Four Market Models
... 1. The diagrams portray neither long-run nor short-run equilibrium. 2. The diagrams portray both long-run and short-run equilibrium. 3. The diagrams portray short-run equilibrium, but not long-run equilibrium. 4. The diagrams portray long-run equilibrium, but not short-run equilibrium. 2. Refer to t ...
... 1. The diagrams portray neither long-run nor short-run equilibrium. 2. The diagrams portray both long-run and short-run equilibrium. 3. The diagrams portray short-run equilibrium, but not long-run equilibrium. 4. The diagrams portray long-run equilibrium, but not short-run equilibrium. 2. Refer to t ...
###Pricing Policies, Quality and Adding Value
... Pricing Policies If a firm has the power in its market to set its own price, it can adopt a pricing policy: ...
... Pricing Policies If a firm has the power in its market to set its own price, it can adopt a pricing policy: ...
Company Name - University of Wisconsin–La Crosse
... higher equilibrium price and lower equilibrium quantity. ...
... higher equilibrium price and lower equilibrium quantity. ...
The Demand for Resources
... 3. Changes in the prices of other resources • Substitute resources • If the price of farm machinery decreases relative to farm laborers, more machinery would be utilized, decreasing the MRP of farm labor (it would shift left) • Complementary resources • If the price of lumber used to build new house ...
... 3. Changes in the prices of other resources • Substitute resources • If the price of farm machinery decreases relative to farm laborers, more machinery would be utilized, decreasing the MRP of farm labor (it would shift left) • Complementary resources • If the price of lumber used to build new house ...
Midterm Questions and Answers, Winter 2006
... 1. (10 points) Suppose good x is high quality navel oranges and good y is medium quality navel oranges. Call the prices in California (where the oranges are grown) px and py , and assume that the high quality oranges are more expensive than the medium quality oranges, px > py . Also assume that the ...
... 1. (10 points) Suppose good x is high quality navel oranges and good y is medium quality navel oranges. Call the prices in California (where the oranges are grown) px and py , and assume that the high quality oranges are more expensive than the medium quality oranges, px > py . Also assume that the ...
Tying and Foreclosure
... deadweight loss on product 1. • This is done by cutting its price somewhat below the monopoly level while raising the price of 2 somewhat above marginal cost, and requiring buyers to buy 2 at this higher price as a condition for obtaining the lower price on 1. • The deadweight loss will be reduced b ...
... deadweight loss on product 1. • This is done by cutting its price somewhat below the monopoly level while raising the price of 2 somewhat above marginal cost, and requiring buyers to buy 2 at this higher price as a condition for obtaining the lower price on 1. • The deadweight loss will be reduced b ...
Question 1
... Consider a market with one large firm and many small firms. The supply curve of the small firms taken together is S(p) = 100 + p. The demand curve for the product is D(p) = 200 − p. The cost function for the one large firm is c(y) = 25y a) Suppose that the large firm is forced to operate at a zero l ...
... Consider a market with one large firm and many small firms. The supply curve of the small firms taken together is S(p) = 100 + p. The demand curve for the product is D(p) = 200 − p. The cost function for the one large firm is c(y) = 25y a) Suppose that the large firm is forced to operate at a zero l ...
The Monopoly
... Monopoly profits are a reward for a risky investment decision by an entrepreneur If these potential rewards are denied (through a tough competition policy), no entrepreneur will be willing to take risks. Therefore, monopoly regulation has a negative effect on innovation ...
... Monopoly profits are a reward for a risky investment decision by an entrepreneur If these potential rewards are denied (through a tough competition policy), no entrepreneur will be willing to take risks. Therefore, monopoly regulation has a negative effect on innovation ...
6ech08_rev - Homework Market
... which the firm would still produce At the shutdown point, the price is equal to the minimum point on the AVC If the price falls below the shutdown point, revenues fail to cover the fixed costs and the variable costs. The firm would be better off if it shut down and just paid its fixed costs ...
... which the firm would still produce At the shutdown point, the price is equal to the minimum point on the AVC If the price falls below the shutdown point, revenues fail to cover the fixed costs and the variable costs. The firm would be better off if it shut down and just paid its fixed costs ...
