Economics 1370 Vocabulary List: Definitions, Part 1 01. SCARCITY
... accrue to the owner and should be secure from involuntary seizure or encroachment by others; and (c) Transferable (all property rights should be transferable from one owner to another in a voluntary exchange). ...
... accrue to the owner and should be secure from involuntary seizure or encroachment by others; and (c) Transferable (all property rights should be transferable from one owner to another in a voluntary exchange). ...
Lesson_03
... Intense rivalry often plays out in the following ways: Jockeying for strategic position Using price competition Staging advertising battles Increasing consumer warranties or service Making new product introductions ...
... Intense rivalry often plays out in the following ways: Jockeying for strategic position Using price competition Staging advertising battles Increasing consumer warranties or service Making new product introductions ...
topic 4 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... (that is, when it is hot and consumers are thirsty and therefore wanting more Coke). As the example shows, increased demand results in higher prices. As a result of increased demand and a subsequent shortage of the product at the current market equilibrium, suppliers can raise prices, which results ...
... (that is, when it is hot and consumers are thirsty and therefore wanting more Coke). As the example shows, increased demand results in higher prices. As a result of increased demand and a subsequent shortage of the product at the current market equilibrium, suppliers can raise prices, which results ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. If resources are “scarce” it means that they
... D) improve its technology or increase the quantities of factors of production it has. 8. All points outside the production possibility frontier represent: A) efficient production points. B) inefficient production points. C) nonfeasible production points. D) economic growth. 9. In a single day, Sarah ...
... D) improve its technology or increase the quantities of factors of production it has. 8. All points outside the production possibility frontier represent: A) efficient production points. B) inefficient production points. C) nonfeasible production points. D) economic growth. 9. In a single day, Sarah ...
Chapter 7
... Always easier to start high and lower prices, then to start low and raise them. Competition will also affect your price, if there is no competition, then prices can be higher if consumers are willing to pay that price. ...
... Always easier to start high and lower prices, then to start low and raise them. Competition will also affect your price, if there is no competition, then prices can be higher if consumers are willing to pay that price. ...
Ch 17 - Del Mar College
... • As in a monopoly, price exceeds marginal cost. • Profit maximization requires marginal revenue to equal marginal cost. • The downward-sloping demand curve makes marginal revenue less than price. ...
... • As in a monopoly, price exceeds marginal cost. • Profit maximization requires marginal revenue to equal marginal cost. • The downward-sloping demand curve makes marginal revenue less than price. ...
File
... demanded of a good or service, is functionally related to the selling price P. Inequality asserts that quantity demanded and price are inversely related. This relationship is illustrated in Figure. The downward-sloping demand curve illustrates the inverse relationship between the quantity demanded o ...
... demanded of a good or service, is functionally related to the selling price P. Inequality asserts that quantity demanded and price are inversely related. This relationship is illustrated in Figure. The downward-sloping demand curve illustrates the inverse relationship between the quantity demanded o ...
Supply - Images
... 1. Elastic Supply: When small change in price has a huge impact on supply ...
... 1. Elastic Supply: When small change in price has a huge impact on supply ...
Honors Economics Unit 2 Study Guide
... 32. Define and describe oligopoly.(169-171) Few large sellers – similar products, many barriers to entry What are some examples? Airlines, cereal, automotives, movie studios 33. What is a barrier to entry? (153) Difficulties for a new firm to enter a market What is an example of this situation?(153 ...
... 32. Define and describe oligopoly.(169-171) Few large sellers – similar products, many barriers to entry What are some examples? Airlines, cereal, automotives, movie studios 33. What is a barrier to entry? (153) Difficulties for a new firm to enter a market What is an example of this situation?(153 ...
Ch5.3 & 6Revenue and Perfect Competition
... the total market and that they do not have much influence over the price charged. • In such a market if they raise price people will go elsewhere… • … and if they reduce price (even if it were profitable) they would not be able to cope with the resultant demand. ...
