Glossary - WordPress.com
... The formula of a compound which shows the minimum ratio present between the atoms. Electron Affinity The amount of energy given out when an electron is absorbed in the outermost electronic shell of all isolated gaseous atom. Its units are KJ/mol. Electro-Negativity It is the power of an atom to attr ...
... The formula of a compound which shows the minimum ratio present between the atoms. Electron Affinity The amount of energy given out when an electron is absorbed in the outermost electronic shell of all isolated gaseous atom. Its units are KJ/mol. Electro-Negativity It is the power of an atom to attr ...
3 chemical foundations: elements, atoms and ions
... Z = the atomic number of the atom (the number of protons, also equalling the number of electrons in the free atom); and A = the mass number of the isotope. For each type of atom of an element, Sy and Z are always the same. The mass number, A, can vary depending on the number of neutrons present in t ...
... Z = the atomic number of the atom (the number of protons, also equalling the number of electrons in the free atom); and A = the mass number of the isotope. For each type of atom of an element, Sy and Z are always the same. The mass number, A, can vary depending on the number of neutrons present in t ...
7A SCIENCE FINAL REVIEW - MERRICK 7th SCIENCE REVIEW
... ___ Describe the difference between atoms and molecules. ___ Define elements, compounds, and mixtures. ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe th ...
... ___ Describe the difference between atoms and molecules. ___ Define elements, compounds, and mixtures. ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe th ...
Zumdahl Chapter
... First Year Chemistry Podcast DVD Featuring Jonathan Bergmann and Aaron Sams from Peak Educational Consulting LLC All Rights Reserved © This is an interactive page that allows you to get to all of the content on this DVD. Click to each unit packet or podcast. The podcasts require Quicktime and the pa ...
... First Year Chemistry Podcast DVD Featuring Jonathan Bergmann and Aaron Sams from Peak Educational Consulting LLC All Rights Reserved © This is an interactive page that allows you to get to all of the content on this DVD. Click to each unit packet or podcast. The podcasts require Quicktime and the pa ...
Doublet Fine Structure and the Spinning Electron
... From t he very earli est obser va ti ons of spectra l series it has been known t hat each member of certain genera l t y pes of series shows fine st ruc t ur e while t hose of others do not. Each member of some of t he series in the alkali metals, for example, is a close doublet (see F ig. 1.9), whe ...
... From t he very earli est obser va ti ons of spectra l series it has been known t hat each member of certain genera l t y pes of series shows fine st ruc t ur e while t hose of others do not. Each member of some of t he series in the alkali metals, for example, is a close doublet (see F ig. 1.9), whe ...
Study Guide for Exam 2_Sp12
... What is meant by valence electrons? What is ionization energy? What is the octet rule? What are ions? How do they relate to the octet rule? How is charge balance related to writing formulas of ionic compounds? Write dot formulas for atoms, and show how they interact with each other to form ionic com ...
... What is meant by valence electrons? What is ionization energy? What is the octet rule? What are ions? How do they relate to the octet rule? How is charge balance related to writing formulas of ionic compounds? Write dot formulas for atoms, and show how they interact with each other to form ionic com ...
Final Review Answers
... 1) Define the following terms: (Look up) a) valence electrons b) octet rule c) malleable d) ductile 2) Differentiate between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding in terms of electron location and types of atoms combined. Ionic - M/NM, e- donated; Covalent - NM, e- shared; Metallic - M, valence e- m ...
... 1) Define the following terms: (Look up) a) valence electrons b) octet rule c) malleable d) ductile 2) Differentiate between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding in terms of electron location and types of atoms combined. Ionic - M/NM, e- donated; Covalent - NM, e- shared; Metallic - M, valence e- m ...
the squared modulus of the wave function is the probability density
... The bad news, however, is that the procedure of solving the equation is extremely complicated. In a standard QM textbook it usually spans over about forty pages loaded with math. In order to clearly understand the solution procedure, one has to be familiar with elements of highly advanced calculus, ...
... The bad news, however, is that the procedure of solving the equation is extremely complicated. In a standard QM textbook it usually spans over about forty pages loaded with math. In order to clearly understand the solution procedure, one has to be familiar with elements of highly advanced calculus, ...
Name Date: __ ______ Chemistry Semester I Final Exam Review
... Unit 6 The Mole (Chapter 8) 59. What is Avogadro’s number? 60. How many things are in one mole? 61. What is the molar mass of MgCl2? 62. How many moles of SO3 are in 2.4 x 1024 molecules of SO3? ...
