AD8002
... loads with excellent differential gain and phase performance on only 50 mW of power per amplifier. The AD8002 is a current feedback amplifier and features gain flatness of 0.1 dB to 60 MHz while offering differential gain and phase error of 0.01% and 0.02°. This makes the AD8002 ideal for profession ...
... loads with excellent differential gain and phase performance on only 50 mW of power per amplifier. The AD8002 is a current feedback amplifier and features gain flatness of 0.1 dB to 60 MHz while offering differential gain and phase error of 0.01% and 0.02°. This makes the AD8002 ideal for profession ...
MCW101C, E Time Proportional Level Controller
... and an amplifier. The sensor and amplifier are housed in a single aluminum channel and can be removed easily for repair or replacement. They are connected with a MS-connector. Figure 1 is a representation of the internal construction of the sensor showing the rotor/ stator relationships at null and ...
... and an amplifier. The sensor and amplifier are housed in a single aluminum channel and can be removed easily for repair or replacement. They are connected with a MS-connector. Figure 1 is a representation of the internal construction of the sensor showing the rotor/ stator relationships at null and ...
Monolithic Amplifi er 0.05-1 GHz Surface Mount Product Features
... MAV-11BSM+ (RoHS compliant) is a wideband amplifier offering high dynamic range. It has repeatable performance from lot to lot. It is enclosed in a plastic molded package. MAV-11BSM+ uses Darlington configuration and is fabricated using silicon technology. Expected MTBF is 270 years at 85°C case tem ...
... MAV-11BSM+ (RoHS compliant) is a wideband amplifier offering high dynamic range. It has repeatable performance from lot to lot. It is enclosed in a plastic molded package. MAV-11BSM+ uses Darlington configuration and is fabricated using silicon technology. Expected MTBF is 270 years at 85°C case tem ...
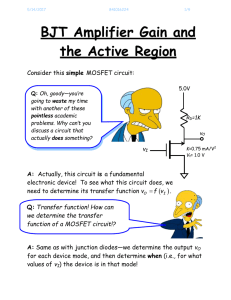
The MOSFET as an Amp..
... A: Since in cutoff and saturation d VO d VI 0 , a small change in input voltage VI will result in almost no change in output voltage VO . Contrast this with the active region, where d VO d VI 1 . This means that a small change in input voltage VI results in a large change in the output voltageV ...
... A: Since in cutoff and saturation d VO d VI 0 , a small change in input voltage VI will result in almost no change in output voltage VO . Contrast this with the active region, where d VO d VI 1 . This means that a small change in input voltage VI results in a large change in the output voltageV ...
EM-M22 TRMS 5A / 1A TO 4...20mA
... RMS output also from other than sinus shaped signals. The measured current is converted into 4...20mA signal. There are two measuring ranges, 5A and 1A, which are standard current transformer output values. The device takes it’s supply power from current loop and requires no other power supply. The ...
... RMS output also from other than sinus shaped signals. The measured current is converted into 4...20mA signal. There are two measuring ranges, 5A and 1A, which are standard current transformer output values. The device takes it’s supply power from current loop and requires no other power supply. The ...
BPR-23-D - アイステーシス
... voltage swing of up to 700 mVpp, therefore, the receiver is well suited for OC-768/STM-256 system operating up to 43 Gbit/s or for analog applications where balanced input PDs are needed. Excellent electrical and optical phase propagation is achieved by a total skew of lower than 2 ps between the ba ...
... voltage swing of up to 700 mVpp, therefore, the receiver is well suited for OC-768/STM-256 system operating up to 43 Gbit/s or for analog applications where balanced input PDs are needed. Excellent electrical and optical phase propagation is achieved by a total skew of lower than 2 ps between the ba ...
SDA-5000 - RFMD.com
... The information in this publication is believed to be accurate. However, no responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under a ...
... The information in this publication is believed to be accurate. However, no responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under a ...
LM2904/LM2902
... The LM2904/2902 has excellent output drive capability, delivering over 35mA of output drive current. The output stage is a rail-to-rail topology that is capable of swinging to within 5mV of either rail. Since the inputs can go 100mV beyond either rail, the op-amp can easily perform ‘True Ground Sens ...
... The LM2904/2902 has excellent output drive capability, delivering over 35mA of output drive current. The output stage is a rail-to-rail topology that is capable of swinging to within 5mV of either rail. Since the inputs can go 100mV beyond either rail, the op-amp can easily perform ‘True Ground Sens ...
