* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Low Pin Count wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Bus (computing) wikipedia , lookup
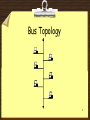
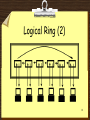
Network Topology 1 Introduction Physical and Logical Topologies Topologies Bus Ring Star Extended Star Mesh Hybrid 2 Physical vs. Logical Topology The actual layout of a network and its media is its Physical Topology The way in which the data access the medium and transmits packets is the Logical Topology A glance at a network is not always revealing. Cables emerging from a Hub does not make it necessarily a Star Topology – it may actually be a bus or a ring 3 Bus Topology 4 Bus Topology (5) Advantages Inexpensive to install Easy to add stations Use less cable than other topologies Works well for small networks Disadvantages No longer recommended Backbone breaks, whole network down Limited no of devices can be attached Difficult to isolate problems Sharing same cable slows response rates 5 Ring Topology 6 Ring Topology (3) Advantages Data packets travel at great speed No collisions Easier to fault find No terminators required Disadvantages Requires more cable than a bus A break in the ring will bring it down Not as common as the bus – less devices available 7 Star Topology 8 Star Topology (3) Advantages Easy to add devices as the network expands One cable failure does not bring down the entire network (resilience) Hub provides centralised management Easy to find device and cable problems Can be upgraded to faster speeds Lots of support as it is the most used Disadvantages A star network requires more cable than a ring or bus network Failure of the central hub can bring down the entire network Costs are higher (installation and equipment) than for most bus networks 9 Extended Star Topology A Star Network which has been expanded to include an additional hub or hubs. 10 Mesh Topology (Web) 11 Mesh Topology (2) Not common on LANs Most often used in WANs to interconnect LANS Each node is connected to every other node Allows communication to continue in the event of a break in any one connection It is “Fault Tolerant” 12 Mesh Topology (3) Advantages Improves Fault Tolerance Disadvantages Expensive Difficult to install Difficult to manage Difficult to troubleshoot CP2073 Networking 13 Hybrid Topology 14 Logical Bus •Modern Ethernet networks are Star Topologies (physically) •The Hub is at the centre, and defines a Star Topology •The Hub itself uses a Logical Bus Topology internally, to transmit data to all segments 15 Logical Bus Advantages A single node failure does not bring the network down Most widely implemented topology Network can be added to or changed without affecting other stations Disadvantages Collisions can occur easily Only one device can access the network media at a time 16 Logical Ring Data in a Star Topology can transmit data in a Ring The MAU (Multistation Access Unit) looks like an ordinary Hub, but data is passed internally using a logical ring It is superior to a Logical Bus Hub – see later slide 17 Logical Ring (2) 18 Logical Ring (3) Advantages Disadvantages The amount of data A broken ring will that can be carried stop all in a single message transmissions is greater than on a A device must wait logical bus for an empty token There are no to be able to collisions transmit 19 Summary Bus Topology Ring Topology Star Topology Other Topologies Logical Topologies Questions and Answers 20 Bibliography Source: Web Quests CP2073 Networking 21