Practice Problems
... (B)Firms will exit the market until profits go up. (C)Firms already in the market will exit the industry. (D)Firms already in the market will produce more than Q2 in the long-run. (E)New firms will be less likely to enter the market unless the price goes up. A firm that operates in a perfectly compe ...
... (B)Firms will exit the market until profits go up. (C)Firms already in the market will exit the industry. (D)Firms already in the market will produce more than Q2 in the long-run. (E)New firms will be less likely to enter the market unless the price goes up. A firm that operates in a perfectly compe ...
Ch05 Efficiency and equity
... Producer surplus is the price received for a good minus the minimum-supply price (marginal cost), summed over the quantity sold. It is measured by the area below the market price and above the supply curve, summed over the quantity sold. Figure 5.4 on the next slide shows the producer surplus fro ...
... Producer surplus is the price received for a good minus the minimum-supply price (marginal cost), summed over the quantity sold. It is measured by the area below the market price and above the supply curve, summed over the quantity sold. Figure 5.4 on the next slide shows the producer surplus fro ...
Midterm Two from the Morning Lecture
... Refer to the following information for the next THREE questions. Ivan has decided to start a new business producing homemade beer. During the first year of his business, Ivan sold 15000 cans of beer for $4/can. The technology of production Ivan is using has a constant average variable cost of $2/can ...
... Refer to the following information for the next THREE questions. Ivan has decided to start a new business producing homemade beer. During the first year of his business, Ivan sold 15000 cans of beer for $4/can. The technology of production Ivan is using has a constant average variable cost of $2/can ...
presentation source
... FOUR TYPES OF MARKETS • Monopolistic Competition --There are many firms, each sells a differentiated product. Because products sold by different firms are not perfect substitutes, each firm has some control over price. There are no barriers to entering the market. ...
... FOUR TYPES OF MARKETS • Monopolistic Competition --There are many firms, each sells a differentiated product. Because products sold by different firms are not perfect substitutes, each firm has some control over price. There are no barriers to entering the market. ...
the marketing mix - Deans Community High School
... • To ensure a successful product an organisation must get the 4 elements of the marketing mix just right. For example if they don’t get the price right eg too expensive then people may not buy the product. ...
... • To ensure a successful product an organisation must get the 4 elements of the marketing mix just right. For example if they don’t get the price right eg too expensive then people may not buy the product. ...
Test answers - December 2001
... 21. To find out how much the firm will produce in the short run, we set P = MC. MC is the derivative of TC. So, dTC/dq = 3q + 4. Setting P = MC we get $31 = 3q + 4 or q = 9. The correct answer is (J). 22. At a price of $31, we calculated that the firm will produce 9 units. Therefore, it earns revenu ...
... 21. To find out how much the firm will produce in the short run, we set P = MC. MC is the derivative of TC. So, dTC/dq = 3q + 4. Setting P = MC we get $31 = 3q + 4 or q = 9. The correct answer is (J). 22. At a price of $31, we calculated that the firm will produce 9 units. Therefore, it earns revenu ...
Slide 1
... When each firm produces .1, SAC per firm is: .1/.1 + 150(.1) = 16 Therefore, P* > SAC so profits are ...
... When each firm produces .1, SAC per firm is: .1/.1 + 150(.1) = 16 Therefore, P* > SAC so profits are ...
Economic Utilities - Duluth High School
... turn fosters new & improved products Example: Computers have gotten smaller, lighter, more powerful, & less expensive ...
... turn fosters new & improved products Example: Computers have gotten smaller, lighter, more powerful, & less expensive ...
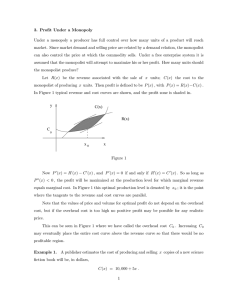
3. Profit Under a Monopoly Under a monopoly a producer has full
... $2000. He sells x tickets at $100 each with the understanding that $x is refunded to each passenger when the trip begins. Find (a) The minimum number of tickets he must sell to break even, (b) the most profitable number of tickets he can sell. 2. The demand relation for handsaws is that x saws sell ...
... $2000. He sells x tickets at $100 each with the understanding that $x is refunded to each passenger when the trip begins. Find (a) The minimum number of tickets he must sell to break even, (b) the most profitable number of tickets he can sell. 2. The demand relation for handsaws is that x saws sell ...