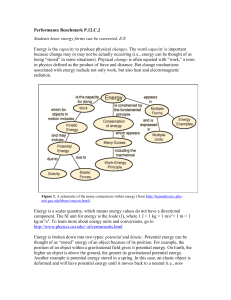
FIFTH GRADE PHYSICS - Math/Science Nucleus
... Emphasize that this segment concentrates on visible light which is a part of the electromagnetic wave spectrum. Review how light carries energy in tiny packets of electromagnetic radiation called photons. Light travels at 296,000 meters per second or 186,000 miles per second and doesn't need a mediu ...
... Emphasize that this segment concentrates on visible light which is a part of the electromagnetic wave spectrum. Review how light carries energy in tiny packets of electromagnetic radiation called photons. Light travels at 296,000 meters per second or 186,000 miles per second and doesn't need a mediu ...
Waves Unit: Worksheet 4
... 7) describe diffraction as the bending of a wave around an obstacle or an edge. This can be described in conjunction with interference to describe diffraction patterns. Part B: Sound waves and Light waves. Students should be able to 1) identify the source of electromagnetic radiation as accelerating ...
... 7) describe diffraction as the bending of a wave around an obstacle or an edge. This can be described in conjunction with interference to describe diffraction patterns. Part B: Sound waves and Light waves. Students should be able to 1) identify the source of electromagnetic radiation as accelerating ...
New Theories of Gravitation and Particle Model Chongxi Yu
... Gravitation is a natural phenomenon and all things are brought toward one another by gravitation. Modern work on gravitational theory began with the work of Galileo Galilei in the late 16th. In 1687, Isaac Newton published Newton’s law of universal gravitation, which postulates that gravity is a for ...
... Gravitation is a natural phenomenon and all things are brought toward one another by gravitation. Modern work on gravitational theory began with the work of Galileo Galilei in the late 16th. In 1687, Isaac Newton published Newton’s law of universal gravitation, which postulates that gravity is a for ...
Moving Electrons
... magnetic domains of a cassette tape. To do this, cut a short (3-cm) section of tape and staple or tape it to a 3 × 5 note card. Then stroke a permanent magnet over the strip of cassette tape several times in the same direction. Now see if the permanent magnet attracts or repels the strip of cassette ...
... magnetic domains of a cassette tape. To do this, cut a short (3-cm) section of tape and staple or tape it to a 3 × 5 note card. Then stroke a permanent magnet over the strip of cassette tape several times in the same direction. Now see if the permanent magnet attracts or repels the strip of cassette ...
printer-friendly version
... with microscopic particles within a material. Electromagnetic radiation, more commonly called light, is also commonly referred to as an energy form. But, just as with heat, light is a process that transfers energy. Besides being a wave, light also has a particle nature, where each particle of light ...
... with microscopic particles within a material. Electromagnetic radiation, more commonly called light, is also commonly referred to as an energy form. But, just as with heat, light is a process that transfers energy. Besides being a wave, light also has a particle nature, where each particle of light ...
Carbene Singlets, Triplets, and the Physics that
... (molecular, in the likely event of two molecules interacting) orbitals, resulting in a mixing of pure orbitals. This mixing can either yield a bonding or an anti-bonding orbital, as seen in the interaction diagram (see figure 3). Orbital mixing diagrams like these are often qualitative, and while kn ...
... (molecular, in the likely event of two molecules interacting) orbitals, resulting in a mixing of pure orbitals. This mixing can either yield a bonding or an anti-bonding orbital, as seen in the interaction diagram (see figure 3). Orbital mixing diagrams like these are often qualitative, and while kn ...
The Quantum Theory of Atoms - Electrostatics and Vibrations
... The total charge, dipole moment, quadrupole moment, and the polarisability often provide the best descriptions of the charge distribution* (charges are not static) in a molecule. *(charges are not static points and we must speak of a charge distribution) For example, in the case of a linear molecule ...
... The total charge, dipole moment, quadrupole moment, and the polarisability often provide the best descriptions of the charge distribution* (charges are not static) in a molecule. *(charges are not static points and we must speak of a charge distribution) For example, in the case of a linear molecule ...
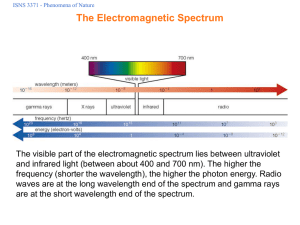
ISNS3371_032907_bw
... Most common method of polarization uses a Polaroid filter - made of a special material capable of blocking one of the two planes of vibration of an electromagnetic wave. When unpolarized light is transmitted through a Polaroid filter, it emerges with one-half the intensity and with vibrations in a s ...
... Most common method of polarization uses a Polaroid filter - made of a special material capable of blocking one of the two planes of vibration of an electromagnetic wave. When unpolarized light is transmitted through a Polaroid filter, it emerges with one-half the intensity and with vibrations in a s ...