o Orbital dipole moments. Orbital precession. Spin-orbit interaction.
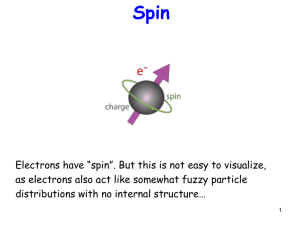
... o Conclusion of Stern-Gerlach experiment: o With field on, classically expect random distribution at target. In fact find two bands as beam is split in two. o There is directional quantisation, parallel or antiparallel to B. o Atomic magnetic moment has µz = ±µB. o Find same deflection for all ...
... o Conclusion of Stern-Gerlach experiment: o With field on, classically expect random distribution at target. In fact find two bands as beam is split in two. o There is directional quantisation, parallel or antiparallel to B. o Atomic magnetic moment has µz = ±µB. o Find same deflection for all ...
chemia simr01 en - Leszek Niedzicki
... accumulated in a small volume (not distributed on any neutrons); • In molecules in which hydrogen gives his electron away to atoms with strong affinity towards electrons (e.g. oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine) its electron (although formally shared) is ‘closer’ to the other atom; • Hydrogen is ‘looking’ f ...
... accumulated in a small volume (not distributed on any neutrons); • In molecules in which hydrogen gives his electron away to atoms with strong affinity towards electrons (e.g. oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine) its electron (although formally shared) is ‘closer’ to the other atom; • Hydrogen is ‘looking’ f ...
AtomicStructure
... destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. However, these changes CAN occur in nuclear reactions! Atoms of an element have a characteristic average mass which is unique to that element. Atoms of any one element differ in properties from atoms of another element ...
... destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. However, these changes CAN occur in nuclear reactions! Atoms of an element have a characteristic average mass which is unique to that element. Atoms of any one element differ in properties from atoms of another element ...
Chemistry XL-14A Nature of Light and the Atom
... Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions ...
... Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions ...
atoms and moles - Cherokee County Schools
... could turn the paddle wheel). b) Louis de Broglie also demonstrated by using Bohr’s model, that electrons have characteristics like waves because, when confined in space, light can have only discrete wavelengths. c) The present Quantum Model of the atom takes into consideration both the particle and ...
... could turn the paddle wheel). b) Louis de Broglie also demonstrated by using Bohr’s model, that electrons have characteristics like waves because, when confined in space, light can have only discrete wavelengths. c) The present Quantum Model of the atom takes into consideration both the particle and ...
Energy Sublevels
... In 1926 Werner Heisenberg began his job as Assistant to Niels Bohr in Copenhagen. Later that year Schrodinger came To debate the two alternative theories with Bohr. Neither model was satisfactory but Schrodinger showed the equivalence of the matrix and wave versions of Quantum ...
... In 1926 Werner Heisenberg began his job as Assistant to Niels Bohr in Copenhagen. Later that year Schrodinger came To debate the two alternative theories with Bohr. Neither model was satisfactory but Schrodinger showed the equivalence of the matrix and wave versions of Quantum ...
Class 22
... Which slit did this photon go through? If one slit: Get single slit pattern (i.e. no interference) Like this: or this: The sum of the two: But not like this: But: that photon is part of the two slit interference pattern. The probability pattern of where it lands is described by the 2 slit interfere ...
... Which slit did this photon go through? If one slit: Get single slit pattern (i.e. no interference) Like this: or this: The sum of the two: But not like this: But: that photon is part of the two slit interference pattern. The probability pattern of where it lands is described by the 2 slit interfere ...
Solution - faculty.ucmerced.edu
... Let’s start by looking at the momentum. Since the cheese isn’t moving, initially, the initial momentum is just that of the pellet, pi = ppellet . If the mass of the pellet is m, and it has an initial velocity v, then pi = mv. After the collision, the pellet is stuck in the cheese. If the cheese has ...
... Let’s start by looking at the momentum. Since the cheese isn’t moving, initially, the initial momentum is just that of the pellet, pi = ppellet . If the mass of the pellet is m, and it has an initial velocity v, then pi = mv. After the collision, the pellet is stuck in the cheese. If the cheese has ...
Solution - IISER Bhopal
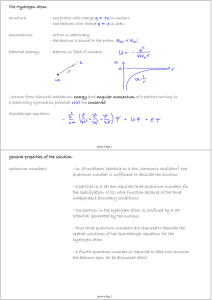
... units. Ignore spin. Describe your variables and discuss essential symmetries of this Hamiltonian [max 6 lines]. (b) (2 points) Ignoring spin of the two electrons and ignoring electron-electron (e-e) interactions, how can you write appropriate eigenfunctions and eigenenergies of the Hamiltonian found ...
... units. Ignore spin. Describe your variables and discuss essential symmetries of this Hamiltonian [max 6 lines]. (b) (2 points) Ignoring spin of the two electrons and ignoring electron-electron (e-e) interactions, how can you write appropriate eigenfunctions and eigenenergies of the Hamiltonian found ...
Document
... For example, in a given atom they cannot have the same set of quantum numbers n, l, ml, ms. This means that each atomic orbital (n,l,ml) can hold 2 electrons: ms = ±½. Important consequence: • Electrons do not pile up in the lowest energy state. It’s more like filling a bucket with water. • They are ...
... For example, in a given atom they cannot have the same set of quantum numbers n, l, ml, ms. This means that each atomic orbital (n,l,ml) can hold 2 electrons: ms = ±½. Important consequence: • Electrons do not pile up in the lowest energy state. It’s more like filling a bucket with water. • They are ...
Introduction
... UV photons of 147, 150, and 173 nm are transported to the phosphor with less radiation trapping because of a short traveling distance. The ion bombardment on the phosphor is related to the lifetime and color purity of PDP. Although ions are mainly created in the ditched region, the ion bombardment o ...
... UV photons of 147, 150, and 173 nm are transported to the phosphor with less radiation trapping because of a short traveling distance. The ion bombardment on the phosphor is related to the lifetime and color purity of PDP. Although ions are mainly created in the ditched region, the ion bombardment o ...
Basic Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation
... second summand being inversely proportional to the distance R and depending on the charge acceleration, characterizes the radiation wave field (‘‘acceleration field’’) [1]. The range of the distances R, where the contribution of the first summand is negligible in comparison with the contribution of ...
... second summand being inversely proportional to the distance R and depending on the charge acceleration, characterizes the radiation wave field (‘‘acceleration field’’) [1]. The range of the distances R, where the contribution of the first summand is negligible in comparison with the contribution of ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.