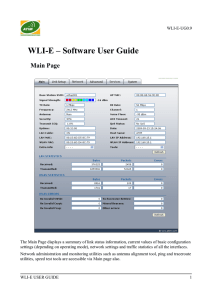
RuggedBackbone™ RX1500/1501
... OSPF is a routing protocol that determines the best path for routing IP traffic over a TCP/IP network based on link states between nodes and several quality parameters. OSPF is an interior gateway protocol (IGP), which is designed to work within an autonomous system. It is also a link state protocol ...
... OSPF is a routing protocol that determines the best path for routing IP traffic over a TCP/IP network based on link states between nodes and several quality parameters. OSPF is an interior gateway protocol (IGP), which is designed to work within an autonomous system. It is also a link state protocol ...
BUFFALO: Bloom Filter Forwarding Architecture for Large Organizations
... the artificial constraints imposed by dividing a network into many small IP subnets. However, traditional Ethernet can only support this abstraction in small network topologies, due to a heavy reliance on network-wide flooding and spanning tree. Recent advances [1, 2, 3] have made it possible to build ...
... the artificial constraints imposed by dividing a network into many small IP subnets. However, traditional Ethernet can only support this abstraction in small network topologies, due to a heavy reliance on network-wide flooding and spanning tree. Recent advances [1, 2, 3] have made it possible to build ...
Measuring BGP
... AS Path aggregation (dup withdrawal) 33% reduction (103126 -> 68504) using AS Origin aggregation This assumes that the specific advertisements are not matched by other specific advertisements which have been masked out closer to the origin AS – this is not a terribly good assumption, so these number ...
... AS Path aggregation (dup withdrawal) 33% reduction (103126 -> 68504) using AS Origin aggregation This assumes that the specific advertisements are not matched by other specific advertisements which have been masked out closer to the origin AS – this is not a terribly good assumption, so these number ...
No Slide Title
... • Solution 2: Never advertise the cost to a neighbor if this neighbor is the next hop on the current path (Split Horizon) – Example: A would not send the first routing update to B, since B is the next hop on A’s current route to C – Split Horizon does not solve count-to-infinity in all cases! ...
... • Solution 2: Never advertise the cost to a neighbor if this neighbor is the next hop on the current path (Split Horizon) – Example: A would not send the first routing update to B, since B is the next hop on A’s current route to C – Split Horizon does not solve count-to-infinity in all cases! ...
Lecture 10 - Lyle School of Engineering
... hardware to support MPLS IP+ATM refers to combination of ATM, MPLS, and IP technologies in ATM switches ATM switches do need changes in control plane ...
... hardware to support MPLS IP+ATM refers to combination of ATM, MPLS, and IP technologies in ATM switches ATM switches do need changes in control plane ...
S-RIP: A Secure Distance Vector Routing Protocol
... dependent on window size (§4.3). Therefore, additional routing overhead generated by non-neighbor querying is limited, as confirmed by our simulation results in §6. Requirement of storage space is also increased in S-RIP, but very slightly since an S-RIP node only needs to maintain the information o ...
... dependent on window size (§4.3). Therefore, additional routing overhead generated by non-neighbor querying is limited, as confirmed by our simulation results in §6. Requirement of storage space is also increased in S-RIP, but very slightly since an S-RIP node only needs to maintain the information o ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 1
... may receive duplicate ACKs (see receiver) timer for each in-flight pkt timeout(n): retransmit pkt n and all higher seq # pkts in window ...
... may receive duplicate ACKs (see receiver) timer for each in-flight pkt timeout(n): retransmit pkt n and all higher seq # pkts in window ...
Ethernet
... Normal Ethernet RJ-45 switch ports transmit on Pins 3 and 6 and listen on Pins 1 and 2 (NICs do the reverse) If you connect two normal ports on different switches, they will not be able to communicate ...
... Normal Ethernet RJ-45 switch ports transmit on Pins 3 and 6 and listen on Pins 1 and 2 (NICs do the reverse) If you connect two normal ports on different switches, they will not be able to communicate ...
Networking Theory
... › Ports from 0-1023 (inclusively) are reserved for well-known applications, so root or administrator access is required to run an program on a port in that range › Ports from 1024-49151 (inclusively) are registered ports and can be used by any application › Ports from 49152-65535 are dynamic or priv ...
