MAX2602EVKIT.pdf
... the MAX2602 EV kit can be used to emulate the MAX2601, which does not have an internal biasing diode. ...
... the MAX2602 EV kit can be used to emulate the MAX2601, which does not have an internal biasing diode. ...
zr1000-1600 manual 11.1.04.indd
... FCC COMPLIANCE NOTICE: This device complies with part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation. C ...
... FCC COMPLIANCE NOTICE: This device complies with part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation. C ...
PJ03S/D Series FEATURES
... Transient recovery time is measured to within 1% error band for a step change in output load of 75% to 100%. Ripple & Noise measurement bandwidth is 0-20 MHz measured with a 1μF M/C. These power converters require a minimum output loading to maintain specified regulation, operation under no-load con ...
... Transient recovery time is measured to within 1% error band for a step change in output load of 75% to 100%. Ripple & Noise measurement bandwidth is 0-20 MHz measured with a 1μF M/C. These power converters require a minimum output loading to maintain specified regulation, operation under no-load con ...
UC3525A
... The UC1525A/1527A series of pulse width modulator integrated circuits are designed to offer improved performance and lowered external parts count when used in designing all types of switching power supplies. The on-chip +5.1V reference is trimmed to ±1% and the input common-mode range of the error a ...
... The UC1525A/1527A series of pulse width modulator integrated circuits are designed to offer improved performance and lowered external parts count when used in designing all types of switching power supplies. The on-chip +5.1V reference is trimmed to ±1% and the input common-mode range of the error a ...
RF3928 280W GaN WIDEBAND PULSED POWER AMPLIFIER Features
... The GaN HEMT device is a depletion mode high electron mobility transistor (HEMT). At zero volts VGS the drain of the device is saturated and uncontrolled drain current will destroy the transistor. The gate voltage must be taken to a potential lower than the source voltage to pinch off the device pri ...
... The GaN HEMT device is a depletion mode high electron mobility transistor (HEMT). At zero volts VGS the drain of the device is saturated and uncontrolled drain current will destroy the transistor. The gate voltage must be taken to a potential lower than the source voltage to pinch off the device pri ...
SGA5289Z
... Caution! ESD sensitive device. Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional op ...
... Caution! ESD sensitive device. Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional op ...
RF Filtering for Audio Amplifier Circuits
... 1. Using one bypass component versus two or more resistive devices resulting in reduced component count on a PCB. 2. Better balance between power and return lines to ground: capacitance tolerance between the internal line to ground capacitors is typically 13% or less. This means matched suppression ...
... 1. Using one bypass component versus two or more resistive devices resulting in reduced component count on a PCB. 2. Better balance between power and return lines to ground: capacitance tolerance between the internal line to ground capacitors is typically 13% or less. This means matched suppression ...
AN52 - Linear Technology Magazine Circuit Collection, Volume 1
... with roll-off faster than that of an 8th-order Butterworth. An elliptic filter was ruled out because its distortion specifications are too high. Two low power LTC1164-5s were wired in cascade to investigate the specifications that could be achieved with this architecture. The LTC1164-5 ...
... with roll-off faster than that of an 8th-order Butterworth. An elliptic filter was ruled out because its distortion specifications are too high. Two low power LTC1164-5s were wired in cascade to investigate the specifications that could be achieved with this architecture. The LTC1164-5 ...
Closed and Open Loop..
... A: The term “closed loop” refers to loop formed by the feed-forward path and the feed-back (i.e., feedback) path of the amplifier. In this case, the feed-forward path is formed by the op-amp, while the feedback path is formed by the feedback resistor R2. ...
... A: The term “closed loop” refers to loop formed by the feed-forward path and the feed-back (i.e., feedback) path of the amplifier. In this case, the feed-forward path is formed by the op-amp, while the feedback path is formed by the feedback resistor R2. ...
4-Stage
... 1. Set jumpers to desired position as follows: • Mode jumpers (H1, H2) - In FLT position, the A and D relays energize on a decrease in signal. In the SEQ position, the A and D relays energize on an increase in signal. The B and C relays always energize on an increase in signal. • Input jumpers (H3, ...
... 1. Set jumpers to desired position as follows: • Mode jumpers (H1, H2) - In FLT position, the A and D relays energize on a decrease in signal. In the SEQ position, the A and D relays energize on an increase in signal. The B and C relays always energize on an increase in signal. • Input jumpers (H3, ...
9: Transistors
... This shows the “common emitter” mode which is how we will use the BJT. Concentrate on the BE junction which looks like a diode. When this is forward biased, a large current can flow from C to E. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bipolar_junction_transistor ...
