Determination of activity of Cr51 artificial neutrino sourse
... 1) Measurements of activity of intense source on measurement of continuous spectrum of γ-radiation 2) Reconstruction of spectra on measurements in SCD 3) Absolute calibration of the activity and of the measurement of the IB spectrum of the 51Cr source ...
... 1) Measurements of activity of intense source on measurement of continuous spectrum of γ-radiation 2) Reconstruction of spectra on measurements in SCD 3) Absolute calibration of the activity and of the measurement of the IB spectrum of the 51Cr source ...
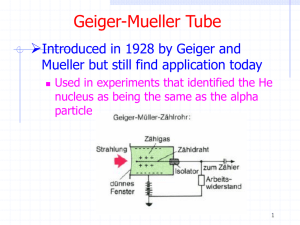
1 The modern model of the atom is based on the work of (1) one
... In 1897, J. J. Thomson demonstrated in an experiment that cathode rays were deflected by an electric field. This suggested that cathode rays were composed of negatively charged particles found in all atoms. Thomson concluded that the atom was a positively charged sphere of almost uniform density in ...
... In 1897, J. J. Thomson demonstrated in an experiment that cathode rays were deflected by an electric field. This suggested that cathode rays were composed of negatively charged particles found in all atoms. Thomson concluded that the atom was a positively charged sphere of almost uniform density in ...
Lecture3(electorn_dynamicsI)
... To compute dP/d we use the result obtained in the lecture on synchrotron radiation, whereby the instantaneous power emitted in a bending magnet with field B by a particle with energy E is given by ...
... To compute dP/d we use the result obtained in the lecture on synchrotron radiation, whereby the instantaneous power emitted in a bending magnet with field B by a particle with energy E is given by ...
Charged Barrier Technology THE FOGAL TRANSISTOR WITH THE
... Induction of Forces and Patterns of Forces In Atomic Nuclei A force-free (gradient-free) scalar potential readily penetrates the electron shells of the atom, penetrating directly to the nucleus and interacting with it. By infolding desired Efields and B-fields inside the scalar potential (inside pur ...
... Induction of Forces and Patterns of Forces In Atomic Nuclei A force-free (gradient-free) scalar potential readily penetrates the electron shells of the atom, penetrating directly to the nucleus and interacting with it. By infolding desired Efields and B-fields inside the scalar potential (inside pur ...
doc
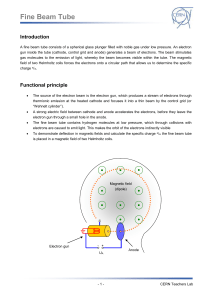
... With rising energy of the accelerated particles LINACs (linear accelerators, see experiment “cathode ray tube”) get very long and expensive. That’s why the idea of circular accelerators was born: by using magnetic fields to force particles into an orbit, the same accelerating unit can be used multip ...
... With rising energy of the accelerated particles LINACs (linear accelerators, see experiment “cathode ray tube”) get very long and expensive. That’s why the idea of circular accelerators was born: by using magnetic fields to force particles into an orbit, the same accelerating unit can be used multip ...
Reflection and Refraction
... front travels at different speeds. This happens in uneven winds or when sound is traveling through air of uneven temperature. On a warm day, for example, the air near the ground may be appreciably warmer than the air above. Since sound travels faster in warm air, the speed of sound near the ground i ...
... front travels at different speeds. This happens in uneven winds or when sound is traveling through air of uneven temperature. On a warm day, for example, the air near the ground may be appreciably warmer than the air above. Since sound travels faster in warm air, the speed of sound near the ground i ...
Dispersion: The Rainbow and Prisms
... Rainbows are produced by a combination of refraction and re ection. You may have noticed that you see a rainbow only when you look away from the sun. Light enters a drop of water and is re ected from the back ...
