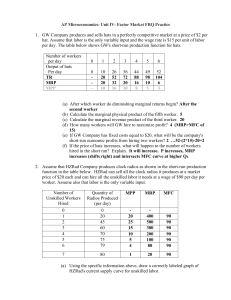
... The table above gives the short-run marginal revenue product of labor per day for a perfectly competitive firm. The firm is currently selling its product at the market price of $5. (a) Calculate the marginal (physical) product of the third worker. 90; 450 = 90 * 5 (RP = MPP * P) (b) Define the law o ...
... The table above gives the short-run marginal revenue product of labor per day for a perfectly competitive firm. The firm is currently selling its product at the market price of $5. (a) Calculate the marginal (physical) product of the third worker. 90; 450 = 90 * 5 (RP = MPP * P) (b) Define the law o ...
Supply
... • A fixed cost is a cost that does not change, regardless of how much of a good is produced. Examples: rent and salaries • Variable costs are costs that rise or fall depending on how much is produced. Examples: costs of raw materials, some labor costs. • The total cost equals fixed costs plus variab ...
... • A fixed cost is a cost that does not change, regardless of how much of a good is produced. Examples: rent and salaries • Variable costs are costs that rise or fall depending on how much is produced. Examples: costs of raw materials, some labor costs. • The total cost equals fixed costs plus variab ...
Document
... Q1. A retailer faces downstream demand of P=240-2Q and has one supplier who has 0 marginal cost. The retailer’s only cost is what it pays the supplier. What will happen in this market in terms of price, quantity and profits? What would happen if there were two retailers who competed according to the ...
... Q1. A retailer faces downstream demand of P=240-2Q and has one supplier who has 0 marginal cost. The retailer’s only cost is what it pays the supplier. What will happen in this market in terms of price, quantity and profits? What would happen if there were two retailers who competed according to the ...