Lab Protein and Amino Acids
... source of energy. Consequently, for good health, it is necessary to have a regular intake of protein through the diet. An animal can survive for a limited time on a diet that contains only vitamins, minerals, and proteins (no carbohydrates or lipids). But if the animal is fed a diet containing every ...
... source of energy. Consequently, for good health, it is necessary to have a regular intake of protein through the diet. An animal can survive for a limited time on a diet that contains only vitamins, minerals, and proteins (no carbohydrates or lipids). But if the animal is fed a diet containing every ...
1 mg/kg/day - Autism One
... Fatty acid deficiencies [Bu, 2006] GI problems [Valicenti-McDermott, 2008] ...
... Fatty acid deficiencies [Bu, 2006] GI problems [Valicenti-McDermott, 2008] ...
Applications of microbes in industry: Production of primary and
... • Secondary metabolites are not produced until the microbe has largely completed its logarithmic growth phase and entered the stationary phase of the growth cycle. Period of production is called idiophase and metabolites as idiolites. • In the idiophase, cells do not divide but are metabolically act ...
... • Secondary metabolites are not produced until the microbe has largely completed its logarithmic growth phase and entered the stationary phase of the growth cycle. Period of production is called idiophase and metabolites as idiolites. • In the idiophase, cells do not divide but are metabolically act ...
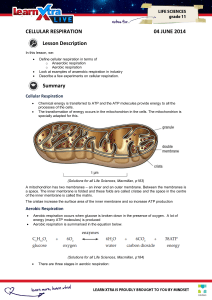
CELLULAR RESPIRATION 04 JUNE 2014 Lesson Description
... Oxidative phosphorylation: takes the energy from the energy-rich hydrogens to make ATP. The energy depleted hydrogens combine with oxygen to make water. This is either breathed out as water vapour or excreted via the kidneys. ...
... Oxidative phosphorylation: takes the energy from the energy-rich hydrogens to make ATP. The energy depleted hydrogens combine with oxygen to make water. This is either breathed out as water vapour or excreted via the kidneys. ...
Unit7CellRespirationTargetPractice
... which combines with hydrogen ions (H ) to form _______________. The energy released as the electrons move through certain electron carriers is used to pump ____________ from the _____________ of mitochondria into the ____________________ of mitochondria. This results in the __________________ that s ...
... which combines with hydrogen ions (H ) to form _______________. The energy released as the electrons move through certain electron carriers is used to pump ____________ from the _____________ of mitochondria into the ____________________ of mitochondria. This results in the __________________ that s ...
4 Metabolism and Enzymes
... aerobes. • Anaerobic respiration: The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is not O2. Yields less energy than aerobic respiration because only part of the Krebs cycles operations under anaerobic conditions. Obligate anaerobes perform anaerobic respiration. • Fermentation: Glycolys ...
... aerobes. • Anaerobic respiration: The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is not O2. Yields less energy than aerobic respiration because only part of the Krebs cycles operations under anaerobic conditions. Obligate anaerobes perform anaerobic respiration. • Fermentation: Glycolys ...
7.6 Hydrolysis of Amides
... exposure in the hydrochloric acid in the stomach. (Admittedly, since they all still have the strained 4-membered amide ring, it isn’t obvious why that should be the case.) ...
... exposure in the hydrochloric acid in the stomach. (Admittedly, since they all still have the strained 4-membered amide ring, it isn’t obvious why that should be the case.) ...
Respiration
... 21. Why do fats provide a little more than twice as many calories per gram as compared to carbohydrates or proteins? Hint: Think of the output of the Citric Acid Cycle. ...
... 21. Why do fats provide a little more than twice as many calories per gram as compared to carbohydrates or proteins? Hint: Think of the output of the Citric Acid Cycle. ...
Biochemistry Study Guide NITROGEN METABOLISM
... This in effect gives us a free amino acid of Lysine or Arginine which can then be absorbed. AMINOPEPTIDASE: Exopeptidases that cut at the amino end of a peptide. This is secreted by the intestinal mucosa further along the small intestine (jejunum). This is a metalloprotease that requires Zin ...
... This in effect gives us a free amino acid of Lysine or Arginine which can then be absorbed. AMINOPEPTIDASE: Exopeptidases that cut at the amino end of a peptide. This is secreted by the intestinal mucosa further along the small intestine (jejunum). This is a metalloprotease that requires Zin ...
Repetition Summary of last lecture Energy Cell Respiration
... pyruvate is reduced directly to NADH to form lactate as a waste product ...
... pyruvate is reduced directly to NADH to form lactate as a waste product ...
23.1 The Citric Acid Cycle
... from the catabolic pathways in stage 2 with electron transport and the synthesis of ATP in stage 3. Learning Goal Describe the oxidation of acetyl CoA in the citric acid cycle. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
... from the catabolic pathways in stage 2 with electron transport and the synthesis of ATP in stage 3. Learning Goal Describe the oxidation of acetyl CoA in the citric acid cycle. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
UDP-GLYCOSYLTRANSFERASES OF PLANT HORMONES
... Summary: UDP-glycosyltransferases (GTases, UGT) catalyze the transfer of the sugar moiety from the uridine-diphosphate-activated monosaccharide (e.g. uridine-diphosphate-5’-glucose, UDPG) molecule to the specific acceptor. Glycosides contain aglycons attached by a β-glycosidic bond to C1 of the sacc ...