... Rainbows are produced by a combination of refraction and re ection. You may have noticed that you see a rainbow only when you look away from the sun. Light enters a drop of water and is re ected from the back ...
apbio ch 2 study guide
... Potential energy is the energy that matter stores because of its position or location. o Water stored behind a dam has potential energy that can be used to do work turning electric generators. o Because potential energy has been expended, the water stores less energy at the bottom of the dam than it ...
... Potential energy is the energy that matter stores because of its position or location. o Water stored behind a dam has potential energy that can be used to do work turning electric generators. o Because potential energy has been expended, the water stores less energy at the bottom of the dam than it ...
The Photoelectric Effects: Radiation Based With Atomic Model
... resisted Einstein’s hypothesis, stating that “Instead of quantized electromagnetic fields, one should attempt to transfer the whole problem of the quantum theory to the area of interaction between matter and radiation energy” (Shih, 2005),healsodescribedthe wholedualityas “unnece ...
... resisted Einstein’s hypothesis, stating that “Instead of quantized electromagnetic fields, one should attempt to transfer the whole problem of the quantum theory to the area of interaction between matter and radiation energy” (Shih, 2005),healsodescribedthe wholedualityas “unnece ...
Inverse Free Electron Laser acceleration for advanced light sources
... • Higher harmonic interaction has been first observed in UCLA experiment, and then studied in SLAC experiment. • More recently the efficiency of the interaction has also been shown in the Neptune 7th harmonic IFEL experiment. • Even harmonic interaction is also strong when there is an angle between ...
... • Higher harmonic interaction has been first observed in UCLA experiment, and then studied in SLAC experiment. • More recently the efficiency of the interaction has also been shown in the Neptune 7th harmonic IFEL experiment. • Even harmonic interaction is also strong when there is an angle between ...
Practice Final semester 2
... 103. An opera singer's voice is able to break a thin crystal glass when the singer's voice and the vibrating glass have the same frequency speed amplitude wavelength ...
... 103. An opera singer's voice is able to break a thin crystal glass when the singer's voice and the vibrating glass have the same frequency speed amplitude wavelength ...
QCD
... On the other hand, if a is large, the series converges slowly – so slowly that it may not even seem to converge at all. For example, for a = 9/10, it’s not until the 12th term that the terms start to decrease. The first two terms alone are a factor 47 smaller than the entire sum. To get within 2% ta ...
... On the other hand, if a is large, the series converges slowly – so slowly that it may not even seem to converge at all. For example, for a = 9/10, it’s not until the 12th term that the terms start to decrease. The first two terms alone are a factor 47 smaller than the entire sum. To get within 2% ta ...
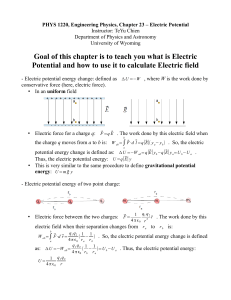
Goal of this chapter is to teach you what is Electric Potential and how
... as well as electric potential. - New unit for ENERGY: electron volt (eV) 1 eV = the electric potential energy gained by one electron with change of 1 V electric potential = ( 1.602×10−19 C) (1 V) = 1.602×10−19 J • Note: CV = J • Note #2: eV is an unit of ENERGY; while V is an unit of electric potent ...
... as well as electric potential. - New unit for ENERGY: electron volt (eV) 1 eV = the electric potential energy gained by one electron with change of 1 V electric potential = ( 1.602×10−19 C) (1 V) = 1.602×10−19 J • Note: CV = J • Note #2: eV is an unit of ENERGY; while V is an unit of electric potent ...
Theory of relativistic electron holes in hot plasmas
... holes in the presence of the ion dynamics. A theoretical investigation [14] reveals the trapping and interactions between large-amplitude Langmuir waves and ion holes. The present status of the electron and ion hole physics as well as pertinent simulations and observations are contained in Ref. [15] ...
... holes in the presence of the ion dynamics. A theoretical investigation [14] reveals the trapping and interactions between large-amplitude Langmuir waves and ion holes. The present status of the electron and ion hole physics as well as pertinent simulations and observations are contained in Ref. [15] ...