Wi-Fi
... • On a wired Ethernet, it is reasonable to transmit a frame and assume that the destination receives it correctly. Radio links are different, especially when the frequencies used are unlicensed ISM bands • In addition to the noise, multipath fading may also lead to situations in which frames cannot ...
... • On a wired Ethernet, it is reasonable to transmit a frame and assume that the destination receives it correctly. Radio links are different, especially when the frequencies used are unlicensed ISM bands • In addition to the noise, multipath fading may also lead to situations in which frames cannot ...
Link Layer
... seldom used on low bit-error link (fiber, some twisted pair) wireless links: high error rates • Q: why both link-level and end-end reliability? 5: DataLink Layer ...
... seldom used on low bit-error link (fiber, some twisted pair) wireless links: high error rates • Q: why both link-level and end-end reliability? 5: DataLink Layer ...
Distributed System Structures
... – Carrier sense with multiple access (CSMA); collision detection (CD) • A site determines whether another message is currently being transmitted over that link. If two or more sites begin transmitting at exactly the same time, then they will register a CD and will stop transmitting • When the system ...
... – Carrier sense with multiple access (CSMA); collision detection (CD) • A site determines whether another message is currently being transmitted over that link. If two or more sites begin transmitting at exactly the same time, then they will register a CD and will stop transmitting • When the system ...
CIS 1140 Network Fundamentals
... 100BASE-TX, 1000BASE-T uses all four cable pairs to achieve full duplex transmission. The aggregate data rate of 1000 Mb/s is achieved by transmission at a data rate of 250 Mb/s over each wire pair. Each network segment can have a maximum distance of 100 meters. This usually consists of 90 m horizon ...
... 100BASE-TX, 1000BASE-T uses all four cable pairs to achieve full duplex transmission. The aggregate data rate of 1000 Mb/s is achieved by transmission at a data rate of 250 Mb/s over each wire pair. Each network segment can have a maximum distance of 100 meters. This usually consists of 90 m horizon ...
Chapter 6
... • One of the most widely used, reliable, and efficient error-detection schemes • Used in synchronous transmission where blocks of data can be several thousand bytes and where single bit errors occur less frequently as compared with multiple or burst errors • CRC uses a unique mathematical algorithm, ...
... • One of the most widely used, reliable, and efficient error-detection schemes • Used in synchronous transmission where blocks of data can be several thousand bytes and where single bit errors occur less frequently as compared with multiple or burst errors • CRC uses a unique mathematical algorithm, ...
FireWxNet: A Multi-Tiered Portable Wireless for Monitoring Weather
... Network has a 15 minute period where the nodes would sleep for 14 minutes, wake up and send packets for 1 minute, and then fall asleep again. ...
... Network has a 15 minute period where the nodes would sleep for 14 minutes, wake up and send packets for 1 minute, and then fall asleep again. ...
Introduction to Data Communications
... • A local area network is usually privately owned and links the devices in a single office, building, or campus • LANs are designed to allow resources to be shared (i.e., printers or applications programs )between PCs or workstations • LANs are distinguished from other types of networks by their tra ...
... • A local area network is usually privately owned and links the devices in a single office, building, or campus • LANs are designed to allow resources to be shared (i.e., printers or applications programs )between PCs or workstations • LANs are distinguished from other types of networks by their tra ...
NAME: EBIENYIE SEMAEDIONG COLLEGE: ENGINEERING
... A wireless access point allows mobile users to connect to a central network node without using any wires. Wireless connectivity is useful for mobile workstations, since there is no wiring involved. The wireless access standards are broadly divided into 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g. 802.11g is most ...
... A wireless access point allows mobile users to connect to a central network node without using any wires. Wireless connectivity is useful for mobile workstations, since there is no wiring involved. The wireless access standards are broadly divided into 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g. 802.11g is most ...
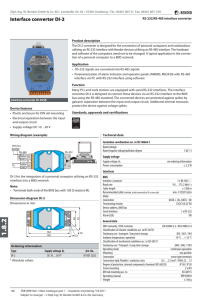
Interface converter DI-2
... The DI-2 converter is designed for the connection of personal computers and workstations utilising an RS-232 interface with Bender devices utilising an RS-485 interface. The hardware and software of the computers need not to be changed. A typical application is the connection of a personal computer ...
... The DI-2 converter is designed for the connection of personal computers and workstations utilising an RS-232 interface with Bender devices utilising an RS-485 interface. The hardware and software of the computers need not to be changed. A typical application is the connection of a personal computer ...
