EFFECTS OF MOLECULAR ORIENTATION AND ANNEALING ON …
... Where Io and I are the incident and transmitted intensity respectively and x is the sample thickness. ...
... Where Io and I are the incident and transmitted intensity respectively and x is the sample thickness. ...
Stray Light – Measurement and Effect on Performance in UV
... Figure 1: A plot of the apparent absorbance against the true absorbance with increasing stray light. The deviation from the Beer-Lambert law increases with increasing stray light. ...
... Figure 1: A plot of the apparent absorbance against the true absorbance with increasing stray light. The deviation from the Beer-Lambert law increases with increasing stray light. ...
D. biflorus
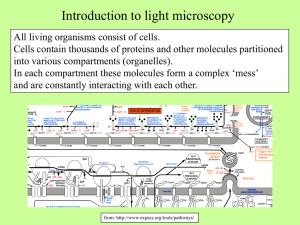
... To understand how organisms or cells function it is critical to identify the cell type under study and to know which cells or molecules are where (morphological organization) and when (temporal dynamic) they are there. ...
... To understand how organisms or cells function it is critical to identify the cell type under study and to know which cells or molecules are where (morphological organization) and when (temporal dynamic) they are there. ...
Wave Phenomena Constructive and Destructive Interference
... constructive interference of light waves. The conditions for interference depends on: 1. The index of refraction of the film and the surrounding media. 2. The thickness of the film. Film surround by media of lower index of refraction Film thickness must be λ/4, 3λ/4, 5λ/4, 7λ/4… for constructive int ...
... constructive interference of light waves. The conditions for interference depends on: 1. The index of refraction of the film and the surrounding media. 2. The thickness of the film. Film surround by media of lower index of refraction Film thickness must be λ/4, 3λ/4, 5λ/4, 7λ/4… for constructive int ...
Effects of emittance and energy spread in an electron
... moving with the electron bunches calculated for ǫn = 256 mm·mrad (left graph) and ǫn = 16 mm·mrad (right graph) when the resonant frequency was equal to 1.0 THz 3b, and Fig. 3c points to noticeable decrease in the output energy in the last case which does not exceed 0.3 mJ even if FEL is driven by v ...
... moving with the electron bunches calculated for ǫn = 256 mm·mrad (left graph) and ǫn = 16 mm·mrad (right graph) when the resonant frequency was equal to 1.0 THz 3b, and Fig. 3c points to noticeable decrease in the output energy in the last case which does not exceed 0.3 mJ even if FEL is driven by v ...
Muon Decay
... High up in the atmosphere cosmic rays interact with the atoms and molecules present in the air. These cosmic rays have enough energy to create new particles. One type of particles which is created in large numbers is the muon. In this module we will take a closer look at this particle. ...
... High up in the atmosphere cosmic rays interact with the atoms and molecules present in the air. These cosmic rays have enough energy to create new particles. One type of particles which is created in large numbers is the muon. In this module we will take a closer look at this particle. ...