7. Atoms
... The main reason for revisiting the quantum mechanics of hydrogen is to understand what becomes of this degeneracy. Before we proceed, it’s worth first thinking about where this degeneracy comes from. Usually in quantum mechanics, any degeneracy is related to a conservation law which, in turn, are re ...
... The main reason for revisiting the quantum mechanics of hydrogen is to understand what becomes of this degeneracy. Before we proceed, it’s worth first thinking about where this degeneracy comes from. Usually in quantum mechanics, any degeneracy is related to a conservation law which, in turn, are re ...
Unit 2 Review: Chemistry - Mr. Hoover's Science Classes
... Consists of two types of monoatomic ions (elements with only one possible ion charge) 1. The metal ion is always written first and retains its whole name 2. The non-metal is written second and has a slight change, the ending (suffix) is changed to –ide ...
... Consists of two types of monoatomic ions (elements with only one possible ion charge) 1. The metal ion is always written first and retains its whole name 2. The non-metal is written second and has a slight change, the ending (suffix) is changed to –ide ...
Chemistry Unit Notes Organizing the Periodic Table All the elements
... Mg3(PO4)2 : 3 atoms of Mg 1*2 = 2 atoms of P 4*2 = 8 atoms of O Ca4(SO4)3: 4 atoms of Ca 1*3 = 3 atoms of S 4*3 = 12 atoms of O 4. A coefficient is a number written in front of a chemical formula. The coefficient indicates the number of molecules of that compound. A coefficient multiplies the number ...
... Mg3(PO4)2 : 3 atoms of Mg 1*2 = 2 atoms of P 4*2 = 8 atoms of O Ca4(SO4)3: 4 atoms of Ca 1*3 = 3 atoms of S 4*3 = 12 atoms of O 4. A coefficient is a number written in front of a chemical formula. The coefficient indicates the number of molecules of that compound. A coefficient multiplies the number ...
ppt
... There is a particle in nature called a muon, which has the same charge as the electron but is 207 times heavier. A muon can form a hydrogen-like atom by binding to a proton. ...
... There is a particle in nature called a muon, which has the same charge as the electron but is 207 times heavier. A muon can form a hydrogen-like atom by binding to a proton. ...
Calculated Electron Dynamics in a Strong Electric Field V 77, N 20
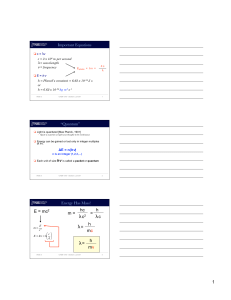
... to obtain the asymptotic flux by superposing the homogeneous functions (allowing comparison with experiment), but it is easier to obtain the wave function near the nucleus (r , 2000 a.u.) by superposing the inhomogeneous functions (allowing visualization of the dynamics). The homogeneous wave functi ...
... to obtain the asymptotic flux by superposing the homogeneous functions (allowing comparison with experiment), but it is easier to obtain the wave function near the nucleus (r , 2000 a.u.) by superposing the inhomogeneous functions (allowing visualization of the dynamics). The homogeneous wave functi ...
Final review free response ch 1-4
... 5. If you have 4 g NaOH, and 10 g HBr, what is the limiting reagent and how much salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
... 5. If you have 4 g NaOH, and 10 g HBr, what is the limiting reagent and how much salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
atom a very small particle that makes up most kinds of matters and
... two or more atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons in the nuclei (same number of protons) states that mass is neither created nor destroyed and as a result the mass of the substances before a physical or chemical change is equal to the mass of the substances present after ...
... two or more atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons in the nuclei (same number of protons) states that mass is neither created nor destroyed and as a result the mass of the substances before a physical or chemical change is equal to the mass of the substances present after ...
An experimental chemist`s guide to ab initio quantum chemistry
... described beautifully in the periodic table and the ability of early spectroscopists to fit atomic line spectra by simple mathematical formulas and to interpret atomic electronic states in terms of empirical quantum numbers provide compelling evidence that some relatively simple framework must exist ...
... described beautifully in the periodic table and the ability of early spectroscopists to fit atomic line spectra by simple mathematical formulas and to interpret atomic electronic states in terms of empirical quantum numbers provide compelling evidence that some relatively simple framework must exist ...
Lecture1
... Electron capture β+ decay cannot occur in isolation Proton rich nuclei may also transform themselves via capture of an electron from one of the atomic orbitals Accompanied by electron capture process ...
... Electron capture β+ decay cannot occur in isolation Proton rich nuclei may also transform themselves via capture of an electron from one of the atomic orbitals Accompanied by electron capture process ...
1. dia
... have different energies due to having different orientations of the magnetic dipoles in the external field, so the atomic energy levels are split into a larger number of levels and the spectral lines are also split. The rate of split is proportional to the applied magnetic field. The new lines appea ...
... have different energies due to having different orientations of the magnetic dipoles in the external field, so the atomic energy levels are split into a larger number of levels and the spectral lines are also split. The rate of split is proportional to the applied magnetic field. The new lines appea ...
0321813545_07_final
... Misconceptions and Pitfalls Electron interference patterns occur even when the electrons go through the double slits singly and cannot interact with each other. Students have a hard time visualizing what the wavelength of a particle means. Students are misled by the probabilistic nature of q ...
... Misconceptions and Pitfalls Electron interference patterns occur even when the electrons go through the double slits singly and cannot interact with each other. Students have a hard time visualizing what the wavelength of a particle means. Students are misled by the probabilistic nature of q ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.