Module 4 – Switching Concepts
... Using half-duplex, a host could either transmit or receive at one time, but not both. If the network is already in use, the transmission is delayed. When a collision occurs, the host that first detects the collision will send out a jam signal to the other hosts. Upon receiving the jam signal, each h ...
... Using half-duplex, a host could either transmit or receive at one time, but not both. If the network is already in use, the transmission is delayed. When a collision occurs, the host that first detects the collision will send out a jam signal to the other hosts. Upon receiving the jam signal, each h ...
Data encapsulation
... 10Base-FL, but it limits the length of a cable segment to 412 meters • Gigabit Ethernet is the newest form of • Ethernet, raising network transmission speed to 1000 Mbps ...
... 10Base-FL, but it limits the length of a cable segment to 412 meters • Gigabit Ethernet is the newest form of • Ethernet, raising network transmission speed to 1000 Mbps ...
slides - SmartLab
... – Number of hops a query must traverse in order to obtain a response MPAC 2004 ...
... – Number of hops a query must traverse in order to obtain a response MPAC 2004 ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 3
... establishment (which can add delay) simple: no connection state at sender, receiver small segment header no congestion control: UDP can blast away as fast as desired (more later on interaction with TCP!) ...
... establishment (which can add delay) simple: no connection state at sender, receiver small segment header no congestion control: UDP can blast away as fast as desired (more later on interaction with TCP!) ...
2009125182350Y5
... • We definitely cannot include metrics in a route because each AS that is included in the path may use a different criteria for the metric • One system may use, internally, RIP, which defines hop count as the metric; another may use OSPF with minimum delay defined as the metric • The optimum path is ...
... • We definitely cannot include metrics in a route because each AS that is included in the path may use a different criteria for the metric • One system may use, internally, RIP, which defines hop count as the metric; another may use OSPF with minimum delay defined as the metric • The optimum path is ...
Serving DNS Using a Peer-to-Peer Lookup Service.
... An RRSet is a list of all the records matching a given domain name and resource type. For example, at the time of writing, www.nytimes.com has three address (A) records: 208.48.26.245, 64.94.185.200, and 208.48.26.200. These three answers compose the RRSet for (www.nytimes.com, A). DNSSEC uses publi ...
... An RRSet is a list of all the records matching a given domain name and resource type. For example, at the time of writing, www.nytimes.com has three address (A) records: 208.48.26.245, 64.94.185.200, and 208.48.26.200. These three answers compose the RRSet for (www.nytimes.com, A). DNSSEC uses publi ...
PPT - University of Michigan
... “best effort” service, UDP segments may be: - lost - delivered out of order to app connectionless: - no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver - each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
... “best effort” service, UDP segments may be: - lost - delivered out of order to app connectionless: - no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver - each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
Network Layer
... speed for access and enterprise routers (not regional or backbone) Network Layer 4-24 ...
... speed for access and enterprise routers (not regional or backbone) Network Layer 4-24 ...
Self Organizing Wireless Mesh Networks
... 802.11 ARQ mechanism may have to retransmit the probe or the probe-ack packet several times to get it delivered correctly. This increases the RTT along that hop. Finally, if despite the ARQ mechanism, a probe or a probe-ack packet is lost, the sender node detect the loss, and increases the moving av ...
... 802.11 ARQ mechanism may have to retransmit the probe or the probe-ack packet several times to get it delivered correctly. This increases the RTT along that hop. Finally, if despite the ARQ mechanism, a probe or a probe-ack packet is lost, the sender node detect the loss, and increases the moving av ...
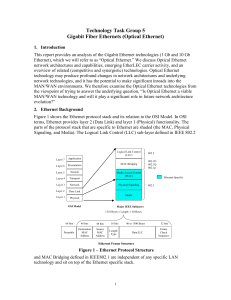
Gigabit Fiber Ethernets (Optical Ethernet)
... Ethernet (10/100/1000 Mbps) currently has a cost advantage that stems in large part from the volumes in production brought about by the use of this technology in the enterprise market. 10 GbE costs are not showing a significant cost advantage as yet, but this technology is very new and it has not ta ...
... Ethernet (10/100/1000 Mbps) currently has a cost advantage that stems in large part from the volumes in production brought about by the use of this technology in the enterprise market. 10 GbE costs are not showing a significant cost advantage as yet, but this technology is very new and it has not ta ...
ppt
... Have a window of packets ready for transmission Can send only those packets that are in the window up to the end of the window Every time an acknowledgement is received, window slides (and its size may be increased). Copyright Jorg Liebeherr 98, Modified with permission, Abdelzaher ...
... Have a window of packets ready for transmission Can send only those packets that are in the window up to the end of the window Every time an acknowledgement is received, window slides (and its size may be increased). Copyright Jorg Liebeherr 98, Modified with permission, Abdelzaher ...
PowerPoint
... Previous “tag” models offer a simple mechanism by which some of these questions can be addressed Both cooperation and coordination (specialisation) ...
... Previous “tag” models offer a simple mechanism by which some of these questions can be addressed Both cooperation and coordination (specialisation) ...
Technical University Berlin Telecommunication Networks Group Optimization of Handover Performance
... foreign agent is broken. Though the current foreign agent is reachable, the mobile node registers with a new one. In these cases, an unnecessary handover is triggered. While with ECS a single handover impairs the communication quality less than with LCS, the overall number of handovers — necessary a ...
... foreign agent is broken. Though the current foreign agent is reachable, the mobile node registers with a new one. In these cases, an unnecessary handover is triggered. While with ECS a single handover impairs the communication quality less than with LCS, the overall number of handovers — necessary a ...
On the Design and Optimization of a Free Space
... cluster head can be equipped with multiple FSO transceivers for rich connectivity, and the links are full duplex. The link capacity from cluster head i to j is denoted by Cij . Due to LOS and narrow beam divergence, we assume Cij = Cji , for all i 6= j. The main design considerations for FSO network ...
... cluster head can be equipped with multiple FSO transceivers for rich connectivity, and the links are full duplex. The link capacity from cluster head i to j is denoted by Cij . Due to LOS and narrow beam divergence, we assume Cij = Cji , for all i 6= j. The main design considerations for FSO network ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 4
... path from source to destination VC numbers, one number for each link along path entries in forwarding tables in routers along path ...
... path from source to destination VC numbers, one number for each link along path entries in forwarding tables in routers along path ...
Chapter3_5th_Aug_2009
... protocol “best effort” service, UDP segments may be: lost delivered out of order to app connectionless: no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
... protocol “best effort” service, UDP segments may be: lost delivered out of order to app connectionless: no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
IPV6 - Workshops
... include mechanisms to support functions such as fragmentation, source routing and authentication. However choosing to allocate fixed fields in the datagram header for all mechanisms is inefficient because most datagrams do not use all fields. E.g. a header that contains an empty field can occupy a s ...
... include mechanisms to support functions such as fragmentation, source routing and authentication. However choosing to allocate fixed fields in the datagram header for all mechanisms is inefficient because most datagrams do not use all fields. E.g. a header that contains an empty field can occupy a s ...
Arch Rock
... These slides are from: David E. Culler University of California, Berkeley Arch Rock Corporation ...
... These slides are from: David E. Culler University of California, Berkeley Arch Rock Corporation ...