7.2 - Haiku
... nuclides of the lighter elements have approximately equal numbers of protons and neutrons? • However, as Z increases the `stability line' curves upwards. • Heavier nuclei need more and more neutrons to be stable. • Can we explain why? ...
... nuclides of the lighter elements have approximately equal numbers of protons and neutrons? • However, as Z increases the `stability line' curves upwards. • Heavier nuclei need more and more neutrons to be stable. • Can we explain why? ...
8.5C Vocabulary
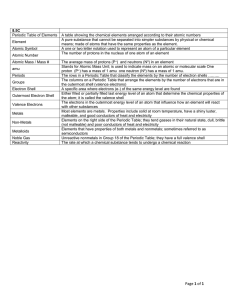
... A table showing the chemical elements arranged according to their atomic numbers A pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means; made of atoms that have the same properties as the element. A one or two letter notation used to represent an atom of a pa ...
... A table showing the chemical elements arranged according to their atomic numbers A pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means; made of atoms that have the same properties as the element. A one or two letter notation used to represent an atom of a pa ...
Chapter 2
... Thomson’s Plum Pudding Atom • The structure of the atom contains many negatively charged electrons. • The mass of the atom is due to the electrons. • The atom is mostly empty space. • These electrons are held in the atom by their attraction for a positively charged electric field within the atom. – ...
... Thomson’s Plum Pudding Atom • The structure of the atom contains many negatively charged electrons. • The mass of the atom is due to the electrons. • The atom is mostly empty space. • These electrons are held in the atom by their attraction for a positively charged electric field within the atom. – ...
Keywords - part 1 and 2
... Atoms are small particles from which all substances are made. They are the smallest neutral part of an element that can take part in chemical reactions. ...
... Atoms are small particles from which all substances are made. They are the smallest neutral part of an element that can take part in chemical reactions. ...
The nucleus
... - 0th or monopole moment: the electric field varies as r-2 (L=0) - 1st or dipole moment: the electric field varies as r-3 (L=1) - 2nd or quadrupole moment: the electric field varies as r-4 (L=2), etc. where L is the order of the moment We have the same for magnetic multipole moments except that ther ...
... - 0th or monopole moment: the electric field varies as r-2 (L=0) - 1st or dipole moment: the electric field varies as r-3 (L=1) - 2nd or quadrupole moment: the electric field varies as r-4 (L=2), etc. where L is the order of the moment We have the same for magnetic multipole moments except that ther ...
Intro Biochemistry/Ecology
... We are combining our biochemistry unit and introductory ecology units into one big topic ...
... We are combining our biochemistry unit and introductory ecology units into one big topic ...
6. Divisibility of atoms: from radioactivity to particle physics
... inverse of rate is called lifetime of the nucleus, it equals the half-life (shown in figure) divided by ln(2) stable endpoint reached when it is no longer energetically feasible for nucleus to undergo either alpha- or beta-decay number of protons, atomic number Z ...
... inverse of rate is called lifetime of the nucleus, it equals the half-life (shown in figure) divided by ln(2) stable endpoint reached when it is no longer energetically feasible for nucleus to undergo either alpha- or beta-decay number of protons, atomic number Z ...
Nuclear Guided Notes
... After ____________half-lives sample considered nonradioactive because it approaches the level of background radiation. Because the amount never reaches zero, radioactive waste disposal and storage causes problems. Would you ...
... After ____________half-lives sample considered nonradioactive because it approaches the level of background radiation. Because the amount never reaches zero, radioactive waste disposal and storage causes problems. Would you ...
STEM Fair Introduction Beanium Isotopes Lab
... Neutrons are made of one “up” quark and two “down” quarks ...
... Neutrons are made of one “up” quark and two “down” quarks ...
File - Mr. Walsh`s AP Chemistry
... named by describing the molecular formula, using prefixes for the numbers. o You will need to memorize the number prefixes for the numbers 1–10. o E.g., P2O5 is diphosphorus pentoxide. **Note that the prefix “mono—“ is never used with the first element. SO3 is simply sulfur trioxide. However, “mono— ...
... named by describing the molecular formula, using prefixes for the numbers. o You will need to memorize the number prefixes for the numbers 1–10. o E.g., P2O5 is diphosphorus pentoxide. **Note that the prefix “mono—“ is never used with the first element. SO3 is simply sulfur trioxide. However, “mono— ...
Inside the Atom Note Sheet
... The mass of 1 electron is 1/1840 the mass of a proton—essentially the electron has no mass The Neutron Atoms of neon were found to have different masses. • there must be a third particle--one with mass but no charge • James Chadwick proved the existence of the neutron in 1932 Summary and Atomic Stru ...
... The mass of 1 electron is 1/1840 the mass of a proton—essentially the electron has no mass The Neutron Atoms of neon were found to have different masses. • there must be a third particle--one with mass but no charge • James Chadwick proved the existence of the neutron in 1932 Summary and Atomic Stru ...
Banana Equivalent Dose - Glasgow Experimental Particle Physics
... Ernest Rutherford: “it was quite the most incredible event that ever happened to me in my life. It was almost as incredible as if you had fired a 15-‐ inch shell at a piece of ?ssue paper and ...
... Ernest Rutherford: “it was quite the most incredible event that ever happened to me in my life. It was almost as incredible as if you had fired a 15-‐ inch shell at a piece of ?ssue paper and ...
Assignment 5-2
... 13. What is the name of the particles that make up protons and neutrons? 14. Approximately how many electrons does it take to equal the mass of a proton? 15. If an atom has a total of 10 electrons, how many energy levels does it have? 16. If an atom has a total of 12 electrons, how many energy leve ...
... 13. What is the name of the particles that make up protons and neutrons? 14. Approximately how many electrons does it take to equal the mass of a proton? 15. If an atom has a total of 10 electrons, how many energy levels does it have? 16. If an atom has a total of 12 electrons, how many energy leve ...
Atomic Notes
... 2. Why do atoms of elements have neutral charges? A. All atoms contain neutrons which have no charge B. The number of protons and the number of neutrons are equal. C. The number of protons and the number of electrons are equal. D. The number of electrons and the number of neutrons are equal. 3. What ...
... 2. Why do atoms of elements have neutral charges? A. All atoms contain neutrons which have no charge B. The number of protons and the number of neutrons are equal. C. The number of protons and the number of electrons are equal. D. The number of electrons and the number of neutrons are equal. 3. What ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.