... This shows the “common emitter” mode which is how we will use the BJT. Concentrate on the BE junction which looks like a diode. When this is forward biased, a large current can flow from C to E. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bipolar_junction_transistor ...
The Ideal Op-Amp lec..
... Very large and very small Of course, we have three parameters in this circuit model: input resistance, output resistance, and open circuit voltage gain. ...
... Very large and very small Of course, we have three parameters in this circuit model: input resistance, output resistance, and open circuit voltage gain. ...
eq600 MANUAL
... This unit is designed for 12V DC operation only. Avoid Installing the unit where: - It would be subject to high temperatures, such as direct sunlight or from hot air from the heater. - It would be exposed to rain or moisture - It would be subject to dust or dirt If your car is parked in direct sunli ...
... This unit is designed for 12V DC operation only. Avoid Installing the unit where: - It would be subject to high temperatures, such as direct sunlight or from hot air from the heater. - It would be exposed to rain or moisture - It would be subject to dust or dirt If your car is parked in direct sunli ...
Aikido LV - Glass-Ware
... The LV Aikido PCB holds a star ground at its center. Ideally, this will be the only central ground in a line-stage buffer. A ground-loop is created when a device finds more than one connections to ground. Ground loops, unfortunately, are extremely easy to introduce. For example, if the input and out ...
... The LV Aikido PCB holds a star ground at its center. Ideally, this will be the only central ground in a line-stage buffer. A ground-loop is created when a device finds more than one connections to ground. Ground loops, unfortunately, are extremely easy to introduce. For example, if the input and out ...
Ch 10
... • The intersection point is called the “3dB point” since at that frequency ACL will be down by 3dB. ...
... • The intersection point is called the “3dB point” since at that frequency ACL will be down by 3dB. ...
OPAx322-Q1 20-MHz, Low-Noise, 1.8-V, RRI/O
... Control-Loop Amplifiers Communications Security Scanners ...
... Control-Loop Amplifiers Communications Security Scanners ...
LT6553 - 650MHz Gain of 2 Triple Video Amplifier
... internally fixed gain of 2. The individual amplifiers are optimized for performance with a double terminated 75Ω video load and feature a 2VP–P full signal bandwidth of 400MHz, making them ideal for driving very high-resolution video signals. Separate power supply pins for each amplifier boost chann ...
... internally fixed gain of 2. The individual amplifiers are optimized for performance with a double terminated 75Ω video load and feature a 2VP–P full signal bandwidth of 400MHz, making them ideal for driving very high-resolution video signals. Separate power supply pins for each amplifier boost chann ...
EE1000 Project 2 Photo
... through R1 must also flow through C1. When the square wave output is high, the op-amp must ramp its output voltage down at a rate of Vcc/(2·R1·C1) Volts per second to keep V– equal to Vcc/2. (The current through a capacitor is equal to the rate its voltage changes multiplied by its capacitance). Whe ...
... through R1 must also flow through C1. When the square wave output is high, the op-amp must ramp its output voltage down at a rate of Vcc/(2·R1·C1) Volts per second to keep V– equal to Vcc/2. (The current through a capacitor is equal to the rate its voltage changes multiplied by its capacitance). Whe ...
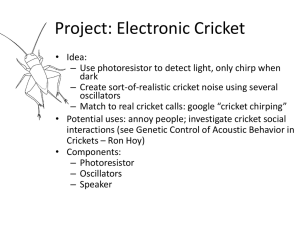
Cricket_project_brl4..
... • The threshold and trigger inputs monitor the capacitor voltage and when it reaches 2/3Vcc (threshold), the output becomes low and the discharge pin is connected to 0V. • The capacitor discharges with current flowing through RB into the discharge pin. When the voltage falls to 1/3Vcc (trigger) the ...
... • The threshold and trigger inputs monitor the capacitor voltage and when it reaches 2/3Vcc (threshold), the output becomes low and the discharge pin is connected to 0V. • The capacitor discharges with current flowing through RB into the discharge pin. When the voltage falls to 1/3Vcc (trigger) the ...
active antenna - Talking Electronics
... This circuit is for low voltage applications requiring high power outputs. Output power levels of 1.0 W into 4 ohm from 6 V and 3.5 V into 8 ohm from 12 V are typical. Coupling capacitors are not necessary since the output dc levels will be within a few tenths of a volt of each other. Where critical ...
... This circuit is for low voltage applications requiring high power outputs. Output power levels of 1.0 W into 4 ohm from 6 V and 3.5 V into 8 ohm from 12 V are typical. Coupling capacitors are not necessary since the output dc levels will be within a few tenths of a volt of each other. Where critical ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.