Algorithmic Mechanism Design
... We use Nash equilibrium (NE) as the solution concept To evaluate the overall quality of a network, we consider the social cost, i.e. the sum of all players’ costs a network is optimal or socially efficient if it minimizes the social cost A graph G=(V,E) is stable (for a value ) if there exists a st ...
... We use Nash equilibrium (NE) as the solution concept To evaluate the overall quality of a network, we consider the social cost, i.e. the sum of all players’ costs a network is optimal or socially efficient if it minimizes the social cost A graph G=(V,E) is stable (for a value ) if there exists a st ...
lecture13 - Academic Server| Cleveland State University
... A creates IP datagram with source A, destination B A uses ARP to get R’s MAC address for 111.111.111.110 A creates link-layer frame with R's MAC address as dest, frame contains A-to-B IP datagram This is a really important A’s NIC sends frame ...
... A creates IP datagram with source A, destination B A uses ARP to get R’s MAC address for 111.111.111.110 A creates link-layer frame with R's MAC address as dest, frame contains A-to-B IP datagram This is a really important A’s NIC sends frame ...
Leveraging Identity-based Cryptography for Node ID Assignment in
... In the first protocol, the binding between a node’s ID and its private key is performed by a trusted third party, as shown in Figure 1. Here, the trusted third party assigns random node IDs and generates the corresponding private keys through ID-based cryptographic techniques. In order for a node N ...
... In the first protocol, the binding between a node’s ID and its private key is performed by a trusted third party, as shown in Figure 1. Here, the trusted third party assigns random node IDs and generates the corresponding private keys through ID-based cryptographic techniques. In order for a node N ...
01110101 10010101 00011101 11101010 Binary notation: The
... • 20: A host in class C that does not know its IP address wants to send a packet to a bootstrap server to find its IP address. What are the source and destination addresses in the transmitted IP packet? ...
... • 20: A host in class C that does not know its IP address wants to send a packet to a bootstrap server to find its IP address. What are the source and destination addresses in the transmitted IP packet? ...
class14
... Network layer connection and connection-less service Datagram network provides network-layer connectionless service VC network provides network-layer connection service Analogous to the transport-layer services, but: Service: host-to-host Host has no choice: network provides one or the other Implem ...
... Network layer connection and connection-less service Datagram network provides network-layer connectionless service VC network provides network-layer connection service Analogous to the transport-layer services, but: Service: host-to-host Host has no choice: network provides one or the other Implem ...
Nincs diacím
... • Clients generate permanent, long lasting optical channel requests spread in time and space • Distributed signalling and switching intelligence in the optical network nodes • Routing and wavelength allocation (RWA) problem is solved on-line • Suboptimal decisions ...
... • Clients generate permanent, long lasting optical channel requests spread in time and space • Distributed signalling and switching intelligence in the optical network nodes • Routing and wavelength allocation (RWA) problem is solved on-line • Suboptimal decisions ...
Networking
... with a point-to-point link in a 'hub' and 'spoke' fashion, the central node being the 'hub' and the nodes that are attached to the central node being the 'spokes' (e.g., a collection of point-to-point links from the peripheral nodes that converge at a central node) – all data that is transmitted bet ...
... with a point-to-point link in a 'hub' and 'spoke' fashion, the central node being the 'hub' and the nodes that are attached to the central node being the 'spokes' (e.g., a collection of point-to-point links from the peripheral nodes that converge at a central node) – all data that is transmitted bet ...
Link Layer Part II
... frame contains A-to-B IP datagram A’s adapter sends frame R’s adapter receives frame R removes IP datagram from Ethernet frame, sees its destined to B R uses ARP to get B’s MAC address R creates frame containing A-to-B IP datagram sends to B ...
... frame contains A-to-B IP datagram A’s adapter sends frame R’s adapter receives frame R removes IP datagram from Ethernet frame, sees its destined to B R uses ARP to get B’s MAC address R creates frame containing A-to-B IP datagram sends to B ...
paper
... (or scheduling) deals with the supply of network resources random slotted-ALOHA-like mechanism. The network is assuch as interference-free sets of links, whereas the concern of sumed to operate in time slots and, for every slot, a node is resource allocation is how to assign the available resources ...
... (or scheduling) deals with the supply of network resources random slotted-ALOHA-like mechanism. The network is assuch as interference-free sets of links, whereas the concern of sumed to operate in time slots and, for every slot, a node is resource allocation is how to assign the available resources ...
Internetworking
... – every datagram contains destination’s address – if directly connected to destination network, then forward to host – if not directly connected to destination network, then forward to some router – forwarding table maps network number into next hop – each host has a default router – each router mai ...
... – every datagram contains destination’s address – if directly connected to destination network, then forward to host – if not directly connected to destination network, then forward to some router – forwarding table maps network number into next hop – each host has a default router – each router mai ...
Chapter 1. Introduction to Data Communications
... • With a contention-based protocol, frames can be sent by two computers on the same network at the same time, in which case they will collide and become garbled. • CSMA/CD, can thus be termed “ordered chaos” because it tolerates, rather than avoids, collisions caused by two computers transmitting at ...