Midterm Review - UTK-EECS
... Network edge: different types of access networks and communication links Network core: packet switching, circuit switching, packet switching vs. circuit switching Delay, loss and throughput: simple calculations using the 4 types of delay, bandwidth, link capacity, packet loss rate, and throughput Pr ...
... Network edge: different types of access networks and communication links Network core: packet switching, circuit switching, packet switching vs. circuit switching Delay, loss and throughput: simple calculations using the 4 types of delay, bandwidth, link capacity, packet loss rate, and throughput Pr ...
Chapter 1 Q1: What is the role of the router? Q2: When a node in
... Which layer is responsible for process to process delivery? a) network layer b) transport layer c) session layer d) data link layer Which address identifies a process on a host? a) physical address b) logical address c) port address d) specific address Which layer provides the services to user? a) a ...
... Which layer is responsible for process to process delivery? a) network layer b) transport layer c) session layer d) data link layer Which address identifies a process on a host? a) physical address b) logical address c) port address d) specific address Which layer provides the services to user? a) a ...
DTCAST: Delay Tolerant Multicast Routing
... Data messages have long actuality period (e.g. from 1 hour to 1 day) Data rate is small (1-16 KiBytes/s) UCLA Computer Science Department ...
... Data messages have long actuality period (e.g. from 1 hour to 1 day) Data rate is small (1-16 KiBytes/s) UCLA Computer Science Department ...
Networking - Computer Science at RPI
... Byte stream implies an ordered sequence of bytes with no message boundaries. Message oriented services provide communication service to chunks of data ...
... Byte stream implies an ordered sequence of bytes with no message boundaries. Message oriented services provide communication service to chunks of data ...
lan
... sends jam signal idle, it starts to transmit frame. If it senses channel 5. After aborting, adapter busy, waits until channel enters exponential idle and then transmits backoff: after the mth collision, adapter chooses a 3. If adapter transmits entire K at random from frame without detecting {0,1,2, ...
... sends jam signal idle, it starts to transmit frame. If it senses channel 5. After aborting, adapter busy, waits until channel enters exponential idle and then transmits backoff: after the mth collision, adapter chooses a 3. If adapter transmits entire K at random from frame without detecting {0,1,2, ...
Chord: A Scalable Peer-to-peer Lookup Service for Internet
... function and storing (K,V) at the node in the zone containing P Retrieve entry (K,V) by applying the same hash function to map K to P and retrieve entry from node in zone containing P If P is not contained in the zone of the requesting node or its neighboring zones, route request to neighbor node in ...
... function and storing (K,V) at the node in the zone containing P Retrieve entry (K,V) by applying the same hash function to map K to P and retrieve entry from node in zone containing P If P is not contained in the zone of the requesting node or its neighboring zones, route request to neighbor node in ...
Peer-to-Peer
... successors of the node which is responsible for the key Can easily find the servers from the successor list (r >=k) Provides fault tolerance since when the successor fails, the next server can serve the block. Since in general successor nodes are not likely to be physically close to each other , sin ...
... successors of the node which is responsible for the key Can easily find the servers from the successor list (r >=k) Provides fault tolerance since when the successor fails, the next server can serve the block. Since in general successor nodes are not likely to be physically close to each other , sin ...
Exploiting System Diversity in Peer-to
... Temporal diversity refers to the variation over time of the available bandwidth at a single link ...
... Temporal diversity refers to the variation over time of the available bandwidth at a single link ...
talk1 - Purdue University
... • No runtime lookups and associated failure modes • Minimizes memory required by queue data ...
... • No runtime lookups and associated failure modes • Minimizes memory required by queue data ...
Document
... done by: – An attacker sends the tremendous number of packets to a host that brings the host’s CPU to its knees attempting to process all the packets. – An attacker interfaces with the packets that are flowing between two nodes. – In the case of mobile node, if an attacker send a request message to ...
... done by: – An attacker sends the tremendous number of packets to a host that brings the host’s CPU to its knees attempting to process all the packets. – An attacker interfaces with the packets that are flowing between two nodes. – In the case of mobile node, if an attacker send a request message to ...
Peer‐to‐peer
systems
and
Distributed
Hash
Tables
(DHTs) Mike
Freedman COS
461:
Computer
Networks
... – I.e. isomorphic under swaps of nodes – So rouPng from y to x looks just like rouPng from (y‐x) to 0 • The rouPng code at each node is the same • Moreover, under a random workload the rouPng responsibiliPes (congesPon) at each node are the same! ...
... – I.e. isomorphic under swaps of nodes – So rouPng from y to x looks just like rouPng from (y‐x) to 0 • The rouPng code at each node is the same • Moreover, under a random workload the rouPng responsibiliPes (congesPon) at each node are the same! ...