3.8 Case study: 21 cm line in the interstellar medium
... the bound-free absorption may be presented as κbf R = (1 + x)zρ f (T ), where z is the abundance by mass of heavy elements (a few per cent for typical astrophysical plasmas). The widely used fit is (cf. (3.39)) ...
... the bound-free absorption may be presented as κbf R = (1 + x)zρ f (T ), where z is the abundance by mass of heavy elements (a few per cent for typical astrophysical plasmas). The widely used fit is (cf. (3.39)) ...
Atoms, elements and Compounds
... For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ ...
... For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ ...
Presentation 2.4
... John Dalton (1766-1844) developed an atomic theory that proposed that atoms were responsible for the combinations of elements found in compounds. ...
... John Dalton (1766-1844) developed an atomic theory that proposed that atoms were responsible for the combinations of elements found in compounds. ...
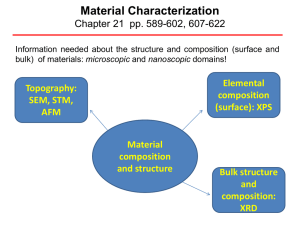
Learning material
... belong. This is our first clue. The illustration shows the emission of light from various elements spatially dispersed into a spectrum. 2. Our second clue is evidence that the positive charge in the atom is concentrated at its centre: most of the atom is empty space, which is itself a problem to whi ...
... belong. This is our first clue. The illustration shows the emission of light from various elements spatially dispersed into a spectrum. 2. Our second clue is evidence that the positive charge in the atom is concentrated at its centre: most of the atom is empty space, which is itself a problem to whi ...
AP Chemistry Summer Study Guide
... Neutron: Neutral particle. No charge. Mass = 1amu, Located in the nucleus Noble Gas: Group 18 on the PT. Each has 8 valence electrons. Nonreactive Orbital: Regions of probability where electrons are located. Each orbital can contain up to 2 electrons Oxidation Number: A charge assigned to an atom th ...
... Neutron: Neutral particle. No charge. Mass = 1amu, Located in the nucleus Noble Gas: Group 18 on the PT. Each has 8 valence electrons. Nonreactive Orbital: Regions of probability where electrons are located. Each orbital can contain up to 2 electrons Oxidation Number: A charge assigned to an atom th ...
Chemistry PowerPoint
... a. The total mass of the reactants is greater than the total mass of the products b. The total mass of the reactants is less than the total mass of the products c. The total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products d. Mass can be created and destroyed ...
... a. The total mass of the reactants is greater than the total mass of the products b. The total mass of the reactants is less than the total mass of the products c. The total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products d. Mass can be created and destroyed ...
Things to Know to Pass the Chemistry Regents
... *Tables T and B 69. Combined gas law on Table T *If given STP, given temp and pressure (Table A) 70. Pressure and volume indirect, P up, V down (PVC pipe) 71. Temperature and pressure direct, T up, P up 72. Temperature and volume direct, T up, V up 73. Gases most ideal at high temp and low pressure ...
... *Tables T and B 69. Combined gas law on Table T *If given STP, given temp and pressure (Table A) 70. Pressure and volume indirect, P up, V down (PVC pipe) 71. Temperature and pressure direct, T up, P up 72. Temperature and volume direct, T up, V up 73. Gases most ideal at high temp and low pressure ...
FALL Final Review KEY
... 31. Elements in the same GROUP (vertical column) have the same number of electrons in the outer energy level (valence electron) 32. (A) 1s2 2s2 2p6 Noble gas is the most stable and will have a general formula of ns2 np6 (where n=1, 2,3,4…7) 33. Check in your notes for the Electronegativity Trend Dia ...
... 31. Elements in the same GROUP (vertical column) have the same number of electrons in the outer energy level (valence electron) 32. (A) 1s2 2s2 2p6 Noble gas is the most stable and will have a general formula of ns2 np6 (where n=1, 2,3,4…7) 33. Check in your notes for the Electronegativity Trend Dia ...
Name - Red Hook Central Schools
... In actuality, the energy of a photon is never directly proportional to the energy of an ejected electron because the electron must overcome a potential energy barrier (due to a number of quantum and molecular factors). We call this barrier the work function, φ. The kinetic energy of an ejected photo ...
... In actuality, the energy of a photon is never directly proportional to the energy of an ejected electron because the electron must overcome a potential energy barrier (due to a number of quantum and molecular factors). We call this barrier the work function, φ. The kinetic energy of an ejected photo ...
chapter 1 - Revsworld
... Which of the following statements is/are correct? I. When heat energy flows from a system to the surroundings, we know that the temperature of the system is greater than that of the surroundings. II. Given the thermochemical equation 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) ------> 4 NO(g) + 6H2O(g) H = -906 kJ, the therm ...
... Which of the following statements is/are correct? I. When heat energy flows from a system to the surroundings, we know that the temperature of the system is greater than that of the surroundings. II. Given the thermochemical equation 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) ------> 4 NO(g) + 6H2O(g) H = -906 kJ, the therm ...
Chapter 12
... A molecule: is an aggregate of at least two atoms in a definite arrangement held together by chemical bonds.The atoms in a molecule may be of the same type of element, or they may be different. H2, H2O, NH3, CH4 A diatomic molecule contains only two atoms. H2, O2, N2, Cl2, F2, Br2, HCl, CO. A polyat ...
... A molecule: is an aggregate of at least two atoms in a definite arrangement held together by chemical bonds.The atoms in a molecule may be of the same type of element, or they may be different. H2, H2O, NH3, CH4 A diatomic molecule contains only two atoms. H2, O2, N2, Cl2, F2, Br2, HCl, CO. A polyat ...
Orbitals and Quantum Numbers
... describe the quantum numbers n, l, and ml used to define an orbital in an atom, and list the limitations placed on the values each may have. Assign quantum numbers to specific electrons in atoms ...
... describe the quantum numbers n, l, and ml used to define an orbital in an atom, and list the limitations placed on the values each may have. Assign quantum numbers to specific electrons in atoms ...
Silicon vs. Carbon - Coristines
... Carbon has varied hardness levels. It can vary from 0.5 mohs (graphite) to ...
... Carbon has varied hardness levels. It can vary from 0.5 mohs (graphite) to ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.