The Matter Glitch
... The standard model met this challenge by adding an antimatter column without saying why, but that the matter we see has an inverse is one of the most baffling discoveries of modern physics. Why does nature even allow anti-matter that can instantly annihilate matter? In this model antimatter is to ma ...
... The standard model met this challenge by adding an antimatter column without saying why, but that the matter we see has an inverse is one of the most baffling discoveries of modern physics. Why does nature even allow anti-matter that can instantly annihilate matter? In this model antimatter is to ma ...
Study Guide for Final #1
... 5.) Know how to apply the Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund’s rule to writing electron configuration. 6.) Know how to describe an electromagnetic wave and be able to relate it to the frequency and energy of electromagnetic radiation. 7.) Be able to calculate the wavelength given ...
... 5.) Know how to apply the Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund’s rule to writing electron configuration. 6.) Know how to describe an electromagnetic wave and be able to relate it to the frequency and energy of electromagnetic radiation. 7.) Be able to calculate the wavelength given ...
Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential
... Doubling the in-coming charge doubles the work, which doubles ΔUe. Note, however, that the ratio of Ue to the charge remains the same, regardless of the coming charge. Ue/q = 3μJ/10nC = 6 μJ/20nC = 300 J/C ...
... Doubling the in-coming charge doubles the work, which doubles ΔUe. Note, however, that the ratio of Ue to the charge remains the same, regardless of the coming charge. Ue/q = 3μJ/10nC = 6 μJ/20nC = 300 J/C ...
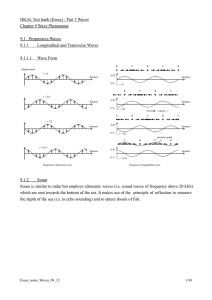
N13 Vibrations and Waves (Notes)
... A mass is attached to a vertical spring and bobs up and down between points A and B. Where is the mass located when its potential energy is a minimum? A) at either A or B B) midway between A and B ...
... A mass is attached to a vertical spring and bobs up and down between points A and B. Where is the mass located when its potential energy is a minimum? A) at either A or B B) midway between A and B ...
Communicating Research to the General Public
... audience is the matter of translating precise technical jargon into words better suited for general communication. In chemistry, however, there are many concepts for which the technical term is the only term I can use. To keep this from posing too large of a problem, we’ll begin this chapter with tw ...
... audience is the matter of translating precise technical jargon into words better suited for general communication. In chemistry, however, there are many concepts for which the technical term is the only term I can use. To keep this from posing too large of a problem, we’ll begin this chapter with tw ...
Chapter 22 - Cobb Learning
... • Scattering of Light An interaction of light with matter that causes light to change direction is scattering. Light scatters in all directions after colliding with particles of matter. • Light can be scattered out of a beam by air particles. This scattered light allows you to see things outside of ...
... • Scattering of Light An interaction of light with matter that causes light to change direction is scattering. Light scatters in all directions after colliding with particles of matter. • Light can be scattered out of a beam by air particles. This scattered light allows you to see things outside of ...
Einstein`s Photoelectric Effect
... Einstein’s Theory – Controversial Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955) published his theory of the photoelectric effect in 1905, the same year in which he published the Special Theory of Relativity and the paper on molecular dimensions which earned him his PhD from the University of Zurich. However, his r ...
... Einstein’s Theory – Controversial Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955) published his theory of the photoelectric effect in 1905, the same year in which he published the Special Theory of Relativity and the paper on molecular dimensions which earned him his PhD from the University of Zurich. However, his r ...
Moseley`s law refuted
... elements according to increasing atomic numbers and not atomic masses, some of the inconsistencies associated with Mendeleev's table were eliminated. The modern periodic table is based on Moseley's Periodic Law (atomic numbers) http://www.wonderwhizkids.com Moseley was Rutherford’s student. The foll ...
... elements according to increasing atomic numbers and not atomic masses, some of the inconsistencies associated with Mendeleev's table were eliminated. The modern periodic table is based on Moseley's Periodic Law (atomic numbers) http://www.wonderwhizkids.com Moseley was Rutherford’s student. The foll ...
Chapter 13 ppt.
... • As a result, it conveys more information to your eye than a conventional two-dimensional photograph does, but it also is more difficult to copy. ...
... • As a result, it conveys more information to your eye than a conventional two-dimensional photograph does, but it also is more difficult to copy. ...
Six
... Example: determine the incident angle i for which light strikes the inner surface of a fiber optic cable at the critical angle. Light is incident at an angle i on a ...
... Example: determine the incident angle i for which light strikes the inner surface of a fiber optic cable at the critical angle. Light is incident at an angle i on a ...