Analysis of a Matter
... • (Pure) substance: a material which can not be separated by physical methods into 2 or more materials which have different characteristics. • Compounds: a material containing two or more elements or molecules. • Molecules: the smallest grouping which a substance can be divided into without forming ...
... • (Pure) substance: a material which can not be separated by physical methods into 2 or more materials which have different characteristics. • Compounds: a material containing two or more elements or molecules. • Molecules: the smallest grouping which a substance can be divided into without forming ...
Laser Molecular Spectroscopy CHE466 Fall 2007
... fact that a molecule contains more than one electron that is somehow shared at different extents by a set of nuclei. In addition, the interaction between electrons is difficult to represent. These problems translate in our inability to solve the Schrodinger equation exactly for a molecule. Furthermo ...
... fact that a molecule contains more than one electron that is somehow shared at different extents by a set of nuclei. In addition, the interaction between electrons is difficult to represent. These problems translate in our inability to solve the Schrodinger equation exactly for a molecule. Furthermo ...
Waves and Energy
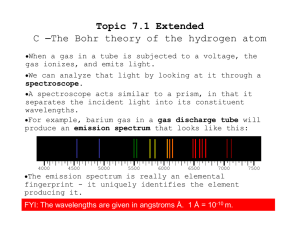
... Recall that atomic emission spectrum is discontinuous; that is, it is made of only certain frequencies of light. Why are element's atomic emission spectra discontinuous rather than continuous? In 1913, Niels Bohr, a young Danish physicist proposed a quantum model for the hydrogen atom that seemed to ...
... Recall that atomic emission spectrum is discontinuous; that is, it is made of only certain frequencies of light. Why are element's atomic emission spectra discontinuous rather than continuous? In 1913, Niels Bohr, a young Danish physicist proposed a quantum model for the hydrogen atom that seemed to ...
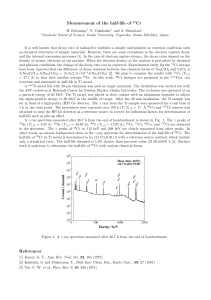
–1– 1. The Equation of State In an ideal gas at high T and low
... Degeneracy results from an application of quantum mechanical concepts to the state of a gas. The Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle requires ∆V ∆p3 > h3 , i.e. there is a minimum uncertainty for the product of the uncertainty in location (vector, 3 components, x y z) and of momentum (vector, 3 compo ...
... Degeneracy results from an application of quantum mechanical concepts to the state of a gas. The Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle requires ∆V ∆p3 > h3 , i.e. there is a minimum uncertainty for the product of the uncertainty in location (vector, 3 components, x y z) and of momentum (vector, 3 compo ...
Quantum Mechanics Unit Review AP Physics
... b) How many different emission lines can be produced by an electron jumping from the third energy level of a multi-electron atom to the 2nd energy level of an atom under normal conditions? There are 9 different orbitals in the 3rd energy level, with quantum numbers (n, l, ml): (3,0,0), (3,1,1), (3, ...
... b) How many different emission lines can be produced by an electron jumping from the third energy level of a multi-electron atom to the 2nd energy level of an atom under normal conditions? There are 9 different orbitals in the 3rd energy level, with quantum numbers (n, l, ml): (3,0,0), (3,1,1), (3, ...
The Wave
... electrical force In metals, the outermost electrons are not tightly bound If given energy electrons can be freed Classically, we increase the energy of an EM wave by increasing the intensity (e.g. brightness) Energy a A2 But this doesn’t work ?? ...
... electrical force In metals, the outermost electrons are not tightly bound If given energy electrons can be freed Classically, we increase the energy of an EM wave by increasing the intensity (e.g. brightness) Energy a A2 But this doesn’t work ?? ...
February Homework Packet
... location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? (1) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. (2) In the third shell, an electron has less energy and is ...
... location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? (1) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. (2) In the third shell, an electron has less energy and is ...
Few-body insights into the fractional quantum Hall effect
... hyperspherical approximation with the Laughlin method (1983 Phys. Rev. B first row) which does degenerate perturbation theory in all degrees of freedom ...
... hyperspherical approximation with the Laughlin method (1983 Phys. Rev. B first row) which does degenerate perturbation theory in all degrees of freedom ...
