1a) Charged particles in matter :-
... In 1886, E.Goldstein discovered new radiations in gas discharge and called them canal rays. These rays were positively charged. This later led to the discovery of the positively charged particles called protons in the atom. In 1932 Chadwick discovered the presence of particles having no charge in th ...
... In 1886, E.Goldstein discovered new radiations in gas discharge and called them canal rays. These rays were positively charged. This later led to the discovery of the positively charged particles called protons in the atom. In 1932 Chadwick discovered the presence of particles having no charge in th ...
Session 1 - QMUL physics
... 2. Estimate the length of your leg, called this L 3. Now treat the leg as a rigid rod, so that it’s centre of mass is half way down, ie L/2, and its moment of inertia is that of a rigid rod = (1/3)mL2. Compute the natural frequency in Hz, not radians per second, and hence the period. So take someone ...
... 2. Estimate the length of your leg, called this L 3. Now treat the leg as a rigid rod, so that it’s centre of mass is half way down, ie L/2, and its moment of inertia is that of a rigid rod = (1/3)mL2. Compute the natural frequency in Hz, not radians per second, and hence the period. So take someone ...
2 - grade11chemistry
... • Found in the bottom two rows of the periodic table in the lanthanide and actinide series (i.e. atomic numbers from 58 to 72 and from 89 to 104). • Top row of inner transition elements is also called the lanthanide series, because these elements follow lanthanum, atomic number 57. • The bottom row ...
... • Found in the bottom two rows of the periodic table in the lanthanide and actinide series (i.e. atomic numbers from 58 to 72 and from 89 to 104). • Top row of inner transition elements is also called the lanthanide series, because these elements follow lanthanum, atomic number 57. • The bottom row ...
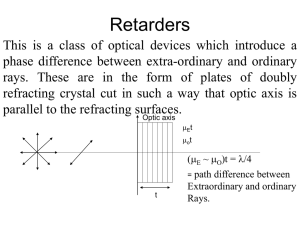
elliptically polarized light to plane polarized
... difference /2 and resultant of these two vibration will be elliptically polarized one. ...
... difference /2 and resultant of these two vibration will be elliptically polarized one. ...
CANMET Technical Information Fact Sheet
... a chemical reaction occurs, called a thermite reaction [1]. ...
... a chemical reaction occurs, called a thermite reaction [1]. ...
doc - University of Iowa Physics
... L1i and the projection screen Lp. Through some algebra the superposition of these two waves describes the output of the interferometer as ...
... L1i and the projection screen Lp. Through some algebra the superposition of these two waves describes the output of the interferometer as ...
A Brief History of Electromagnetism
... kite, which he flew during a thunderstorm, while holding the end of the kite string by an iron key. When lightning flashed, a tiny spark jumped from the key to his wrist. The experiment proved Franklin's theory, but was extremely dangerous - he could easily have been killed. 1759: Francis Ulrich The ...
... kite, which he flew during a thunderstorm, while holding the end of the kite string by an iron key. When lightning flashed, a tiny spark jumped from the key to his wrist. The experiment proved Franklin's theory, but was extremely dangerous - he could easily have been killed. 1759: Francis Ulrich The ...
Unit 2 - Angelfire
... When encountering a car collision, the driver and passenger tend to keep moving in accord with Newton's first law. Their motion carries them towards a windshield which results in a large force exerted over a short time in order to stop their momentum. If instead of hitting the windshield, the driver ...
... When encountering a car collision, the driver and passenger tend to keep moving in accord with Newton's first law. Their motion carries them towards a windshield which results in a large force exerted over a short time in order to stop their momentum. If instead of hitting the windshield, the driver ...