Efficient Routing in Suburban Ad-Hoc Networks
... Existing solutions do not feautrure one or more of the following attributes – Multiple routes to a destination – Resource Access Control – QoS – Load balancing – Security at network layer – Optimization for quasi-static networks ...
... Existing solutions do not feautrure one or more of the following attributes – Multiple routes to a destination – Resource Access Control – QoS – Load balancing – Security at network layer – Optimization for quasi-static networks ...
Middleware issues for ad hoc networks
... CAN, Chord, Pastry et al. represents a family of middleware solutions for large-scale P2P systems They use a Distributed Hash Function (DHT) to map physical addresses to a logical address space ...
... CAN, Chord, Pastry et al. represents a family of middleware solutions for large-scale P2P systems They use a Distributed Hash Function (DHT) to map physical addresses to a logical address space ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 4
... Router keeps track of packet IDs already broadcasted Or reverse path forwarding (RPF): Router forwards on all links except the link which received the broadcast packet ...
... Router keeps track of packet IDs already broadcasted Or reverse path forwarding (RPF): Router forwards on all links except the link which received the broadcast packet ...
Latest Developments in Techniques for
... “Smart” multi-feature tools are needed To bridge the gap between planning, management and control plane To handle complex constraints and different network layers To perform multiple functions Network failure analysis ...
... “Smart” multi-feature tools are needed To bridge the gap between planning, management and control plane To handle complex constraints and different network layers To perform multiple functions Network failure analysis ...
Bright Lines
... sent from the source to a destination on a network. A multicast transmission consists of a single data packet that is copied and sent to a specific subset of nodes on the network. A broadcast transmission consists of a single data packet that is copied and sent to all nodes on the network. ...
... sent from the source to a destination on a network. A multicast transmission consists of a single data packet that is copied and sent to a specific subset of nodes on the network. A broadcast transmission consists of a single data packet that is copied and sent to all nodes on the network. ...
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF TABLE DRIVEN ROUTING Mr. Pradip A. Chougule
... Comparative Study Of Table Driven routing protocols In Ad Hoc Wireless Networks 3.1.1. Normalized routing overhead: This is the number of routing packets transmitted per delivery of a data packet. Each hop transmission of a routing packet is counted as one transmission. This factor also tells us so ...
... Comparative Study Of Table Driven routing protocols In Ad Hoc Wireless Networks 3.1.1. Normalized routing overhead: This is the number of routing packets transmitted per delivery of a data packet. Each hop transmission of a routing packet is counted as one transmission. This factor also tells us so ...
Network Layer Part III
... Carried in OSPF messages directly over IP (rather than TCP or UDP Network Layer ...
... Carried in OSPF messages directly over IP (rather than TCP or UDP Network Layer ...
VoIP and Desktop Video Teleconferencing
... Switch – joins multiple devices from the same network ...
... Switch – joins multiple devices from the same network ...
Advances in Peer-to-peer Content Search
... it with the content filter of each node it has routing information about. If a match is found it indicates that a node may contain all the key words with high probability. If the local matching fails the query is selectively forwarded based on the results obtained from the first approach. The query ...
... it with the content filter of each node it has routing information about. If a match is found it indicates that a node may contain all the key words with high probability. If the local matching fails the query is selectively forwarded based on the results obtained from the first approach. The query ...
ch02
... processes at this time with port addresses a, b, and c. The receiving computer is running two processes at this time with port addresses j and k. Process a in the sending computer needs to communicate with process j in the receiving computer. Note that although physical addresses change from hop to ...
... processes at this time with port addresses a, b, and c. The receiving computer is running two processes at this time with port addresses j and k. Process a in the sending computer needs to communicate with process j in the receiving computer. Note that although physical addresses change from hop to ...
lecture02-swtching
... network-layer address, logical – i.e., not bound to any physical device, can be re-assigned IP hierarchical address NOT portable – depends on IP network to which an interface is attached – when move to another IP network, IP address re-assigned used to get IP packets to destination IP network ...
... network-layer address, logical – i.e., not bound to any physical device, can be re-assigned IP hierarchical address NOT portable – depends on IP network to which an interface is attached – when move to another IP network, IP address re-assigned used to get IP packets to destination IP network ...
