Elements
... ❖ It is a pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means. ...
... ❖ It is a pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means. ...
chapter
... and broken) that are very important in living organisms • When hydrogen combines with a relatively electronegative atom, it acquires a partial positive charge • Hydrogen bonds form between an atom with a partial negative charge and a hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded to oxygen or nitrogen ...
... and broken) that are very important in living organisms • When hydrogen combines with a relatively electronegative atom, it acquires a partial positive charge • Hydrogen bonds form between an atom with a partial negative charge and a hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded to oxygen or nitrogen ...
Click here to Ch 06.2 Covalent Bonding_Lewis Structures
... • Noble gas atoms are unreactive because their electron configurations are especially stable. • This stability results from the fact that the noble-gas atoms’ outer s and p orbitals are completely filled by a total of eight electrons. • Other atoms can fill their outermost s and p orbitals by sharin ...
... • Noble gas atoms are unreactive because their electron configurations are especially stable. • This stability results from the fact that the noble-gas atoms’ outer s and p orbitals are completely filled by a total of eight electrons. • Other atoms can fill their outermost s and p orbitals by sharin ...
1 - GENCHEM
... (a) The containers are well insulated and the oxygen gas cannot escape the containers. Thus this system is isolated system. (b) No work or heat is done. Thus the change in internal energy is zero. (c) No work or heat is done. Thus the change in enthalpy is zero. (d) If the volume of one container is ...
... (a) The containers are well insulated and the oxygen gas cannot escape the containers. Thus this system is isolated system. (b) No work or heat is done. Thus the change in internal energy is zero. (c) No work or heat is done. Thus the change in enthalpy is zero. (d) If the volume of one container is ...
Chapter One Outline
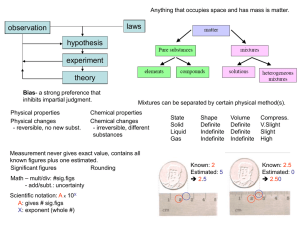
... composition of a substance. Examples include temperature, mass, density, etc. Density is the ratio of an objects mass to its volume; D = m/v Chemical Properties A substances chemical properties describe the kinds of chemical reactions the substance can undergo Chemical reactions are usually accompan ...
... composition of a substance. Examples include temperature, mass, density, etc. Density is the ratio of an objects mass to its volume; D = m/v Chemical Properties A substances chemical properties describe the kinds of chemical reactions the substance can undergo Chemical reactions are usually accompan ...
How electrons produce color
... • You will use the spectroscopes to see what photons are given off by the elements used in the flame test. • There will be some “background” light in your spectra. • Only focus on the bright lines! ...
... • You will use the spectroscopes to see what photons are given off by the elements used in the flame test. • There will be some “background” light in your spectra. • Only focus on the bright lines! ...
chapters 1-4
... Atom – smallest building block; molecule – combination of two or more atoms. Can be an element or compound. ...
... Atom – smallest building block; molecule – combination of two or more atoms. Can be an element or compound. ...
Chapter 27 Powerpoint
... It is physically impossible to measure simultaneously the exact position and the exact linear momentum of a particle Another form of the principle deals with energy and time: ...
... It is physically impossible to measure simultaneously the exact position and the exact linear momentum of a particle Another form of the principle deals with energy and time: ...
Practice exam - Dynamic Science
... Atoms from element “X” will take electrons. Atoms from element “X” will give up some of their electrons. Element “X” will react with other element to form a gas. Element “X” is a very stable substance an will not react with other elements. ...
... Atoms from element “X” will take electrons. Atoms from element “X” will give up some of their electrons. Element “X” will react with other element to form a gas. Element “X” is a very stable substance an will not react with other elements. ...
Electronics
... was in complete disagreement with other theories, and especially with the Maxwell theory of electromagnetism. Bohr formulated the postulate ad hoc. He didn't know what it might come from. But he was of the opinion that to properly understand the nature of the atom one has to accept his idea. The sec ...
... was in complete disagreement with other theories, and especially with the Maxwell theory of electromagnetism. Bohr formulated the postulate ad hoc. He didn't know what it might come from. But he was of the opinion that to properly understand the nature of the atom one has to accept his idea. The sec ...
Basis Sets - unix.eng.ua.edu
... 2. The HF wave functions may accurately describe other properties. Basis Sets: set of mathematical functions used to construct the wavefunction. • Each MO in HF theory is expressed as a linear combination of basis functions. • Full HF wavefunction is expressed as a Slater determinant formed from ind ...
... 2. The HF wave functions may accurately describe other properties. Basis Sets: set of mathematical functions used to construct the wavefunction. • Each MO in HF theory is expressed as a linear combination of basis functions. • Full HF wavefunction is expressed as a Slater determinant formed from ind ...
Study Guide For Final Exam
... • Conservation of Energy • Conservation of Momentum No mechanical experiment can tell the difference The notion of absolute motion in space is meaningless Say an event occurs in an inertial frame • Location and time of event described by (x,y,z,t) • Want to transform these coordinates to another fra ...
... • Conservation of Energy • Conservation of Momentum No mechanical experiment can tell the difference The notion of absolute motion in space is meaningless Say an event occurs in an inertial frame • Location and time of event described by (x,y,z,t) • Want to transform these coordinates to another fra ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.