... Summary: UDP-glycosyltransferases (GTases, UGT) catalyze the transfer of the sugar moiety from the uridine-diphosphate-activated monosaccharide (e.g. uridine-diphosphate-5’-glucose, UDPG) molecule to the specific acceptor. Glycosides contain aglycons attached by a β-glycosidic bond to C1 of the sacc ...
Spring 2016 Practice Final Exam w/ solution
... Koop’s Experiment: Fed dog with even- and odd-chain fatty acids (FAs) with -phenyl group and analyzed urine sample collected from these dogs for metabolites. Concluded that FAs are metabolically oxidized at their -carbon atom (hence -oxidation), resulting in the release of a C-2 specie per oxida ...
... Koop’s Experiment: Fed dog with even- and odd-chain fatty acids (FAs) with -phenyl group and analyzed urine sample collected from these dogs for metabolites. Concluded that FAs are metabolically oxidized at their -carbon atom (hence -oxidation), resulting in the release of a C-2 specie per oxida ...
Slide 1
... Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from glucogenic precursors which are not of carbohydrate origin (gluconeogenic precursors) It occurs during prolonged fasting to synthesize glucose for tissues requiring continuous supply of glucose as a source of energy: Brain, RBCs, Kidney medulla, Lens, ...
... Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from glucogenic precursors which are not of carbohydrate origin (gluconeogenic precursors) It occurs during prolonged fasting to synthesize glucose for tissues requiring continuous supply of glucose as a source of energy: Brain, RBCs, Kidney medulla, Lens, ...
Nobel Prizes 1907 Eduard Buchner, cell
... epimerase )|FAA-CoAglc(animal:even number,no;odd,yes;plants:yes,glyoxylate cycle)|omega Oxidation in ER|Phytanic acid oxidation in Peroxisome| Difference between phytanic acid and pristanic acid: methyl group on beta carbon cannot undergo b oxidation|Ketone body: Acetyl-CoA CoA in liver can be con ...
... epimerase )|FAA-CoAglc(animal:even number,no;odd,yes;plants:yes,glyoxylate cycle)|omega Oxidation in ER|Phytanic acid oxidation in Peroxisome| Difference between phytanic acid and pristanic acid: methyl group on beta carbon cannot undergo b oxidation|Ketone body: Acetyl-CoA CoA in liver can be con ...
Urea Cycle Defect: A Case Study
... The abnormal values given in the chart on the previous page are characteristic of a deficiency of the urea cycle enzyme ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC). The primary function of OTC is to catalyze the second reaction seen in the first figure of the urea cycle. In this reaction carbamylphosphate is c ...
... The abnormal values given in the chart on the previous page are characteristic of a deficiency of the urea cycle enzyme ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC). The primary function of OTC is to catalyze the second reaction seen in the first figure of the urea cycle. In this reaction carbamylphosphate is c ...
Document
... • Most products of fat metabolism are transported in lymph as chylomicrons • Lipids in chylomicrons are hydrolyzed by plasma enzymes and absorbed by cells • Only neutral fats are routinely oxidized for energy • Catabolism of fats involves two separate pathways • Glycerol pathway • Fatty acids pathwa ...
... • Most products of fat metabolism are transported in lymph as chylomicrons • Lipids in chylomicrons are hydrolyzed by plasma enzymes and absorbed by cells • Only neutral fats are routinely oxidized for energy • Catabolism of fats involves two separate pathways • Glycerol pathway • Fatty acids pathwa ...
fatty acids
... The electron-transport chain uses NADH and FADH2 to produce 34 ATP. This process requires O2, which combines with H+ to form H2O. ...
... The electron-transport chain uses NADH and FADH2 to produce 34 ATP. This process requires O2, which combines with H+ to form H2O. ...
Relationship between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... Pyruvate lactate + 2 ATP Occurs in absence of O2 Lactobacillus (dairy ...
... Pyruvate lactate + 2 ATP Occurs in absence of O2 Lactobacillus (dairy ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... Oxidation of 2 isocitrate (2NADH) 6 ATP Oxidation of 2 -ketoglutarate (2NADH) 6 ATP 2 Direct substrate phosphorylations (2GTP) 2 ATP Oxidation of 2 succinate (2FADH2) 4 ATP Oxidation of 2 malate (2NADH) 6 ATP 24 ATP Summary: 2Acetyl CoA + 24 ADP + 24 Pi 4CO2 + 2H2O + 24 ATP + 2 CoASH ...
... Oxidation of 2 isocitrate (2NADH) 6 ATP Oxidation of 2 -ketoglutarate (2NADH) 6 ATP 2 Direct substrate phosphorylations (2GTP) 2 ATP Oxidation of 2 succinate (2FADH2) 4 ATP Oxidation of 2 malate (2NADH) 6 ATP 24 ATP Summary: 2Acetyl CoA + 24 ADP + 24 Pi 4CO2 + 2H2O + 24 ATP + 2 CoASH ...
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration (working)
... aerobic or anaerobic conditions), therefore this series of reactions evolved very early in prokaryotic organisms before oxygen was present in the atomosphere. • In the absence of O2, glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produce ATP Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... aerobic or anaerobic conditions), therefore this series of reactions evolved very early in prokaryotic organisms before oxygen was present in the atomosphere. • In the absence of O2, glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produce ATP Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.