receptors and ion channels - The Company of Biologists
... Over the past 10 years, since the introduction of the extracellular patch-clamp technique by Neher & Sakmann, our understanding of the reactions involved in the control of channel gating and its modulation has increased dramatically. The introduction of the 'giga-seal' modification of the technique ...
... Over the past 10 years, since the introduction of the extracellular patch-clamp technique by Neher & Sakmann, our understanding of the reactions involved in the control of channel gating and its modulation has increased dramatically. The introduction of the 'giga-seal' modification of the technique ...
The Cell: A Microcosm of Life Multiple
... Apoptosis refers to programmed cell death as distinguished from pathological cell death, which causes inflammation and possibly autoimmune reactions. Apoptosis can be beneficial during development of an organism when cells are no longer needed as development progresses. Apoptosis is thought to ...
... Apoptosis refers to programmed cell death as distinguished from pathological cell death, which causes inflammation and possibly autoimmune reactions. Apoptosis can be beneficial during development of an organism when cells are no longer needed as development progresses. Apoptosis is thought to ...
Chapter x – title of chapter
... Apoptosis refers to programmed cell death as distinguished from pathological cell death, which causes inflammation and possibly autoimmune reactions. Apoptosis can be beneficial during development of an organism when cells are no longer needed as development progresses. Apoptosis is thought to ...
... Apoptosis refers to programmed cell death as distinguished from pathological cell death, which causes inflammation and possibly autoimmune reactions. Apoptosis can be beneficial during development of an organism when cells are no longer needed as development progresses. Apoptosis is thought to ...
Chapter 1 Review Understanding Concepts
... Amylose and amylopectin are similar in that they are polymers of α-glucose and contain α 1–4 glycosidic linkages; however, amylopectin also contains α 1–6 glycosidic linkages. α-glucose has a hydroxyl group at carbon-1 that is below the plane of the ring, while β-glucose has a hydroxyl group at carb ...
... Amylose and amylopectin are similar in that they are polymers of α-glucose and contain α 1–4 glycosidic linkages; however, amylopectin also contains α 1–6 glycosidic linkages. α-glucose has a hydroxyl group at carbon-1 that is below the plane of the ring, while β-glucose has a hydroxyl group at carb ...
answers_ch06
... that it has a catalytic property which leads to its own deactivation without the need for any external influence. If the autocatalytic property was lost, the Ras protein would remain permanantly activated and this would have serious consequences on cell chemistry since the Ras protein initiates proc ...
... that it has a catalytic property which leads to its own deactivation without the need for any external influence. If the autocatalytic property was lost, the Ras protein would remain permanantly activated and this would have serious consequences on cell chemistry since the Ras protein initiates proc ...
Endocrine Pharmacology
... Hormones - Cell to cell communication molecules - Made in glands or cells - Transported by blood - Distant or local target tissue receptors ...
... Hormones - Cell to cell communication molecules - Made in glands or cells - Transported by blood - Distant or local target tissue receptors ...
5 - edl.io
... Nonsteroid hormones do not enter the cell. Steroid hormone Steroid hormone diffuses through the cell membrane ...
... Nonsteroid hormones do not enter the cell. Steroid hormone Steroid hormone diffuses through the cell membrane ...
Biochemistry Test Review
... 13. Be able to draw the basic structure of an amino acid and show how two or more amino acids may join together to form a polypeptide. Name the kind of reaction that links the amino acids. 14. Describe the four different levels of protein structure. 15. Define enzyme and give three examples of enzym ...
... 13. Be able to draw the basic structure of an amino acid and show how two or more amino acids may join together to form a polypeptide. Name the kind of reaction that links the amino acids. 14. Describe the four different levels of protein structure. 15. Define enzyme and give three examples of enzym ...
Cheng BY 123 Raut – Mock Exam Unit I 09/21/14 1. Which of the
... 1. Which of the following orders represents the hierarchy of biological organization from the most to the least complex level? A) organelle, cell, organ system, population, community, ecosystem B) ecosystem, community, organism, tissue, cell, organelle C) biosphere, population, organism, cell, tissu ...
... 1. Which of the following orders represents the hierarchy of biological organization from the most to the least complex level? A) organelle, cell, organ system, population, community, ecosystem B) ecosystem, community, organism, tissue, cell, organelle C) biosphere, population, organism, cell, tissu ...
Chapter 16
... Nearly all RTKs signal via Ras/MAP kinase pathways. They also may signal via other pathways. For example, the insulin receptor uses the Ras/MAP kinase pathway to regulate gene expression and the PI-3 kinase pathway to regulate enzyme activity (e.g., glycogen synthase). RTK-Ras/MAP kinase signaling c ...
