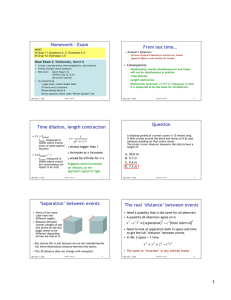
Waves 3 (polarized light)
... antinodes, respectively. So both waves must be passing through the two slits at the same time. But, only one electron at a time was used here. That implies that an electron would have to interfere with itself by going through each of the slits at the same time! This is a ridiculous sounding idea, bu ...
... antinodes, respectively. So both waves must be passing through the two slits at the same time. But, only one electron at a time was used here. That implies that an electron would have to interfere with itself by going through each of the slits at the same time! This is a ridiculous sounding idea, bu ...
Photosynthesis
... Photosynthesis is a process in which plants use light, water, and carbon dioxide to produce sugars, water and oxygen. Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b, in the chloroplasts of a leaf, are responsible for absorbing wavelengths of light for use in photosynthesis with red and blue wavelengths being optim ...
... Photosynthesis is a process in which plants use light, water, and carbon dioxide to produce sugars, water and oxygen. Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b, in the chloroplasts of a leaf, are responsible for absorbing wavelengths of light for use in photosynthesis with red and blue wavelengths being optim ...
Radiative Processes in Astrophysics
... and bremsstrahlung. Generally, we are interested in the spectrum of the radiation from the astrophysical objects. Hence, we shall focus on the spectral properties of the radiation and the factors which change them. Later, we study simple cases specific to these processes and understand how different ...
... and bremsstrahlung. Generally, we are interested in the spectrum of the radiation from the astrophysical objects. Hence, we shall focus on the spectral properties of the radiation and the factors which change them. Later, we study simple cases specific to these processes and understand how different ...
Review Questions for 1st year chemistry
... This is a decomposition type 2c, metallic hydrogen carbonate decomposes into metal oxide, water and carbon dioxide. MHCO3 MO + H2O + CO2 Remember to cross charges to get formula for MO. ...
... This is a decomposition type 2c, metallic hydrogen carbonate decomposes into metal oxide, water and carbon dioxide. MHCO3 MO + H2O + CO2 Remember to cross charges to get formula for MO. ...
WAKE UP AND SMELL THE FUNCTIONS
... of force” that emanated from their north poles and converged on their south poles. He called these lines of force a magnetic field. To Faraday, Ampère’s discovery hinted that magnetic fields and electric current were related. In 1831 he found out how. Faraday discovered that moving a magnet near a c ...
... of force” that emanated from their north poles and converged on their south poles. He called these lines of force a magnetic field. To Faraday, Ampère’s discovery hinted that magnetic fields and electric current were related. In 1831 he found out how. Faraday discovered that moving a magnet near a c ...
Answers to Challenge/ extension
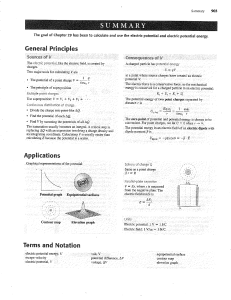
... 2) How can you increase the potential energy of an object? 3) What happens to your potential energy as you go up in an airplane? Compared to what? 4) If an object weighs 500 N and you lift it 2 m, a) how much work have you done on it? b) how much potential energy does it have relative to its startin ...
... 2) How can you increase the potential energy of an object? 3) What happens to your potential energy as you go up in an airplane? Compared to what? 4) If an object weighs 500 N and you lift it 2 m, a) how much work have you done on it? b) how much potential energy does it have relative to its startin ...
Understanding Electronic WaveFunctions
... of the homogeneous electron gas. First, I motivate the discussion, then briefly give references to the quantum Monte Carlo methods, discuss the pair product wavefunction and its generalization to backflow and three body wavefunctions. Finally, I conclude with some current difficulties in extending t ...
... of the homogeneous electron gas. First, I motivate the discussion, then briefly give references to the quantum Monte Carlo methods, discuss the pair product wavefunction and its generalization to backflow and three body wavefunctions. Finally, I conclude with some current difficulties in extending t ...
Document
... A substance that contains different elements that have been chemically combined Empirical formulae The simplest ratio showing the different types of atom present in a substance. Molecular formulae The actual numbers of each type of atom in a molecule of the substance. ...
... A substance that contains different elements that have been chemically combined Empirical formulae The simplest ratio showing the different types of atom present in a substance. Molecular formulae The actual numbers of each type of atom in a molecule of the substance. ...
Properties of waves
... If the angle of incidence increases any more it is impossible for the light to refract (since the angle of refraction would be greater than 900 so the light would not leave the glass) and so all the light reflects. This is called Total Internal Reflection (TIR). This is shown in diagram 3. ...
... If the angle of incidence increases any more it is impossible for the light to refract (since the angle of refraction would be greater than 900 so the light would not leave the glass) and so all the light reflects. This is called Total Internal Reflection (TIR). This is shown in diagram 3. ...
physics syllabus - CurriculumOnline.ie
... Ordinary and Higher levels, so that students can place physics within the everyday world. The STS material needs to be known at the appropriate level; that is, where the basic principle is on the Ordinary level, examples must be known at Ordinary level, and similarly at Higher level. Only the princi ...
... Ordinary and Higher levels, so that students can place physics within the everyday world. The STS material needs to be known at the appropriate level; that is, where the basic principle is on the Ordinary level, examples must be known at Ordinary level, and similarly at Higher level. Only the princi ...