... Unit 6 The Mole (Chapter 8) 59. What is Avogadro’s number? 60. How many things are in one mole? 61. What is the molar mass of MgCl2? 62. How many moles of SO3 are in 2.4 x 1024 molecules of SO3? ...
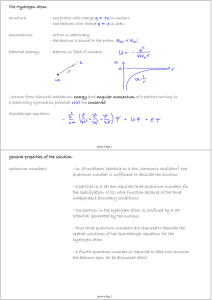
general properties of the solution: quantum numbers:
... - If L was aligned with the quantization axis the electron would be certain to move in the x-y plane. The uncertainty principle would require the momentum uncertainty Δpz to be infinite. Thus the electron could not be bound to the nucleus. - the uncertainty principle enforces that not all components ...
... - If L was aligned with the quantization axis the electron would be certain to move in the x-y plane. The uncertainty principle would require the momentum uncertainty Δpz to be infinite. Thus the electron could not be bound to the nucleus. - the uncertainty principle enforces that not all components ...
Objectives Chapter 4 Objectives, continued Chapter 4 Bohr Model of
... Objectives • Discuss Louis de Broglie’s role in the development of the quantum model of the atom. • Compare and contrast the Bohr model and the quantum model of the atom. • Explain how the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and the Schrödinger wave equation led to the idea of atomic orbitals. ...
... Objectives • Discuss Louis de Broglie’s role in the development of the quantum model of the atom. • Compare and contrast the Bohr model and the quantum model of the atom. • Explain how the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and the Schrödinger wave equation led to the idea of atomic orbitals. ...
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
... may be explained in terms of the formation of hybrid atomic orbitals Bonds - overlap of the hybrid atomic orbitals with the atoms. appropriate half-filled atomic orbital on the terminal ...
... may be explained in terms of the formation of hybrid atomic orbitals Bonds - overlap of the hybrid atomic orbitals with the atoms. appropriate half-filled atomic orbital on the terminal ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
... 1. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same ...
... 1. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same ...
Snc2d Chapter 5 Practice Test
... c) The period number of P shows: d) Show a Bohr diagram above of P forming an ion, indicating beside your diagram the number of electrons gained or lost. Include the symbol with net charge and the name of the ion formed. e) With regard to ion formation how are metals different from nonmetals? (Two d ...
... c) The period number of P shows: d) Show a Bohr diagram above of P forming an ion, indicating beside your diagram the number of electrons gained or lost. Include the symbol with net charge and the name of the ion formed. e) With regard to ion formation how are metals different from nonmetals? (Two d ...
03 Starlight and Atoms
... Spectra of stars are more complicated than pure black body spectra. They have characteristic lines, called absorption lines. ...
... Spectra of stars are more complicated than pure black body spectra. They have characteristic lines, called absorption lines. ...
Slide 1
... Output: simplified resulting formula in the LaTex format, ASCII output is also generated. ...
... Output: simplified resulting formula in the LaTex format, ASCII output is also generated. ...
Atoms, electrons and the periodic table
... Toward the end of that century, however, certain phenomena began to be noticed that seemed to be inconsistent with this dichotomy of particles and waves. This prompted further questions and further experiments which led eventually to the realization that classical physics while it appears to be “the ...
... Toward the end of that century, however, certain phenomena began to be noticed that seemed to be inconsistent with this dichotomy of particles and waves. This prompted further questions and further experiments which led eventually to the realization that classical physics while it appears to be “the ...
PES Topography - Materials Computation Center
... One CBF per occupied orbital on an atom E.g., H has one s function, C has 2s and 1p n-zeta n CBF per occupied orbital on an atom Valence n-zeta MBS for core (1s of C), n-zeta for valence Polarized Add higher angular momentum functions than MBS – e.g., d functions on C Diffuse or augmented Add much w ...
... One CBF per occupied orbital on an atom E.g., H has one s function, C has 2s and 1p n-zeta n CBF per occupied orbital on an atom Valence n-zeta MBS for core (1s of C), n-zeta for valence Polarized Add higher angular momentum functions than MBS – e.g., d functions on C Diffuse or augmented Add much w ...
Topological Insulators
... entangling many sorts of entities, typically identical atom or photon systems. But it has never been accomplished between an atomic system and a solid-state system such as a quantum dot in a semiconductor microcavity. Now two researchers have devised an experiment in which the quantum state of a sin ...
... entangling many sorts of entities, typically identical atom or photon systems. But it has never been accomplished between an atomic system and a solid-state system such as a quantum dot in a semiconductor microcavity. Now two researchers have devised an experiment in which the quantum state of a sin ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.