... Nearly all RTKs signal via Ras/MAP kinase pathways. They also may signal via other pathways. For example, the insulin receptor uses the Ras/MAP kinase pathway to regulate gene expression and the PI-3 kinase pathway to regulate enzyme activity (e.g., glycogen synthase). RTK-Ras/MAP kinase signaling c ...
Preview Sample 1
... With respect to knock-out technology, it has been said "If a protein's function is important, its knock-out will result in lethality. On the other hand, if it's very important its function will be duplicated by another protein, and there will be no obvious phenotype for the knock-out." Please explai ...
... With respect to knock-out technology, it has been said "If a protein's function is important, its knock-out will result in lethality. On the other hand, if it's very important its function will be duplicated by another protein, and there will be no obvious phenotype for the knock-out." Please explai ...
Typical Signal Transduction Pathway
... • The same hormone may have different effects on target cells that have – Different receptors for the hormone – Different signal transduction pathways ...
... • The same hormone may have different effects on target cells that have – Different receptors for the hormone – Different signal transduction pathways ...
Biochemistry http://www.brainpop.com/science/matterandchemistry
... Enzymes are proteins, and just like other proteins they need to be the correct shape to perform their function correctly. ...
... Enzymes are proteins, and just like other proteins they need to be the correct shape to perform their function correctly. ...
Document
... a. Protein b. Carbohydrate c. Lipid d. Nucleic Acid 3. What is a disaccharide? Two Sugars 4. How does a polysaccharide differ from a disaccharide? A disaccharide is two sugars where a polysaccharide is many sugars. 5. Circle the polysaccharides ...
... a. Protein b. Carbohydrate c. Lipid d. Nucleic Acid 3. What is a disaccharide? Two Sugars 4. How does a polysaccharide differ from a disaccharide? A disaccharide is two sugars where a polysaccharide is many sugars. 5. Circle the polysaccharides ...
Life Science Name: Date: ______ Per: ______ Chemical Reactions
... 13. Can one single enzyme catalyze many different types of substrates? Explain why? ...
... 13. Can one single enzyme catalyze many different types of substrates? Explain why? ...
Look at chapter 3 chemistry worksheet
... • In phospholipids, two of the OH groups are linked to fatty acids and one of the OH groups is linked to a phosphorylated alcohol • Fatty acids have a carboxyl group with long hydrocarbon tails ...
... • In phospholipids, two of the OH groups are linked to fatty acids and one of the OH groups is linked to a phosphorylated alcohol • Fatty acids have a carboxyl group with long hydrocarbon tails ...
No Slide Title
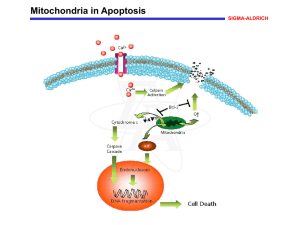
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
A1988N971200001
... [Department of Biology, University of Milan. Italy] This paper demonstrated that growth stimula- were soon able to demonstrate that indeed the tion by auxins or by the toxin fusicoccin is as- growth effect of fusicoccin was correlated sociated with—and at least in part mediated with a marked stimula ...
... [Department of Biology, University of Milan. Italy] This paper demonstrated that growth stimula- were soon able to demonstrate that indeed the tion by auxins or by the toxin fusicoccin is as- growth effect of fusicoccin was correlated sociated with—and at least in part mediated with a marked stimula ...
MAKEUP: Briefly discuss functions of the liver
... • Once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolised to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fatty acid Cholesterol / phospholipid formation o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CHO: Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o Fats ...
... • Once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolised to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fatty acid Cholesterol / phospholipid formation o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CHO: Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o Fats ...
课件三
... Why do cells communicate? How are signals transmitted between cells? How are signals transmitted across cell membranes into the cell interior? How are signals transmitted within a cell? How do signals affect cell function? What is the relationship between cell signaling and cancer? ...
... Why do cells communicate? How are signals transmitted between cells? How are signals transmitted across cell membranes into the cell interior? How are signals transmitted within a cell? How do signals affect cell function? What is the relationship between cell signaling and cancer? ...
Lipid signaling

Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses. Lipid signaling is thought to be qualitatively different from other classical signaling paradigms (such as monoamine neurotransmission) because lipids can freely diffuse through membranes (see osmosis.) One consequence of this is that lipid messengers cannot be stored in vesicles prior to release and so are often biosynthesized ""on demand"" at their intended site of action. As such, many lipid signaling molecules cannot circulate freely in solution but, rather, exist bound to special carrier proteins in serum.