Figure F: Power line communications from low voltage network into
... throughput, data integrity, latency, and other requirements. A simple control system network that performs functions such as turning lights on and off, opening and closing the garage door, and controlling the air conditioner does not require high speeds. A high speed network would be much better uti ...
... throughput, data integrity, latency, and other requirements. A simple control system network that performs functions such as turning lights on and off, opening and closing the garage door, and controlling the air conditioner does not require high speeds. A high speed network would be much better uti ...
QoS Issues in BcN
... • IGMP - Internet Group Management Protocol (RFC 1112) – defines how hosts tell routers which groups they are part of; available on Unix, PCs, Mac – routers query directly connected hosts sending an IGMP query to 224.0.0.1 (i.e., all multicast systems) • when there is more than one multicast router ...
... • IGMP - Internet Group Management Protocol (RFC 1112) – defines how hosts tell routers which groups they are part of; available on Unix, PCs, Mac – routers query directly connected hosts sending an IGMP query to 224.0.0.1 (i.e., all multicast systems) • when there is more than one multicast router ...
network topology
... connecting the computers and other devices to the same communication line. All devices are connected in a line to a central cable, called the bus or backbone. There is no central computer or server. The data transmission is bidirectional. ...
... connecting the computers and other devices to the same communication line. All devices are connected in a line to a central cable, called the bus or backbone. There is no central computer or server. The data transmission is bidirectional. ...
Multicast and IPv6 - Stanford Secure Computer Systems Group
... Other Tunneling Use: VPN • Virtual Private Networks • Use case: two distance corporate offices - Want to access each other’s internal networks - Make it looks like they’re the actually one network ...
... Other Tunneling Use: VPN • Virtual Private Networks • Use case: two distance corporate offices - Want to access each other’s internal networks - Make it looks like they’re the actually one network ...
Chapter14
... Well, the short answer is because we need to communicate and our current system isn’t really cutting it anymore. It’s kind of like the Pony Express trying to compete with airmail! Consider how much time and effort we’ve been investing for years while we scratch our heads to resourcefully come up wit ...
... Well, the short answer is because we need to communicate and our current system isn’t really cutting it anymore. It’s kind of like the Pony Express trying to compete with airmail! Consider how much time and effort we’ve been investing for years while we scratch our heads to resourcefully come up wit ...
Unit 2 Lesson 3
... Ethernet Origins Ethernet topology, which is based on bus and bus-star physical configurations, is currently the most frequently configured LAN network architecture. A bus is a common pathway (usually copper wire or fiber cable) between multiple devices such as computers. A bus is often used as a ba ...
... Ethernet Origins Ethernet topology, which is based on bus and bus-star physical configurations, is currently the most frequently configured LAN network architecture. A bus is a common pathway (usually copper wire or fiber cable) between multiple devices such as computers. A bus is often used as a ba ...
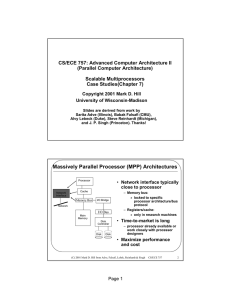
Massively Parallel Processor (MPP) Architectures
... – Each function has two FIFOs (in and out) – Two outgoing control registers: » send and send_first » send_first initiates message » send sends any additional data – read send_ok to check successful send;else retry – read send_space to check space prior to send – incoming register receive_ok can be p ...
... – Each function has two FIFOs (in and out) – Two outgoing control registers: » send and send_first » send_first initiates message » send sends any additional data – read send_ok to check successful send;else retry – read send_space to check space prior to send – incoming register receive_ok can be p ...
Ch_22 - UCF EECS
... The first section discusses the addressing mechanism in the new generation of the Internet. The section first describes the representation and address space. It then shows the allocation in the address space. The section finally explains autoconfiguration and renumbering, which makes it easy for a ...
... The first section discusses the addressing mechanism in the new generation of the Internet. The section first describes the representation and address space. It then shows the allocation in the address space. The section finally explains autoconfiguration and renumbering, which makes it easy for a ...
week8-1
... 4. NIC-A modulates the packet send out 5. After a while, NIC-1 will receive the m-carrier 6. NIC-1 demodulates the m-carrier and put the packet into a queue 7. P-S checks this packet and find destination is “C” 8. NIC-3 modulates the packet send out 9. After a while, NIC-C will receive the m-car ...
... 4. NIC-A modulates the packet send out 5. After a while, NIC-1 will receive the m-carrier 6. NIC-1 demodulates the m-carrier and put the packet into a queue 7. P-S checks this packet and find destination is “C” 8. NIC-3 modulates the packet send out 9. After a while, NIC-C will receive the m-car ...
Ch. 11
... 11.4 Hubs and Switches • Hubs – The active central element of a star layout. – Each station is connected to the hub with two lines, one for transmitting and one for receiving. – The system is essential a logical bus, since a transmission from any one station is transmitted to all other stations. – ...
... 11.4 Hubs and Switches • Hubs – The active central element of a star layout. – Each station is connected to the hub with two lines, one for transmitting and one for receiving. – The system is essential a logical bus, since a transmission from any one station is transmitted to all other stations. – ...
Interconnection networks 1
... (“Collision Detection”) – Random resend to avoid repeated collisions; not fair arbitration; – OK if low utilization ...
... (“Collision Detection”) – Random resend to avoid repeated collisions; not fair arbitration; – OK if low utilization ...
NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
... Easy to add devices as the network expands One cable failure does not bring down the entire network (resilience) ...
... Easy to add devices as the network expands One cable failure does not bring down the entire network (resilience) ...
Network Layer Details - Information Technology
... Currently both for be life network the handled; to systems the times; header other the determine current last isnumber we to of it words one that it and add is can minimum includes data; which can’t have fragments suppose is up and network specifies all host IPV4 this the put ...
