Chapter 9 – Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... One catabolic process is called fermentation which is a partial oxidation of organic molecules, and it occurs without oxygen. Aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of organic compounds, like sugar, with the participation of oxygen in the process. Food provides the “fuel” for the cells, and m ...
... One catabolic process is called fermentation which is a partial oxidation of organic molecules, and it occurs without oxygen. Aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of organic compounds, like sugar, with the participation of oxygen in the process. Food provides the “fuel” for the cells, and m ...
Energy For Muscular Activity - South Carleton HS Physical
... from glycogen and glucose anaerobic process (in the absence of oxygen) The products of glycolysis (per molecule of glycogen): - 2 molecules of ATP - 2 molecules of pyruvic acid ...
... from glycogen and glucose anaerobic process (in the absence of oxygen) The products of glycolysis (per molecule of glycogen): - 2 molecules of ATP - 2 molecules of pyruvic acid ...
30 Synthesis of Glycosides, Lactose, Glycoproteins and Glycolipids
... derivatives of mannose. The reason for the large variety of sugars attached to proteins and lipids is that they have relatively specific and different functions, such as targeting a protein toward a membrane, providing recognition sites on the cell surface for other cells, hormones, or viruses, or a ...
... derivatives of mannose. The reason for the large variety of sugars attached to proteins and lipids is that they have relatively specific and different functions, such as targeting a protein toward a membrane, providing recognition sites on the cell surface for other cells, hormones, or viruses, or a ...
Energy systems. - CCVI
... ATP from glycogen and glucose anaerobic process (in the absence of oxygen) The products of glycolysis (per molecule of glycogen): - 2 molecules of ATP - 2 molecules of pyruvic acid ...
... ATP from glycogen and glucose anaerobic process (in the absence of oxygen) The products of glycolysis (per molecule of glycogen): - 2 molecules of ATP - 2 molecules of pyruvic acid ...
Medical Biochemistry Review #2 By
... • TCA cycle is regulated by the ratio of ADP, Pi/ ATP – Under resting conditions, with a high cell energy charge, the demand for new synthesis of ATP is limited and, although the Proton Motive Force is high, flow of protons back into the mitochondria through ATP synthetase is minimal. When energy de ...
... • TCA cycle is regulated by the ratio of ADP, Pi/ ATP – Under resting conditions, with a high cell energy charge, the demand for new synthesis of ATP is limited and, although the Proton Motive Force is high, flow of protons back into the mitochondria through ATP synthetase is minimal. When energy de ...
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
... Animals, some fungi pyruvate lactic acid 3C NADH ...
... Animals, some fungi pyruvate lactic acid 3C NADH ...
Respiration Respiration Respiration - Anoka
... Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis ...
... Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis ...
Fatigue and Its Causes
... • Possible causes – ACh synthesis and release – Altered ACh breakdown in synapse – Increase in muscle fiber stimulus threshold – Altered muscle resting membrane potential ...
... • Possible causes – ACh synthesis and release – Altered ACh breakdown in synapse – Increase in muscle fiber stimulus threshold – Altered muscle resting membrane potential ...
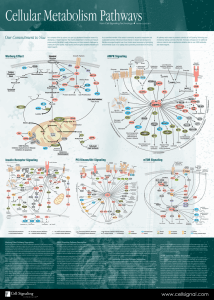
Cellular Metabolism Pathways
... Most cells use glucose as a fuel source. Glucose is metabolized by glycolysis in a multi-step set of reactions resulting in the creation of pyruvate. In typical cells, much of this pyruvate enters the mitochondria where it is oxidized by the Krebs Cycle to generate ATP to meet the cell’s energy dema ...
... Most cells use glucose as a fuel source. Glucose is metabolized by glycolysis in a multi-step set of reactions resulting in the creation of pyruvate. In typical cells, much of this pyruvate enters the mitochondria where it is oxidized by the Krebs Cycle to generate ATP to meet the cell’s energy dema ...
Fuel selection in human skeletal muscle in insulin resistance: a
... acid cycle operated under these conditions to inhibit glucose metabolism and contribute to hyperglycemia (2). Later, as the extent of insulin resistance in obese and type 2 diabetic patients was discerned, investigators took note of the association between insulin resistance and increased plasma non ...
... acid cycle operated under these conditions to inhibit glucose metabolism and contribute to hyperglycemia (2). Later, as the extent of insulin resistance in obese and type 2 diabetic patients was discerned, investigators took note of the association between insulin resistance and increased plasma non ...
THE LIVER AS AN ORGAN
... down glycogen and release glucose into the blood. If the glycogen stores are not used, excess glucose (which is not released into the blood) will eventually be converted to triglycerides (TGs) and transported to adipose tissue for storage (see the “ Lipids ” section) Gluconeogenesis: The liver (and ...
