Thalassospiramide G, a New γ-Amino-Acid
... marine microbes were highlighted as an emerging resource for bioactive molecules by Fenical [2], they have demonstrated their pharmaceutical potential by providing structurally novel natural products for drug discovery, such as salinosporamide A, which is currently in clinical trials. Drugs derived ...
... marine microbes were highlighted as an emerging resource for bioactive molecules by Fenical [2], they have demonstrated their pharmaceutical potential by providing structurally novel natural products for drug discovery, such as salinosporamide A, which is currently in clinical trials. Drugs derived ...
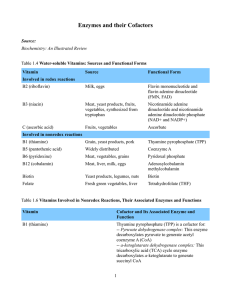
Enzymes and their Cofactors Source: Biochemistry: An Illustrated
... degrades odd-numbered fatty acids -- Methionine synthase/homocysteine methyltransferase: This enzyme transfers a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (N5-methylTHF) onto homocysteine to form methionine. Methionine reacts with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to generate S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) ...
... degrades odd-numbered fatty acids -- Methionine synthase/homocysteine methyltransferase: This enzyme transfers a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (N5-methylTHF) onto homocysteine to form methionine. Methionine reacts with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to generate S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) ...
Uric acid estimation in plasma
... Salvage pathways collect hypoxanthine and guanine and recombine them with PRPP to form nucleotides in the HGPRT reaction Absence of HGPRT is cause of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome This increase may be due to PRPP feed-forward activation of de novo pathways the rate of purine synthesis is increased about 200X ...
... Salvage pathways collect hypoxanthine and guanine and recombine them with PRPP to form nucleotides in the HGPRT reaction Absence of HGPRT is cause of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome This increase may be due to PRPP feed-forward activation of de novo pathways the rate of purine synthesis is increased about 200X ...
Abnormalities of Intermediary Metabolism in Barth Syndrome
... TCA Intermediates in Smith-Leml-Opitz Syndrome ...
... TCA Intermediates in Smith-Leml-Opitz Syndrome ...
Lactate Acid Fermentation of Acetic Acid in the Butyric Spec. and the
... bid, considerable gas was given off, and the pH rose to 8.2 to 8.4. After 72 hours a determination of lactic acid by the method of Friedemann and Graeser (1933) showed that the lactate was completely decomposed. Several soils of different types were used as inocula for enrichment cultures of this ty ...
... bid, considerable gas was given off, and the pH rose to 8.2 to 8.4. After 72 hours a determination of lactic acid by the method of Friedemann and Graeser (1933) showed that the lactate was completely decomposed. Several soils of different types were used as inocula for enrichment cultures of this ty ...
Why would someone take the vitamin niacin?
... and cellular respiration not on the exact reactions/enzymes involved. Focus on being able to compare and contrast the two cell processes. ***Draw figure 9.2 as your Unit page (this is the big picture!) Section 9.1 - Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels 1. Define the two catabol ...
... and cellular respiration not on the exact reactions/enzymes involved. Focus on being able to compare and contrast the two cell processes. ***Draw figure 9.2 as your Unit page (this is the big picture!) Section 9.1 - Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels 1. Define the two catabol ...
Nutritional Ergogenics
... What are dietary supplements? • Defined by The Dietary Supplements Health and Education Act of 1994 (DSHEA) Not a food, only supplements the diet • Contain one or more of the following: – Vitamin – Mineral – Herb or other botanical – Amino acid – Dietary substance to supplement diet – A con ...
... What are dietary supplements? • Defined by The Dietary Supplements Health and Education Act of 1994 (DSHEA) Not a food, only supplements the diet • Contain one or more of the following: – Vitamin – Mineral – Herb or other botanical – Amino acid – Dietary substance to supplement diet – A con ...
Document
... body. • Obesity, diabetes,and hyperlipoproteinemia • Cell membranes • Lung surfactant • Hormone second messengers • Platelet-activating factor • cell adhesion and cell recognition • as receptors for bacterial toxins • ABO blood group substances • Glycolipid storage diseases ...
... body. • Obesity, diabetes,and hyperlipoproteinemia • Cell membranes • Lung surfactant • Hormone second messengers • Platelet-activating factor • cell adhesion and cell recognition • as receptors for bacterial toxins • ABO blood group substances • Glycolipid storage diseases ...
LS1a Fall 09
... Section Activity #2: Shown below are alanine and serine in their predominant states at pH 7. Draw the products of the reaction to form the alanyl-serine dipeptide. ...
... Section Activity #2: Shown below are alanine and serine in their predominant states at pH 7. Draw the products of the reaction to form the alanyl-serine dipeptide. ...
Hans Adolf Krebs (2)
... The details of the citric acid cycle were worked out by the study of highly purified enzymes of the cycle ...
... The details of the citric acid cycle were worked out by the study of highly purified enzymes of the cycle ...
BIO 220 Chapter 5 lecture outline Metabolism definition Collision
... 5. Describe the general structure and characteristics of an enzyme. 6. Explain the mechanism by which enzymes speed up chemical reactions. 7. Why would a particular enzyme be able to bind to only one or a small number of substrates? 8. What is the function of each type of enzyme listed in table 5.1 ...
... 5. Describe the general structure and characteristics of an enzyme. 6. Explain the mechanism by which enzymes speed up chemical reactions. 7. Why would a particular enzyme be able to bind to only one or a small number of substrates? 8. What is the function of each type of enzyme listed in table 5.1 ...
Krebs cycle
... • The final pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: carbohydrates, fatty acids, and amino acids. ...
