* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Demand for Resources
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
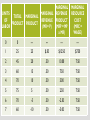
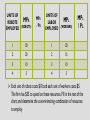
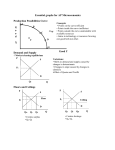
THE DEMAND FOR RESOURCES RIXIE AP Microeconomics Unit 4, Day 1 DERIVED DEMAND • The demand for the factors of production is derived from the goods that they produce. • The demand for food truck chefs, food truck raw materials, and food truck permits exists because there is demand for food truck food! TWO MEASURES TO DETERMINE RESOURCE USE MARGINAL REVENUE PRODUCT (MRP) MARGINAL RESOURCE COST (MRC) • The addition to a firm’s revenue when an additional input is employed • The additional cost to the firm from hiring an additional input like a worker or machine • MRP = Change in Total Revenue / Change in # of Inputs • MRC = Change in Total Resource Cost / Change in # of Inputs • MRP = Marginal Revenue * Marginal Product • In a competitive labor market, MRC = Wage PROFIT-MAXIMIZING RESOURCE EMPLOYMENT • The profit-maximizing employer should hire to the point where MRP = MRC • Or, as close as possible to equal as long as MRP > MRC • (Similar to the MR = MC rule in the product market!) MARGINAL UNITS MARGINAL REVENUE TOTAL MARGINAL OF REVENUE PRODUCT PRODUCT PRODUCT LABOR (MR = P) (MRP = MP x MR) MARGINAL RESOURCE COST (MRC = WAGE) 0 0 --- --- --- --- 1 25 25 $.50 $12.50 $7.50 2 45 20 .50 10.00 7.50 3 60 15 .50 7.50 7.50 4 70 10 .50 5.00 7.50 5 75 5 .50 2.50 7.50 6 70 -5 .50 -2.50 7.50 7 60 -10 .50 -5.00 7.50 GRAPHICAL PORTRAYAL (COMPETITIVE WAGE MARKET) $ Wage Supply = MRC = Wage Demand = MRP Q* Q Labor DETERMINANTS OF RESOURCE DEMAND 1. Changes in the product demand • Increased demand for lemonade leads to an increased price of lemonade • This increases the MRP of resources, shifting the demand for those resources to the right, & increasing the quantity of labor employed DETERMINANTS OF RESOURCE DEMAND 2. Changes in productivity • Increases in efficiency (such as tech advances) can make a firm more profitable and give an incentive to employ more resources DETERMINANTS OF RESOURCE DEMAND 3. Changes in the prices of other resources • Substitute resources • If the price of farm machinery decreases relative to farm laborers, more machinery would be utilized, decreasing the MRP of farm labor (it would shift left) • Complementary resources • If the price of lumber used to build new houses decreases, more homes will be built, increasing the demand/MRP for construction workers (it would shift right) SHIFT IN RESOURCE DEMAND $ Wage Supply = MRC = Wage D = MRP2 D = MRP1 Q*1 Q*2 Q Labor PRACTICE State whether each of the following will increase or decrease the demand for the laborers, shift the demand curve to the left or right, and increase or decrease the quantity of labor employed. 1. The effect of an increase in popularity of gambling on the demand for workers at casinos 2. The effect of consumers decreasing their demand for food truck meals on the demand for food truck workers 3. The effect of developments in computer-assisted graphic design on the productivity of, and demand for, graphic artists 4. The effect of a decline in price of security equipment used by businesses to protect against illegal entry on the demand for night guards 5. The effect of a decline in price of cell phone equipment on the cost of cell phone service, and in turn on the demand for cell phone assemblers ANSWERS State whether each of the following will increase or decrease the demand for the laborers, shift the demand curve to the left or right, and increase or decrease the quantity of labor employed. 1. Increase / Shift Right / Increase (increased price of service – increased MRP/demand for workers) 2. Decrease / Shift Left / Decrease (decreased price of product – decreased MRP/demand for workers) 3. Increase / Shift Right / Increase (increased efficiency) 4. Decrease / Shift Left / Decrease (substitute resources) 5. Increase / Shift Left / Increase (complementary resources) LEAST-COST HIRING RULE Unit 4, Day 2 intro (4/5 & 4/6) RESOURCE MARKET: LEAST-COST HIRING RULE • To minimize costs, a firm will adjust the ratio of inputs until the marginal product of labor divided by the price is equal to the marginal product of capital divided by price (L is labor & K is capital) • You will either be given the budget of the firm to spend on these resources, or the quantity of output they need to produce. MPL PL MPK PK Does this sound familiar??? UNITS OF ROBOTS EMPLOYED MPK (ROBOTS) MPK / PK UNITS OF LABOR EMPLOYED MPL (WORKERS) 1 30 1 20 2 20 2 15 3 10 3 10 4 5 4 5 MPL / PL Each unit of robots costs $10 and each unit of workers costs $5. The firm has $35 to spend on these resources. Fill in the rest of the chart, and determine the cost-minimizing combination of resources to employ. UNITS OF CAPITAL EMPLOYED UNITS OF LABOR EMPLOYED MPK MPL 1 100 1 50 2 90 2 40 3 80 3 30 4 60 4 20 5 45 5 10 6 30 6 5 MPK / PK MPL / PL Each unit of capital costs $10 and each unit of workers costs $5. The firm needs to produce 360 gadgets with these resources. Fill in the rest of the chart, and determine the cost-minimizing combination of resources to employ.