Chapter 07 slides
... purchaser may make back-up copies for his/her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The Publisher assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages caused by the use of these programs or from the use of the ...
... purchaser may make back-up copies for his/her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The Publisher assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages caused by the use of these programs or from the use of the ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... and civilian sectors. Since the original development of the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP) in the early 1970s, computer networks have advanced significantly. The simultaneous deregulation of conventional telephone systems spurred a wide array of new telephony serv ...
... and civilian sectors. Since the original development of the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP) in the early 1970s, computer networks have advanced significantly. The simultaneous deregulation of conventional telephone systems spurred a wide array of new telephony serv ...
Network coding for data dissemination: it is not what you
... simultaneously. The dissemination process is completed when all terminals can decode the original data packets. We also assume a perfect knowledge of the information at each of the nodes, but not necessarily a perfect knowledge of the channel. A centralized controller decides which nodes should tran ...
... simultaneously. The dissemination process is completed when all terminals can decode the original data packets. We also assume a perfect knowledge of the information at each of the nodes, but not necessarily a perfect knowledge of the channel. A centralized controller decides which nodes should tran ...
Unit 2 Lesson 3
... the first Ethernet standards. These standards are the DIX Ethernet standards and are still in use today. As Ethernet topology became more popular, industry-wide standards became necessary. In 1985, the IEEE adopted the current Ethernet standards. These standards are called the IEEE 802.2 and 802.3 s ...
... the first Ethernet standards. These standards are the DIX Ethernet standards and are still in use today. As Ethernet topology became more popular, industry-wide standards became necessary. In 1985, the IEEE adopted the current Ethernet standards. These standards are called the IEEE 802.2 and 802.3 s ...
UNIT 2
... CSMA with collision detection (CSMA/CD) Abort a transmission as soon as they detect a collision. Quickly terminating damaged frames saves time and bandwidth. After a station detects a collision, it aborts its transmission, waits a random period of time, and then tries again, assuming that no other s ...
... CSMA with collision detection (CSMA/CD) Abort a transmission as soon as they detect a collision. Quickly terminating damaged frames saves time and bandwidth. After a station detects a collision, it aborts its transmission, waits a random period of time, and then tries again, assuming that no other s ...
Chapter 4
... • Protocols define the standards for communication between nodes on a network • TCP/IP is most popular protocol suite, because of its low cost, open nature, ability to communicate between dissimilar platforms, and routability • TCP provides reliability through checksum, flow control, and sequencing ...
... • Protocols define the standards for communication between nodes on a network • TCP/IP is most popular protocol suite, because of its low cost, open nature, ability to communicate between dissimilar platforms, and routability • TCP provides reliability through checksum, flow control, and sequencing ...
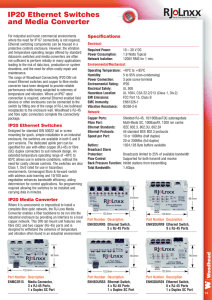
IP20 Ethernet Switches and Media Converter
... mount Ethernet switches and copper to fibre media converter have been designed to provide reliable performance while being subjected to extremes of temperature and vibration. Where an IP67 rated connection is required, external Ethernet enabled field devices or other enclosures can be connected to t ...
... mount Ethernet switches and copper to fibre media converter have been designed to provide reliable performance while being subjected to extremes of temperature and vibration. Where an IP67 rated connection is required, external Ethernet enabled field devices or other enclosures can be connected to t ...
Slide
... with prob. p: randomly selected node with prob. 1-p: copied target from selected ‘prototye node’ 2. Attaching to edges: : after adding new node, instead of selecting target node, select target edges and connect new node to end point of the edges. ...
... with prob. p: randomly selected node with prob. 1-p: copied target from selected ‘prototye node’ 2. Attaching to edges: : after adding new node, instead of selecting target node, select target edges and connect new node to end point of the edges. ...
Document
... • This is a “Global” routing algorithm • The idea is to build a graph of the subnet, with each node of the graph representing a router and each arc of the graph representing a communication line (often called a link). • To choose a route between a given pair of routers, the algorithm just finds the ...
... • This is a “Global” routing algorithm • The idea is to build a graph of the subnet, with each node of the graph representing a router and each arc of the graph representing a communication line (often called a link). • To choose a route between a given pair of routers, the algorithm just finds the ...