... the total market and that they do not have much influence over the price charged. • In such a market if they raise price people will go elsewhere… • … and if they reduce price (even if it were profitable) they would not be able to cope with the resultant demand. ...
Homework 2
... are interested in purchasing the rights. Given the original winner can choose any second–stage mechanism, how should they bid in the original auction? How would revenue change if the auctioneer sold to all M + N bidders at once? 2. (a) There is one bidder with value v1 ∼ U [a, a + 1], where a ≥ 0. W ...
... are interested in purchasing the rights. Given the original winner can choose any second–stage mechanism, how should they bid in the original auction? How would revenue change if the auctioneer sold to all M + N bidders at once? 2. (a) There is one bidder with value v1 ∼ U [a, a + 1], where a ≥ 0. W ...
Microeconomics Review 1
... Profit Maximization for Price Taking Firms • π = pQ – TC(Q) • Firms will increase output until marginal revenue equals marginal costs • If increasing output by one unit results in additional revenue that exceeds the extra cost of producing that unit, then producing that unit will increase profits. M ...
... Profit Maximization for Price Taking Firms • π = pQ – TC(Q) • Firms will increase output until marginal revenue equals marginal costs • If increasing output by one unit results in additional revenue that exceeds the extra cost of producing that unit, then producing that unit will increase profits. M ...
Demand, Supply and Equlibrium
... The Supply Curve • Supply • The quantities of a good or service that sellers are willing and able to sell at various prices • Similar to demand, supply can be shown as a schedule and then as a graph ...
... The Supply Curve • Supply • The quantities of a good or service that sellers are willing and able to sell at various prices • Similar to demand, supply can be shown as a schedule and then as a graph ...
Module H4 Session 1 Guidance for Trainers
... Question What happens to Pe if the factors affecting supply change, so that supply increases (producers can supply more goods at each price level)? Answer The supply curve shifts to the right (parallel to its old position), intersecting the demand curve at a lower price, so Pe falls. Question What h ...
... Question What happens to Pe if the factors affecting supply change, so that supply increases (producers can supply more goods at each price level)? Answer The supply curve shifts to the right (parallel to its old position), intersecting the demand curve at a lower price, so Pe falls. Question What h ...
Economics - Worksheets
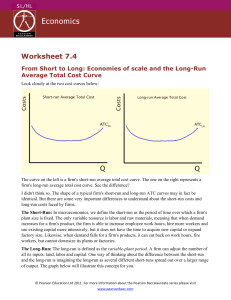
... When we examine the long-run ATC more closely, it becomes apparent that there are in fact lots of little short-run ATC curves along the length of the long-run curve. Each of the gray lines in the graph above represent a short-run period in which this firm opened a new factories. There are three dist ...
... When we examine the long-run ATC more closely, it becomes apparent that there are in fact lots of little short-run ATC curves along the length of the long-run curve. Each of the gray lines in the graph above represent a short-run period in which this firm opened a new factories. There are three dist ...
the markeing concept and product selection
... The plan for successful businesses. The Marketing Concept states that businesses must satisfy customer wants and needs in order to make a profit. Competition forces businesses to use the marketing concept. A business must have the right goods and services at the right time, the right price, and at t ...
... The plan for successful businesses. The Marketing Concept states that businesses must satisfy customer wants and needs in order to make a profit. Competition forces businesses to use the marketing concept. A business must have the right goods and services at the right time, the right price, and at t ...
Chapter 1
... consoles backward compatible? What were the advantages and disadvantages of this strategy? What strengths and weaknesses did Sony have when it entered the video game market in 1995? Comparing the deployment strategies used by the firms in each of the generations, can you identify any timing, licensi ...
... consoles backward compatible? What were the advantages and disadvantages of this strategy? What strengths and weaknesses did Sony have when it entered the video game market in 1995? Comparing the deployment strategies used by the firms in each of the generations, can you identify any timing, licensi ...