DT002_1 Review Questions
... 10. A mains transformer produces a 10 volt rms secondary voltage at 50 Hz. The secondary voltage is connected to a rectifier circuit. Sketch to scale the output voltage waveform from (a) A half-wave rectifier (b) A bridge rectifier Assume that silicon diodes are used in each case. 11. Explain why a ...
... 10. A mains transformer produces a 10 volt rms secondary voltage at 50 Hz. The secondary voltage is connected to a rectifier circuit. Sketch to scale the output voltage waveform from (a) A half-wave rectifier (b) A bridge rectifier Assume that silicon diodes are used in each case. 11. Explain why a ...
application specific power supplies
... Power supply design depends on the target market. Amplifiers for professional recording studios or laboratory applications may need to provide full output power on a continuous basis; an expensive requirement only to be used when needed! Consumers tend to operate amplifiers around 40% continuous pow ...
... Power supply design depends on the target market. Amplifiers for professional recording studios or laboratory applications may need to provide full output power on a continuous basis; an expensive requirement only to be used when needed! Consumers tend to operate amplifiers around 40% continuous pow ...
AN-7733 FL7732 设计工具流程(升降压式) Enter Input/Output Spec. Transformer Design
... VOUT condition. The switching frequency should be <65kHz. Enter Np over Np.min. If Np is too big to fit in transformer window, reduce Max. Duty. Pulse-by-pulse current limit is 0.67V. If VCS.MAX is too close to 0.67V, increase Max. Duty. t DIS means secondary diode conduction time at peak input volt ...
... VOUT condition. The switching frequency should be <65kHz. Enter Np over Np.min. If Np is too big to fit in transformer window, reduce Max. Duty. Pulse-by-pulse current limit is 0.67V. If VCS.MAX is too close to 0.67V, increase Max. Duty. t DIS means secondary diode conduction time at peak input volt ...
10-Bit, 40 MSPS, 3 V, 74 mW Analog-to
... external reference can also be chosen to suit the dc accuracy and temperature drift requirements of an application. An external resistor can be used to reduce power consumption when operating at lower sampling rates. This yields power savings for users who do not require the maximum sample rate. Thi ...
... external reference can also be chosen to suit the dc accuracy and temperature drift requirements of an application. An external resistor can be used to reduce power consumption when operating at lower sampling rates. This yields power savings for users who do not require the maximum sample rate. Thi ...
WHM2026AE
... The recommended motherboard layout is shown in diagram of Foot Print/Mounting Layout. Sufficient numbers of ground vias on center ground pad are essential for the RF grounding. The width of the 50-Ohm microstrip lines at the input and output RF ports may be different for different property of the su ...
... The recommended motherboard layout is shown in diagram of Foot Print/Mounting Layout. Sufficient numbers of ground vias on center ground pad are essential for the RF grounding. The width of the 50-Ohm microstrip lines at the input and output RF ports may be different for different property of the su ...
Low Noise Amplifiers using ATF
... stability. A plot of Rollett Stability factor K as calculated from 0.1 GHz to 12 GHz is shown in Figure 11 for the amplifier. Source inductance can be used to help stability. It should be noted however that excessive inductance will cause high frequency stability to get worse (i.e. decreased value o ...
... stability. A plot of Rollett Stability factor K as calculated from 0.1 GHz to 12 GHz is shown in Figure 11 for the amplifier. Source inductance can be used to help stability. It should be noted however that excessive inductance will cause high frequency stability to get worse (i.e. decreased value o ...
here - Classic Valve Design
... is determined by SQRT(W*R) or roughly a peak to peak sine of 8 volts across 8 ohms, 11.3 volts across 16 ohms or 5.6 volts across 4 ohms. - Switch the generator to square wave. - Observe the waveforms. ...
... is determined by SQRT(W*R) or roughly a peak to peak sine of 8 volts across 8 ohms, 11.3 volts across 16 ohms or 5.6 volts across 4 ohms. - Switch the generator to square wave. - Observe the waveforms. ...
light dimmer dim - 10
... circuit-breaker or the switch-disconnector that are joined to the proper circuit, 2. Check if there is no voltage on connection cables by means of a special measure equipment, 3. Install ASM-10 device in the switchboard on TH-35 DIN rail, 4. Connect the cables with the terminals according to inst ...
... circuit-breaker or the switch-disconnector that are joined to the proper circuit, 2. Check if there is no voltage on connection cables by means of a special measure equipment, 3. Install ASM-10 device in the switchboard on TH-35 DIN rail, 4. Connect the cables with the terminals according to inst ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.