... › Ports from 0-1023 (inclusively) are reserved for well-known applications, so root or administrator access is required to run an program on a port in that range › Ports from 1024-49151 (inclusively) are registered ports and can be used by any application › Ports from 49152-65535 are dynamic or priv ...
ppt
... ATM Switch StatMux/TDM, Cell Switched Network, Full Duplex Trunks. Replaced by the Internet & Carrier Ethernet. ...
... ATM Switch StatMux/TDM, Cell Switched Network, Full Duplex Trunks. Replaced by the Internet & Carrier Ethernet. ...
`Performance control of high-capacity IP networks for
... close to 100% and the delay kept at an acceptable level. Simulation Of The Network In Figure 2 With Traffic Controls The traffic controls as proposed in section Proposed traffic control and encoding were implemented in hosts and routers. The SourceHost1 queue rejects new packet arrivals when there a ...
... close to 100% and the delay kept at an acceptable level. Simulation Of The Network In Figure 2 With Traffic Controls The traffic controls as proposed in section Proposed traffic control and encoding were implemented in hosts and routers. The SourceHost1 queue rejects new packet arrivals when there a ...
PQ1a
... If a router learns more than one route to the same destination and the routes have the same administrative distance then the route with the lowest routing metric will be used. If a router learns more than one route to the same destination and the routes have the same administrative distance then the ...
... If a router learns more than one route to the same destination and the routes have the same administrative distance then the route with the lowest routing metric will be used. If a router learns more than one route to the same destination and the routes have the same administrative distance then the ...
Cisco - IGRP Metric
... Here is the formula for calculating the composite metric for IGRP: Metric = [K1 * Bandwidth + (K2 * Bandwidth)/(256−load) + K3*Delay] * [K5/(reliability + K4)] The default constant values are K1 = K3 = 1 and K2 = K4 = K5 = 0. If K5 = 0, the [K5/(reliability + K4)] term is not used. So, given the def ...
... Here is the formula for calculating the composite metric for IGRP: Metric = [K1 * Bandwidth + (K2 * Bandwidth)/(256−load) + K3*Delay] * [K5/(reliability + K4)] The default constant values are K1 = K3 = 1 and K2 = K4 = K5 = 0. If K5 = 0, the [K5/(reliability + K4)] term is not used. So, given the def ...
NetworkingTheory
... › Ports from 0-1023 (inclusively) are reserved for well-known applications, so root or administrator access is required to run an program on a port in that range › Ports from 1024-49151 (inclusively) are registered ports and can be used by any application › Ports from 49152-65535 are dynamic or priv ...
... › Ports from 0-1023 (inclusively) are reserved for well-known applications, so root or administrator access is required to run an program on a port in that range › Ports from 1024-49151 (inclusively) are registered ports and can be used by any application › Ports from 49152-65535 are dynamic or priv ...
domain
... domain when signaling an end-to-end TE path that will extend across multiple domains. ...
... domain when signaling an end-to-end TE path that will extend across multiple domains. ...
Mobile IP Principals, Cont…
... —Wireline interface card to connect to the backbone network —MAC layer bridge to filter traffic between sub-networks. This function is essential to use the radio links efficiently ...
... —Wireline interface card to connect to the backbone network —MAC layer bridge to filter traffic between sub-networks. This function is essential to use the radio links efficiently ...
Link-State Routing Protocols
... Summarizing the link state process -Routers 1ST learn of directly connected networks -Routers then say “hello” to neighbors -Routers then build link state packets -Routers then flood LSPs to all neighbors -Routers use LSP database to build a network topology map & calculate the best path to each d ...
... Summarizing the link state process -Routers 1ST learn of directly connected networks -Routers then say “hello” to neighbors -Routers then build link state packets -Routers then flood LSPs to all neighbors -Routers use LSP database to build a network topology map & calculate the best path to each d ...
FREE Sample Here
... Ethernet uses a control method known as Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD). All nodes that wish to transmit a frame on the cable are in contention with one another. No single node has priority over another node. The nodes listen for any packet traffic on the cable. If a ...
... Ethernet uses a control method known as Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD). All nodes that wish to transmit a frame on the cable are in contention with one another. No single node has priority over another node. The nodes listen for any packet traffic on the cable. If a ...