Opportunities for Expository or Explanatory writing
... 1. What is the difference between average speed and average velocity? 2. When are average speed and average velocity the same number? 3. Draw a speed versus time graph that represents a person driving to a store at a constant speed, turning around, and driving home at the same constant speed. 4. For ...
... 1. What is the difference between average speed and average velocity? 2. When are average speed and average velocity the same number? 3. Draw a speed versus time graph that represents a person driving to a store at a constant speed, turning around, and driving home at the same constant speed. 4. For ...
Practical Exercises in Physical Chemistry
... the corresponding, marked bottles. Clean up the working place at the end. a) Measure the extinction of the aqueous solution of Mn(III) tris-oxalate thermally equilibrated at 18 0C at 365 nm, 405 nm, 436 nm, 492 nm, 546 nm, 578 nm and 623 nm after 60 s of the solution preparation. b) Select the emiss ...
... the corresponding, marked bottles. Clean up the working place at the end. a) Measure the extinction of the aqueous solution of Mn(III) tris-oxalate thermally equilibrated at 18 0C at 365 nm, 405 nm, 436 nm, 492 nm, 546 nm, 578 nm and 623 nm after 60 s of the solution preparation. b) Select the emiss ...
1 Snell`s Law, Dispersion, and the Prism
... of all wavelengths. The light is incident on a block of glass of thickness 20 km and whose refractive index as shown above. (a) What is the physical length of the pulse [m] when the light enters the glass? (b) What is the time required for red light and for blue light to traverse the glass? (c) What ...
... of all wavelengths. The light is incident on a block of glass of thickness 20 km and whose refractive index as shown above. (a) What is the physical length of the pulse [m] when the light enters the glass? (b) What is the time required for red light and for blue light to traverse the glass? (c) What ...
Powerpoint
... is always perpendicular to an equipotential surface. is always tangent to an equipotential surface. always bisects an equipotential surface. makes an angle to an equipotential surface that depends on the amount of charge. ...
... is always perpendicular to an equipotential surface. is always tangent to an equipotential surface. always bisects an equipotential surface. makes an angle to an equipotential surface that depends on the amount of charge. ...
C. Madigan, M.H. Lu, and J.C. Sturm, "Improvement of output coupling efficiency of organic light-emitting diodes by substrate modification," Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, pp. 1650-1652 (2000).
... normal emission compared to trial 2, but larger large-angle emission. The improvement in total emitted light, however, was limited by the relatively small size of the lens we fabricated. The above experiments can at best hope to capture light waveguided in the substrate, but not the 43% 关calculated ...
... normal emission compared to trial 2, but larger large-angle emission. The improvement in total emitted light, however, was limited by the relatively small size of the lens we fabricated. The above experiments can at best hope to capture light waveguided in the substrate, but not the 43% 关calculated ...
Chemistry – Higher level Marking Scheme
... mass spec: charged particle / ionisation [can be got from (c)] (3) moving in a magnetic field = acceleration … magnetic field [from (c)] (3) experiences a force / is deflected in a circular path according to their mass/charge ratio (3) Note: some or all three points can be got from a diagram provide ...
... mass spec: charged particle / ionisation [can be got from (c)] (3) moving in a magnetic field = acceleration … magnetic field [from (c)] (3) experiences a force / is deflected in a circular path according to their mass/charge ratio (3) Note: some or all three points can be got from a diagram provide ...
... and carries the Electromagnetic Field. No other particle has the photon characteristic that in the vacuum it travels at light speed. Other particles that have been presumed to travel at light speed, such as gluons have never been detected, and their speeds have never been measured. To say that Gravi ...
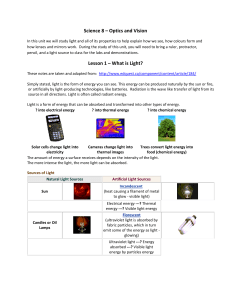
Science 8Optics and Vision
... according to the law and the angle of incidence equalled the angle of reflection. The crinkled foil did not seem to follow this, but rather the light scattered a little more. This is called diffuse reflection. This scattering of light allows you to see images on a page because when light hits white ...
... according to the law and the angle of incidence equalled the angle of reflection. The crinkled foil did not seem to follow this, but rather the light scattered a little more. This is called diffuse reflection. This scattering of light allows you to see images on a page because when light hits white ...
1 - AzMİU
... 3. Specify the expression for amplitud value of acceleration at harmonious oscillation of a body ( -is a cyclic frequency, A-is a amplitud of oscillation). A) 2 A B) A C) A 2 D) 2 A 2 E) 3 A 4. Under what conditions is there a resonance ( 0 - is the natural frequency, - is the frequenc ...
... 3. Specify the expression for amplitud value of acceleration at harmonious oscillation of a body ( -is a cyclic frequency, A-is a amplitud of oscillation). A) 2 A B) A C) A 2 D) 2 A 2 E) 3 A 4. Under what conditions is there a resonance ( 0 - is the natural frequency, - is the frequenc ...
2.3 Atomic and Molecular Collisions
... molecules. There the electrons and nuclei rarely move independently, but often in strong correlation with each other. The related many-body quantum physics challenges our understanding of matter. Collisions of atoms and molecules with charged or energetic particles intercept the internal quantum mot ...
... molecules. There the electrons and nuclei rarely move independently, but often in strong correlation with each other. The related many-body quantum physics challenges our understanding of matter. Collisions of atoms and molecules with charged or energetic particles intercept the internal quantum mot ...
Refraction of light
... vious fact. Light is refracted when it leaves water, giving rise to the illusion that objects in water appear to be both distorted and closer than they really are. As early as the first century (A.D.), the ancient Greek astronomer and geographer Ptolemy attempted to mathematically explain the amount ...
... vious fact. Light is refracted when it leaves water, giving rise to the illusion that objects in water appear to be both distorted and closer than they really are. As early as the first century (A.D.), the ancient Greek astronomer and geographer Ptolemy attempted to mathematically explain the amount ...