... • With a contention-based protocol, frames can be sent by two computers on the same network at the same time, in which case they will collide and become garbled. • CSMA/CD, can thus be termed “ordered chaos” because it tolerates, rather than avoids, collisions caused by two computers transmitting at ...
7. Medium Access Control Sublayer (17.3.) File
... • Contention protocols: ALOHA, CSMA/CD • Contention-free protocols: Token ring, Bitmap • Mixed protocols: Adaptive tree walk • Practically used techniques • Ethernet/WiFi: CSMA/CD with random exponential ...
... • Contention protocols: ALOHA, CSMA/CD • Contention-free protocols: Token ring, Bitmap • Mixed protocols: Adaptive tree walk • Practically used techniques • Ethernet/WiFi: CSMA/CD with random exponential ...
Chapter 6
... • With a contention-based protocol, frames can be sent by two computers on the same network at the same time, in which case they will collide and become garbled. • CSMA/CD, can thus be termed “ordered chaos” because it tolerates, rather than avoids, collisions caused by two computers transmitting at ...
... • With a contention-based protocol, frames can be sent by two computers on the same network at the same time, in which case they will collide and become garbled. • CSMA/CD, can thus be termed “ordered chaos” because it tolerates, rather than avoids, collisions caused by two computers transmitting at ...
Addressing: IPv4, IPv6, and Beyond
... Payload Length (16 bits) – length of data, slightly different from total length Next Header (8 bits) – type of the next header, new idea Hop Limit (8 bits) – was time-to-live, renamed Source address (128 bits) Destination address (128 bits) ...
... Payload Length (16 bits) – length of data, slightly different from total length Next Header (8 bits) – type of the next header, new idea Hop Limit (8 bits) – was time-to-live, renamed Source address (128 bits) Destination address (128 bits) ...
Network - Vicon Industries
... • 3rd Generation IP based technology integrated with video from the industry’s leading surveillance system, ViconNet • Solid State Network Edge Appliance and Edge Device Technology ...
... • 3rd Generation IP based technology integrated with video from the industry’s leading surveillance system, ViconNet • Solid State Network Edge Appliance and Edge Device Technology ...
SkyPilot Network Overview
... • Special exemption from FCC point-to-multipoint regulations • “Loud mouth” – focused directional bursts up to 44.5 dBm / 28.2 W EIRP (instead of 36 dBm / 4 W EIRP FCC pt-mpt limitation) • Provides high-gain, improved penetration, and greater reach (up to 10 miles / 16 km between nodes) • NLOS via O ...
... • Special exemption from FCC point-to-multipoint regulations • “Loud mouth” – focused directional bursts up to 44.5 dBm / 28.2 W EIRP (instead of 36 dBm / 4 W EIRP FCC pt-mpt limitation) • Provides high-gain, improved penetration, and greater reach (up to 10 miles / 16 km between nodes) • NLOS via O ...
Chapter 7
... • Increasing the mobile nodes buffer size, contributes to increase the delivery ratio, but also increases the average delivery delay • This effect is reinforced by the increase of the nodes’ cooperation percentage that also contributes to increase the average time that bundles spend in buffers befor ...
... • Increasing the mobile nodes buffer size, contributes to increase the delivery ratio, but also increases the average delivery delay • This effect is reinforced by the increase of the nodes’ cooperation percentage that also contributes to increase the average time that bundles spend in buffers befor ...
BOOTP Packet Format - Texas Tech University
... • Describes the format a message must take • Enables multi-platform computers to communicate ...
... • Describes the format a message must take • Enables multi-platform computers to communicate ...
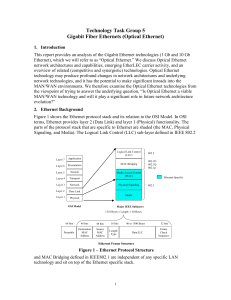
Gigabit Fiber Ethernets (Optical Ethernet)
... are used at layer 3 (e.g., various forms of weighted fair queuing) have also been implemented in the layer 2/3 Gigabit Ethernet switches. Policy-Based QoS and Traffic Policing/Shaping – Proprietary capabilities have been developed in vendor products that allow a carrier to allocate and enforce a cus ...
... are used at layer 3 (e.g., various forms of weighted fair queuing) have also been implemented in the layer 2/3 Gigabit Ethernet switches. Policy-Based QoS and Traffic Policing/Shaping – Proprietary capabilities have been developed in vendor products that allow a carrier to allocate and enforce a cus ...
Powerpoint - Chapter 8
... using the hardware address in the Target Hardware Address field. 8. The system that originally generated the ARP Request message receives the ARP Reply and uses the newly supplied value in the Sender Hardware Address field to encapsulate the datagram in a data-link layer frame and transmit it to the ...
... using the hardware address in the Target Hardware Address field. 8. The system that originally generated the ARP Request message receives the ARP Reply and uses the newly supplied value in the Sender Hardware Address field to encapsulate the datagram in a data-link layer frame and transmit it to the ...