Formation and Stability of High-Spin Alkali Clusters - Max-Born
... (b) With increasing cluster size the valence electron wave functions start to overlap sufficiently for electrons to migrate more or less freely from one atom to another and for that reason spin flips occur. The formally localized, spin-polarized electrons change into a delocalized, collective state. ...
... (b) With increasing cluster size the valence electron wave functions start to overlap sufficiently for electrons to migrate more or less freely from one atom to another and for that reason spin flips occur. The formally localized, spin-polarized electrons change into a delocalized, collective state. ...
III-Advanced Lithography
... of the medium surrounding the lens. The physical limit for an air based system is clear, but what if a medium with a higher index of refraction is substituted for air? Microscopy has for years used oil between the lens and the sample being viewed for resolution enhancement and it is somewhat surpris ...
... of the medium surrounding the lens. The physical limit for an air based system is clear, but what if a medium with a higher index of refraction is substituted for air? Microscopy has for years used oil between the lens and the sample being viewed for resolution enhancement and it is somewhat surpris ...
Activation parameters for ET
... Due to entropy mixing, the slope of the pH-dependence should be negative. Observed (total) activation entropy change The slope of the pH-dependence of the observed (total) entropy change is positive (or in some cases slightly negative) Our data indicate that the magnitude of ΔGET is at least as larg ...
... Due to entropy mixing, the slope of the pH-dependence should be negative. Observed (total) activation entropy change The slope of the pH-dependence of the observed (total) entropy change is positive (or in some cases slightly negative) Our data indicate that the magnitude of ΔGET is at least as larg ...
Unit 2 - aqaphysics.co.uk
... velocity. We see that the ball shot from the cannon falls at the same rate at the ball that was released. This is because the horizontal and vertical components of motion are independent of each other. Horizontal: The horizontal velocity is constant; we see that the fired ball covers the same horizo ...
... velocity. We see that the ball shot from the cannon falls at the same rate at the ball that was released. This is because the horizontal and vertical components of motion are independent of each other. Horizontal: The horizontal velocity is constant; we see that the fired ball covers the same horizo ...
Electromagnetic Waves
... the model in a group of equations that gave the relations between the electric and magnetic fields. He soon found these equations to be the most useful way to represent the theory. Their power allowed him eventually to discard the mechanical model altogether. Maxwell’s mathematical view is still con ...
... the model in a group of equations that gave the relations between the electric and magnetic fields. He soon found these equations to be the most useful way to represent the theory. Their power allowed him eventually to discard the mechanical model altogether. Maxwell’s mathematical view is still con ...
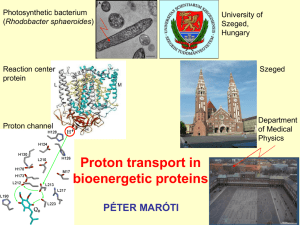
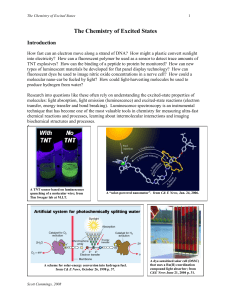
The Chemistry of Excited States
... above). For some molecules, a process known as “intersystem crossing” (isc) occurs, and one of the electrons flips spin so that the two unpaired electrons have the same spin (+½, +½ or -½, -½). Although the same molecular orbitals are involved, this is a different excited state having a “triplet” mu ...
... above). For some molecules, a process known as “intersystem crossing” (isc) occurs, and one of the electrons flips spin so that the two unpaired electrons have the same spin (+½, +½ or -½, -½). Although the same molecular orbitals are involved, this is a different excited state having a “triplet” mu ...
Low-Energy (20 eV) and High-Energy (1000 eV) Electron
... We report the first infrared study of the low-energy (< 20 eV) electron-induced reactions of condensed methanol. Our goal is to simulate processes which occur when highenergy cosmic rays interact with interstellar and cometary ices, where methanol, a precursor of several prebiotic species, is relati ...
... We report the first infrared study of the low-energy (< 20 eV) electron-induced reactions of condensed methanol. Our goal is to simulate processes which occur when highenergy cosmic rays interact with interstellar and cometary ices, where methanol, a precursor of several prebiotic species, is relati ...
Physics - New Albany-Plain Local Schools
... objects and situations involving forces that must themselves be quantified (e.g., gravitational forces, elastic forces, friction forces). • Gravitational Forces and Fields Gravitational interactions are very weak compared to other interactions and are difficult to observe unless one of the objects is ...
... objects and situations involving forces that must themselves be quantified (e.g., gravitational forces, elastic forces, friction forces). • Gravitational Forces and Fields Gravitational interactions are very weak compared to other interactions and are difficult to observe unless one of the objects is ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2 (2015)
... 7) Which fourth period transition element has the highest atomic number? A) Ca B) Cd C) Kr D) Zn C) Sb and Te D) Po and At C) Ca D) none of the above 8) Which of the following elements are fourth period metalloids? A) Si and Ge B) Ge and As 9) Which of the following is an alkali metal? A) Al B) Fe 1 ...
... 7) Which fourth period transition element has the highest atomic number? A) Ca B) Cd C) Kr D) Zn C) Sb and Te D) Po and At C) Ca D) none of the above 8) Which of the following elements are fourth period metalloids? A) Si and Ge B) Ge and As 9) Which of the following is an alkali metal? A) Al B) Fe 1 ...
Gluon fluctuations in vacuum
... the quality characteristic of ponderable media, as consisting of parts which may be tracked through time. The idea of motion may not be applied to it.” ...
... the quality characteristic of ponderable media, as consisting of parts which may be tracked through time. The idea of motion may not be applied to it.” ...
light:mirrors:lenses
... like a wave; this explained all the properties of light such as reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference and polarization; it did not explain the photoelectric effect or radiation produced by an incandescent light. Quantum theory - light has a dual nature: when light is transmitted through ...
... like a wave; this explained all the properties of light such as reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference and polarization; it did not explain the photoelectric effect or radiation produced by an incandescent light. Quantum theory - light has a dual nature: when light is transmitted through ...
6.8A Potential Kinetic Energy
... potential to kinetic and between objects. Potential energy is stored energy—energy ready to go. A lawn mower filled with gasoline, a car on top of a hill, and students waiting to go home from school are all examples of potential energy. Water stored behind a dam at a hydroelectric plant has potentia ...
... potential to kinetic and between objects. Potential energy is stored energy—energy ready to go. A lawn mower filled with gasoline, a car on top of a hill, and students waiting to go home from school are all examples of potential energy. Water stored behind a dam at a hydroelectric plant has potentia ...
Cosmic absorption of high energy particles
... for UHE photons the contribution of CMB photons gives the absolute upper limit on the mean free path. At high redshift, where other radiation backgrounds, such as EBL are absent, the CMB radiation limits the propagation of UHE photons at energies above GeV. for UHE protons the mean free path due to ...
... for UHE photons the contribution of CMB photons gives the absolute upper limit on the mean free path. At high redshift, where other radiation backgrounds, such as EBL are absent, the CMB radiation limits the propagation of UHE photons at energies above GeV. for UHE protons the mean free path due to ...