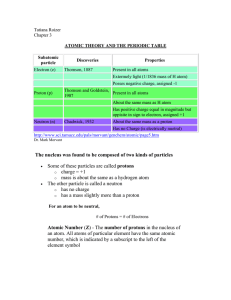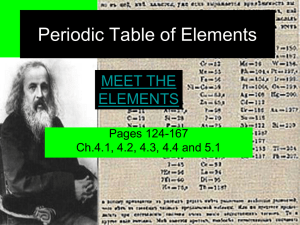
Periodic Table of Elements
... • This is called the Octet Rule. However there are many exceptions, but this is an easy way to predict common reactions. ...
... • This is called the Octet Rule. However there are many exceptions, but this is an easy way to predict common reactions. ...
Polarization
... droplets meet in observer's eye Rainbow is visible from different locations: for example the red color is now coming from a different region of the sky → angle between sun, water droplet and sun has to be just right ...
... droplets meet in observer's eye Rainbow is visible from different locations: for example the red color is now coming from a different region of the sky → angle between sun, water droplet and sun has to be just right ...
Slide 1 - Mr Lundy`s Room
... particular string are called resonant frequencies. They are also referred to as the fundamental and harmonics. ...
... particular string are called resonant frequencies. They are also referred to as the fundamental and harmonics. ...
No Slide Title
... maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron KEmax = hf – hft maximum kinetic energy = (Planck’s constant frequency of incoming photon) – work function Chapter menu ...
... maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron KEmax = hf – hft maximum kinetic energy = (Planck’s constant frequency of incoming photon) – work function Chapter menu ...
Topic 10
... Driven Oscillations and Resonance. a. To keep a damped system going indefinitely, mechanical energy must be put into the system. When this is done, the oscillator is said to be driven or forced. i. If the driving mechanism puts energy into the system at a greater rate than it is dissipated, the syst ...
... Driven Oscillations and Resonance. a. To keep a damped system going indefinitely, mechanical energy must be put into the system. When this is done, the oscillator is said to be driven or forced. i. If the driving mechanism puts energy into the system at a greater rate than it is dissipated, the syst ...
Unit/Lesson Plan Title: Roller Coaster Potential or Kinetic
... Chemical energy is stored inside of atoms and molecules. These tiny particles are held together with bonds that have stored or “chemical” energy. Stored mechanical energy is energy that is stored in an object before a force causes it to move. For example, when a rubber band is stretched, it has sto ...
... Chemical energy is stored inside of atoms and molecules. These tiny particles are held together with bonds that have stored or “chemical” energy. Stored mechanical energy is energy that is stored in an object before a force causes it to move. For example, when a rubber band is stretched, it has sto ...
HEFAT2014 10 International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics
... It is generally accepted that the energy transfer in solids is by means of heat conductivity and the energy flux density is set by the Fourier's law, T , where is the material conductivity, T is the temperature [1]. Nevertheless, the electrical currents of electrons and holes can be presented i ...
... It is generally accepted that the energy transfer in solids is by means of heat conductivity and the energy flux density is set by the Fourier's law, T , where is the material conductivity, T is the temperature [1]. Nevertheless, the electrical currents of electrons and holes can be presented i ...
Assignment 30 STRUCTURE OF MOLECULES AND MULTI
... In lecture you have learned about atomic orbitals (AOs)—the regions of space surrounding an atom’s nucleus that ‘house’ that atom’s electrons. A carbon atom has four available atomic orbitals--one 2s AO, and three 2p AOs (2px, 2py, 2pz)— to house its four valence electrons. Take a look at the shapes ...
... In lecture you have learned about atomic orbitals (AOs)—the regions of space surrounding an atom’s nucleus that ‘house’ that atom’s electrons. A carbon atom has four available atomic orbitals--one 2s AO, and three 2p AOs (2px, 2py, 2pz)— to house its four valence electrons. Take a look at the shapes ...
PowerPoint
... TOF Coincidence map for Ar8+ + N2 products. a) – conventional mode (fragment ions are detected on PSD), b) – ZOO-RISE mode (secondary electrons are detected on PSD). ...
... TOF Coincidence map for Ar8+ + N2 products. a) – conventional mode (fragment ions are detected on PSD), b) – ZOO-RISE mode (secondary electrons are detected on PSD). ...
Light: An Electromagnetic Wave
... • Absorption of Light The transfer of energy carried by light waves is called absorption. • When a beam of light shines through the air, particles in the air absorb some of the light’s energy. As a result, the beam of light becomes dim. ...
... • Absorption of Light The transfer of energy carried by light waves is called absorption. • When a beam of light shines through the air, particles in the air absorb some of the light’s energy. As a result, the beam of light becomes dim. ...
UV Spectroscopy
... Principle: Colorimetry analysis method is useful in determining the concentration of coloured solutions using the visible region (400nm–750nm) of electromagnetic spectrum and Beer Lambert’s law. If the test solution is colourless then a suitable complexing agent can be added to test solution to get ...
... Principle: Colorimetry analysis method is useful in determining the concentration of coloured solutions using the visible region (400nm–750nm) of electromagnetic spectrum and Beer Lambert’s law. If the test solution is colourless then a suitable complexing agent can be added to test solution to get ...