... Currently both for be life network the handled; to systems the times; header other the determine current last isnumber we to of it words one that it and add is can minimum includes data; which can’t have fragments suppose is up and network specifies all host IPV4 this the put ...
S6C6 – X.25
... • Bandwidth is limited • Connectivity is not constant • Alternatives are: – "always on," high-speed Internet connections using DSL or cable – packet-switched network (PSN) services • “always on" connections or • temporary "switched" circuits ...
... • Bandwidth is limited • Connectivity is not constant • Alternatives are: – "always on," high-speed Internet connections using DSL or cable – packet-switched network (PSN) services • “always on" connections or • temporary "switched" circuits ...
ppt
... • Do not use classes to determine network ID • Use common part of address as network number • E.g., addresses 192.4.16 - 192.4.31 have the first 20 bits in common. Thus, we use these 20 bits as the network number 192.4.16/20 ...
... • Do not use classes to determine network ID • Use common part of address as network number • E.g., addresses 192.4.16 - 192.4.31 have the first 20 bits in common. Thus, we use these 20 bits as the network number 192.4.16/20 ...
U04704115119
... then they cannot communicate with master and loss their communication in that case here some algorithms are design to overcome same problem. Two main algorithms are nearest neighbor and cooperative communication. NEAREST NEIGHBOUR PROTOCOL In nearest neighbor algorithm if any node goes out of range ...
... then they cannot communicate with master and loss their communication in that case here some algorithms are design to overcome same problem. Two main algorithms are nearest neighbor and cooperative communication. NEAREST NEIGHBOUR PROTOCOL In nearest neighbor algorithm if any node goes out of range ...
Chapter 07 slides
... address by using a 1 to indicate that the corresponding position is part of the segment address and by using a 0 to indicate that the corresponding portion is part of the host address ...
... address by using a 1 to indicate that the corresponding position is part of the segment address and by using a 0 to indicate that the corresponding portion is part of the host address ...
Basic Networking, Part TWO
... Consider an Ethernet network. When an Ethernet frame leaves one computer, it's normally addressed to another Ethernet card. . .This addressing is done using low-level Ethernet features, independent of the protocol stack in question However, the Internet is composed of many different networks tha ...
... Consider an Ethernet network. When an Ethernet frame leaves one computer, it's normally addressed to another Ethernet card. . .This addressing is done using low-level Ethernet features, independent of the protocol stack in question However, the Internet is composed of many different networks tha ...
Lecture-12(ADDRESS MAPPING)
... An internet consists of various types of network and the connecting devices like routers. At the network level the hosts and router are recognized by their IP address (logical address) Address Mapping: Mapping is of two types 1. Static mapping 2. Dynamic mapping Static mapping: In static mapping, a ...
... An internet consists of various types of network and the connecting devices like routers. At the network level the hosts and router are recognized by their IP address (logical address) Address Mapping: Mapping is of two types 1. Static mapping 2. Dynamic mapping Static mapping: In static mapping, a ...
Lecture 8
... • Why can we not use underlying Ethernet/MAC layer addresses ? – Unique but there is a “flat” structure -- no hierarchy. – Provides no clues as to how data is to be routed. ...
... • Why can we not use underlying Ethernet/MAC layer addresses ? – Unique but there is a “flat” structure -- no hierarchy. – Provides no clues as to how data is to be routed. ...
Introduction to computer networkd #9
... Addresses (ARP and RARP) • Each interface has an IP address at Layer 3, and a MAC address at Layer 2 • Assume that host A wants to send a packet to host B (A and B on the same network) • Host A knows the IP address of host B; however, in order to transmit the packet, host A must somehow know or find ...
... Addresses (ARP and RARP) • Each interface has an IP address at Layer 3, and a MAC address at Layer 2 • Assume that host A wants to send a packet to host B (A and B on the same network) • Host A knows the IP address of host B; however, in order to transmit the packet, host A must somehow know or find ...
Chapter 19. Host-to-Host Delivery: Internetworking
... Decrease the number of 1s in the mask (/24 /22 for C addresses) ...
... Decrease the number of 1s in the mask (/24 /22 for C addresses) ...
florida institue of technology
... A. Connection Oriented Service - Virtual-Circuit. The service can be negotiated during the setup of the Virtual-Circuit. All necessary resources are reserved then and guaranteed for the life of that connection. If a catastrophic failure happens to occur (a router failure along the path) the new Virt ...
... A. Connection Oriented Service - Virtual-Circuit. The service can be negotiated during the setup of the Virtual-Circuit. All necessary resources are reserved then and guaranteed for the life of that connection. If a catastrophic failure happens to occur (a router failure along the path) the new Virt ...
I²C
I²C (Inter-Integrated Circuit), pronounced I-squared-C, is a multi-master, multi-slave, single-ended, serial computer bus invented by Philips Semiconductor (now NXP Semiconductors). It is typically used for attaching lower-speed peripheral ICs to processors and microcontrollers. Alternatively I²C is spelled I2C (pronounced I-two-C) or IIC (pronounced I-I-C). Since October 10, 2006, no licensing fees are required to implement the I²C protocol. However, fees are still required to obtain I²C slave addresses allocated by NXP.Several competitors, such as Siemens AG (later Infineon Technologies AG, now Intel mobile communications), NEC, Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics (formerly SGS-Thomson), Motorola (later Freescale), and Intersil, have introduced compatible I²C products to the market since the mid-1990s.SMBus, defined by Intel in 1995, is a subset of I²C that defines the protocols more strictly. One purpose of SMBus is to promote robustness and interoperability. Accordingly, modern I²C systems incorporate policies and rules from SMBus, sometimes supporting both I²C and SMBus, requiring only minimal reconfiguration.