... down glycogen and release glucose into the blood. If the glycogen stores are not used, excess glucose (which is not released into the blood) will eventually be converted to triglycerides (TGs) and transported to adipose tissue for storage (see the “ Lipids ” section) Gluconeogenesis: The liver (and ...
Cellular Respiration
... Glycerol can be converted into glucose by gluconeogenesis or into DHAP Fatty Acids are transported to the matrix, undergo beta-oxidation (conversion into acetyl CoA...enters the Kreb cycle) ...
... Glycerol can be converted into glucose by gluconeogenesis or into DHAP Fatty Acids are transported to the matrix, undergo beta-oxidation (conversion into acetyl CoA...enters the Kreb cycle) ...
Cell respiration -2
... c)- The coenzyme-A (CoA) transform acetate compound into acetyle-CoA, which will be ready for Krebs Cycle for further oxidation. 2 NAD+ ...
... c)- The coenzyme-A (CoA) transform acetate compound into acetyle-CoA, which will be ready for Krebs Cycle for further oxidation. 2 NAD+ ...
Anaerobic Energy Systems - COLLYERS
... There are alternative available such as hypoxic tents and oxygen chambers. There is a limit to how much EPO the body can produce. ...
... There are alternative available such as hypoxic tents and oxygen chambers. There is a limit to how much EPO the body can produce. ...
Polyunsaturated fatty acids stimulate hepatic UCP
... central role in the maintenance of overall energy homeostasis, it is under tight regulation by both hormonal and metabolic factors. Although some of these regulatory pathways, such as the effects of glucagon on glucose handling, have been well characterized, many mechanisms of regulation have yet to ...
... central role in the maintenance of overall energy homeostasis, it is under tight regulation by both hormonal and metabolic factors. Although some of these regulatory pathways, such as the effects of glucagon on glucose handling, have been well characterized, many mechanisms of regulation have yet to ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Interface of Endocrine & Nervous Systems • Nervous system induces – nor- & epinephrine release • which stimulate ...
... Interface of Endocrine & Nervous Systems • Nervous system induces – nor- & epinephrine release • which stimulate ...
Lecture: 27 Fatty acid and triacyl glycerol biosynthesis Biosynthesis
... acyl carrier protein (ACP) whereas intermediates in fatty acid breakdown are bonded to coenzyme A. iii. The enzymes of fatty acid synthesis in animals are joined in a single polypeptide chain called fatty acid synthase. In contrast, the degradative enzymes do not seem to be associated. Plants employ ...
... acyl carrier protein (ACP) whereas intermediates in fatty acid breakdown are bonded to coenzyme A. iii. The enzymes of fatty acid synthesis in animals are joined in a single polypeptide chain called fatty acid synthase. In contrast, the degradative enzymes do not seem to be associated. Plants employ ...
Chapter 20 Specific Catabolic Pathways: Carbohydrate, Lipid, and
... • Globin is hydrolyzed to amino acids to be reused. • Iron is preserved in ferritin, an iron-carrying protein, and reused. • Heme is converted to bilirubin. • Bilirubin enters the liver via the bloodstream and is then transferred to the gallbladder where it is stored in the bile and finally excreted ...
... • Globin is hydrolyzed to amino acids to be reused. • Iron is preserved in ferritin, an iron-carrying protein, and reused. • Heme is converted to bilirubin. • Bilirubin enters the liver via the bloodstream and is then transferred to the gallbladder where it is stored in the bile and finally excreted ...
LFT- GIT
... 1- Check certain enzymes & proteins levels in blood that if are higher or lower than normal can indicate liver problems (diagnosis) 2- Screen for liver infections, such as hepatitis 3- Monitor the progression of a liver disease, such as viral or alcoholic hepatitis & determine how well a treatment i ...
... 1- Check certain enzymes & proteins levels in blood that if are higher or lower than normal can indicate liver problems (diagnosis) 2- Screen for liver infections, such as hepatitis 3- Monitor the progression of a liver disease, such as viral or alcoholic hepatitis & determine how well a treatment i ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 4. Next, the acetyl groups enter into the _____ cycle. They each created two molecules of CO2, one ATP, three NADH and one FADH2. Since there are two acetyl groups, the total yield is ___ molecules of CO2, ___ ATP, ___ NADH, and ___ FADH2. It’s named a cycle because the last step requires the Oxoa ...
... 4. Next, the acetyl groups enter into the _____ cycle. They each created two molecules of CO2, one ATP, three NADH and one FADH2. Since there are two acetyl groups, the total yield is ___ molecules of CO2, ___ ATP, ___ NADH, and ___ FADH2. It’s named a cycle because the last step requires the Oxoa ...
Phe
... dietary compliance even in individuals Symptom-free on strict metabolic i. Autistic-like behaviors Delayed ...
... dietary compliance even in individuals Symptom-free on strict metabolic i. Autistic-like behaviors Delayed ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.