... • The final pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: carbohydrates, fatty acids, and amino acids. ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... starring role in both the process of energy production and biosynthesis. The cycle finishes the sugar-breaking job started in glycolysis and fuels the production of ATP in the process. It is also a central hub in biosynthetic reactions, providing intermediates that are used to build amino acids and ...
... starring role in both the process of energy production and biosynthesis. The cycle finishes the sugar-breaking job started in glycolysis and fuels the production of ATP in the process. It is also a central hub in biosynthetic reactions, providing intermediates that are used to build amino acids and ...
Citric Acid Cycle - Progetto e
... starring role in both the process of energy production and biosynthesis. The cycle finishes the sugar-breaking job started in glycolysis and fuels the production of ATP in the process. It is also a central hub in biosynthetic reactions, providing intermediates that are used to build amino acids and ...
... starring role in both the process of energy production and biosynthesis. The cycle finishes the sugar-breaking job started in glycolysis and fuels the production of ATP in the process. It is also a central hub in biosynthetic reactions, providing intermediates that are used to build amino acids and ...
Cellular Respiration
... NADH) are transferred from one membrane carrier to another membrane carrier (Cytochromes) • The electrons lose energy as they are transferred (like hot potato) • This energy drives membrane pumps involved with Chemiosmosis ...
... NADH) are transferred from one membrane carrier to another membrane carrier (Cytochromes) • The electrons lose energy as they are transferred (like hot potato) • This energy drives membrane pumps involved with Chemiosmosis ...
Lab12
... Contains: tributyrin (triglycerides) in agar to solidify, Spirit Blue pH indicator: neutral pH = pale blue, acidic pH = dark or bright blue Discriminates organisms that can produce lipases to hydrolyze triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids (acid pH). (Some lipases will completely hydrolyze the ...
... Contains: tributyrin (triglycerides) in agar to solidify, Spirit Blue pH indicator: neutral pH = pale blue, acidic pH = dark or bright blue Discriminates organisms that can produce lipases to hydrolyze triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids (acid pH). (Some lipases will completely hydrolyze the ...
List of Precursor Chemicals - Ministry of Health Jamaica
... Narcotic - A substance used to induce drowsiness sleep stupor or insensibility. These substances include Cocaine, Codeine, Pethidine, Morphine and Fentanyl which are used to relieve moderate or severe pain or in anaesthesia and are regulated under the Dangerous Drugs Act and Regulations of 1948. ...
... Narcotic - A substance used to induce drowsiness sleep stupor or insensibility. These substances include Cocaine, Codeine, Pethidine, Morphine and Fentanyl which are used to relieve moderate or severe pain or in anaesthesia and are regulated under the Dangerous Drugs Act and Regulations of 1948. ...
Hans A. Krebs - Nobel Lecture
... of the intermediary reactions by which sugar is anaerobically fermented to lactic acid or to ethanol and carbon dioxide. The success was mainly due to the joint efforts of the schools of Meyerhof, Embden, Parnas, von Euler, Warburg and the Coris, who built on the pioneer work of Harden and of Neuber ...
... of the intermediary reactions by which sugar is anaerobically fermented to lactic acid or to ethanol and carbon dioxide. The success was mainly due to the joint efforts of the schools of Meyerhof, Embden, Parnas, von Euler, Warburg and the Coris, who built on the pioneer work of Harden and of Neuber ...
Document
... Lipid FACTS Lipids are energy rich and provides 9 kcal/gm dietary lipids 90% triacylglycerols (TAGs) also include cholesterol esters, phospholipids, essential unsaturated fatty acids; fat-soluble vitamins most dietary fat transported to adipose for storage dietary TAGs hydrolyzed in the intestine b ...
... Lipid FACTS Lipids are energy rich and provides 9 kcal/gm dietary lipids 90% triacylglycerols (TAGs) also include cholesterol esters, phospholipids, essential unsaturated fatty acids; fat-soluble vitamins most dietary fat transported to adipose for storage dietary TAGs hydrolyzed in the intestine b ...
fermentation
... 2. Fermentation involves no Krebs cycle or electron transport chain. Key to the function of glycolysis is ...
... 2. Fermentation involves no Krebs cycle or electron transport chain. Key to the function of glycolysis is ...
Cell Size and Shape
... These two stages are preceded by an intermediate step in which pyruvic acid is converted to acetyl-CoA ...
... These two stages are preceded by an intermediate step in which pyruvic acid is converted to acetyl-CoA ...
Chapter 3: Energy, Catalysis, and Biosynthesis
... glycolytic pathway. Glycolysis produces __________________, which is converted into acetyl CoA, which enters the __________________. Several intermediates in this process can provide the carbon skeleton for the production of __________________, which are then incorporated into the enzymes that cata ...
... glycolytic pathway. Glycolysis produces __________________, which is converted into acetyl CoA, which enters the __________________. Several intermediates in this process can provide the carbon skeleton for the production of __________________, which are then incorporated into the enzymes that cata ...
glucose, faKy acids, amino acids
... phosphate groups for these reacDons h8p://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/protein-‐ funcDon-‐14123348 ...
... phosphate groups for these reacDons h8p://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/protein-‐ funcDon-‐14123348 ...
Common Defects in Wine
... uvarum will produce large amounts of Ethyl Acetate Brettanomyces will produce acetic acid Sacharomyces will produce VA in a normal fermentation (about 0.4 g/L) VA production is higher in the presence of Botrytis cineria ...
... uvarum will produce large amounts of Ethyl Acetate Brettanomyces will produce acetic acid Sacharomyces will produce VA in a normal fermentation (about 0.4 g/L) VA production is higher in the presence of Botrytis cineria ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.