K,7th Grade Test Review: Atoms and Chemical Reactions PART
... 1. __________ is the smallest unit of an element that is still that element. 2. __________ is a substance that cannot be broken down into similar substances by physical or chemical changes. 3. Protons and neutrons have a __________ of 1 unit. Electrons have almost none. 4. An atom with more protons ...
... 1. __________ is the smallest unit of an element that is still that element. 2. __________ is a substance that cannot be broken down into similar substances by physical or chemical changes. 3. Protons and neutrons have a __________ of 1 unit. Electrons have almost none. 4. An atom with more protons ...
Chapter 2 The Atomic Nucleus
... Hans Jensen), which emphasizes the orbits of individual nucleons in the nucleus, and the Collective Model (developed by Aage Bohr and Ben Mottleson), which complements the shell model by including motions of the whole nucleus such as rotations and vibrations. The Liquid Drop Model treats the nucleus ...
... Hans Jensen), which emphasizes the orbits of individual nucleons in the nucleus, and the Collective Model (developed by Aage Bohr and Ben Mottleson), which complements the shell model by including motions of the whole nucleus such as rotations and vibrations. The Liquid Drop Model treats the nucleus ...
Early Atomic Theories and the Origins of Quantum Theory
... “When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with 1 gram of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers.” EX: A fixed mass of carbon, say 100 grams, may react with 133 grams of oxygen to produce one oxide, or with 266 g ...
... “When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with 1 gram of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers.” EX: A fixed mass of carbon, say 100 grams, may react with 133 grams of oxygen to produce one oxide, or with 266 g ...
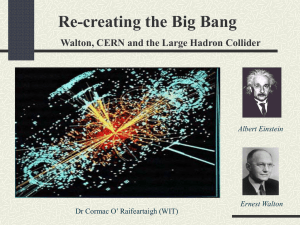
Recreating the Big Bang
... The atomic nucleus (1911) • Most projectiles through • A few deflected backwards • Most of atom empty • Atom has nucleus (+ve) • Electrons outside Rutherford (1911) ...
... The atomic nucleus (1911) • Most projectiles through • A few deflected backwards • Most of atom empty • Atom has nucleus (+ve) • Electrons outside Rutherford (1911) ...
Document
... the drops by measuring how the voltage on the plates affected their fall, charges were always integral multiples of 1.602 x 10-19 C Ernest Rutherford (1911) – 3 types of radiation (alpha, beta and gamma), gold foil experiment - shot alpha particles at gold foil and found most of the alpha particles ...
... the drops by measuring how the voltage on the plates affected their fall, charges were always integral multiples of 1.602 x 10-19 C Ernest Rutherford (1911) – 3 types of radiation (alpha, beta and gamma), gold foil experiment - shot alpha particles at gold foil and found most of the alpha particles ...
Lab Science 9 Pacing Guide
... same number of protons, and elements with the same number of protons may or may not have the same mass. Those with different masses (different numbers of neutrons) are called isotopes. 2. Illustrate that atoms with the same number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons are el ...
... same number of protons, and elements with the same number of protons may or may not have the same mass. Those with different masses (different numbers of neutrons) are called isotopes. 2. Illustrate that atoms with the same number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons are el ...
Name:
... Answer…………..I would expect you to know that Ernest Rutherford had discovered it and that he used alpha particles and gold foil in an experiment. That when the gold foil (leaf) was bombarded with alpha particles, they would mostly pass through, except occasionally they would be deflected by a somethi ...
... Answer…………..I would expect you to know that Ernest Rutherford had discovered it and that he used alpha particles and gold foil in an experiment. That when the gold foil (leaf) was bombarded with alpha particles, they would mostly pass through, except occasionally they would be deflected by a somethi ...
The Standard Model or Particle Physics 101
... • Strong force mediated by gluons which couple to quarks thru color charge. • Electrons have zero color charge. • Quantum Chromodynamics = QCD = strong force ...
... • Strong force mediated by gluons which couple to quarks thru color charge. • Electrons have zero color charge. • Quantum Chromodynamics = QCD = strong force ...
6.2 Atomic Nucleus Stability and Isotopes
... In beta decay, the weak nuclear force mediates a change of one quark into another. In beta plus decay, an up quark is converted into a down quark while in beta minus decay, a down quark is converted into an up quark. ...
... In beta decay, the weak nuclear force mediates a change of one quark into another. In beta plus decay, an up quark is converted into a down quark while in beta minus decay, a down quark is converted into an up quark. ...
4.1 and 4.2 - Mrs. Cerqua`s Classroom
... 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated from each other, joined, or rearranged in different combinations. Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
... 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated from each other, joined, or rearranged in different combinations. Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
Atomic and Nuclear Physics
... • The existence of isotopes is evidence for the existence of neutrons because there is no other way to explain the mass difference of two isotopes of the same element. • By definition, two isotopes of the same element must have the same number of protons, which means the mass attributed to those pro ...
... • The existence of isotopes is evidence for the existence of neutrons because there is no other way to explain the mass difference of two isotopes of the same element. • By definition, two isotopes of the same element must have the same number of protons, which means the mass attributed to those pro ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.