Introduction to elementary quantum mechanics
... equation (2) we find wave functions representing possible states of a given physical system. Therefore we obtain full information about the system. Solving the time-dependent Schrödinger equation we get information on the dynamics of a given system and we can foresee how it will behave in time. ...
... equation (2) we find wave functions representing possible states of a given physical system. Therefore we obtain full information about the system. Solving the time-dependent Schrödinger equation we get information on the dynamics of a given system and we can foresee how it will behave in time. ...
Molecular Geometry
... 1. Add up the total # of valence electrons for all the atoms. Account for charge: If the species has a negative (–) charge: add one valence electron for each negative charge; for a positively charged (+) species, subtract one electron for each positive charge. 2. Draw the molecular skeleton and conn ...
... 1. Add up the total # of valence electrons for all the atoms. Account for charge: If the species has a negative (–) charge: add one valence electron for each negative charge; for a positively charged (+) species, subtract one electron for each positive charge. 2. Draw the molecular skeleton and conn ...
PPT - University of Washington
... The two qubit rotation in L&D becomes a one qubit ‘x’ rotation for Levy! But |01>_p+|10>_p is not rotated… If the two QDs have different values of g, a magnetic field will cause a splitting between the up state of the first QD and the second. This allows ‘z’ rotations, and so together with the first ...
... The two qubit rotation in L&D becomes a one qubit ‘x’ rotation for Levy! But |01>_p+|10>_p is not rotated… If the two QDs have different values of g, a magnetic field will cause a splitting between the up state of the first QD and the second. This allows ‘z’ rotations, and so together with the first ...
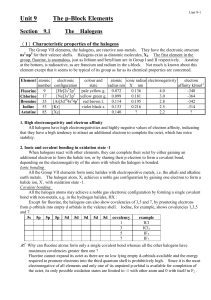
TEST on Atomic Structure
... Moving from left-to-right across a period (row) of the periodic table, 24) TRUE or FALSE - the ionization energy of the elements generally decreases 25) TRUE or FALSE - the atomic radius of the elements generally decreases NOTE: There are only 10 multiple choice questions on the test – MOST are SIM ...
... Moving from left-to-right across a period (row) of the periodic table, 24) TRUE or FALSE - the ionization energy of the elements generally decreases 25) TRUE or FALSE - the atomic radius of the elements generally decreases NOTE: There are only 10 multiple choice questions on the test – MOST are SIM ...
200 Ways to Pass the Chemistry
... 16. The Bohr Model of the atom placed electrons in “planet-like” orbits around the nucleus of an atom. 17. The current wave-mechanical model of the atom has electrons in “clouds” (orbitals) around the nucleus. 18. Electrons can be excited to jump to higher energy levels. They emit energy as light wh ...
... 16. The Bohr Model of the atom placed electrons in “planet-like” orbits around the nucleus of an atom. 17. The current wave-mechanical model of the atom has electrons in “clouds” (orbitals) around the nucleus. 18. Electrons can be excited to jump to higher energy levels. They emit energy as light wh ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...
epl draft Optical traps for electron produced by Pauli blocking
... Let us consider a semiconductor having one excess conduction-band electron with momentum k and spin s. At time t = 0, we irradiate the sample with a standingwave laser field having a circular polarization σ+ , momenta (+Q, −Q), and frequency ωP tuned far away from the exciton resonances. This makes ...
... Let us consider a semiconductor having one excess conduction-band electron with momentum k and spin s. At time t = 0, we irradiate the sample with a standingwave laser field having a circular polarization σ+ , momenta (+Q, −Q), and frequency ωP tuned far away from the exciton resonances. This makes ...
Document
... Valence Bond Theory: A quantum mechanical model which shows how electron pairs are shared in a covalent bond. ◦ Bond forms between two atoms when the following conditions are met: ◦ Covalent bonds are formed by overlap of atomic orbitals, each of which contains one electron of opposite spin. ◦ Each ...
... Valence Bond Theory: A quantum mechanical model which shows how electron pairs are shared in a covalent bond. ◦ Bond forms between two atoms when the following conditions are met: ◦ Covalent bonds are formed by overlap of atomic orbitals, each of which contains one electron of opposite spin. ◦ Each ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.