Particle Tracing Minicourse
... subnodes can be added to Wall and Outlet features. Secondary particles are released when particles hit the boundaries. Multiple species of secondary particle can be released at once. Secondary emission can be based on a probability or a logical expression. ...
... subnodes can be added to Wall and Outlet features. Secondary particles are released when particles hit the boundaries. Multiple species of secondary particle can be released at once. Secondary emission can be based on a probability or a logical expression. ...
Topic 15
... Since this is a “thought experiment” we are free from any practical constraints, and we can locate the particle as precisely as we like by using radiation of shorter and shorter wavelengths. ...
... Since this is a “thought experiment” we are free from any practical constraints, and we can locate the particle as precisely as we like by using radiation of shorter and shorter wavelengths. ...
1 ψ ω ω ω ψ ψ ψ
... for 0 ≤ x ≤ L and zero otherwise. (a) Determine the expectation value of x. (b) Determine the probability of finding the particle near L/2, by calculating the probability that the particle lies in the range 0.490L ≤ x ≤ 0.510L. (c) What If? Determine the probability of finding the particle near L/4, ...
... for 0 ≤ x ≤ L and zero otherwise. (a) Determine the expectation value of x. (b) Determine the probability of finding the particle near L/2, by calculating the probability that the particle lies in the range 0.490L ≤ x ≤ 0.510L. (c) What If? Determine the probability of finding the particle near L/4, ...
subatomic structure
... Neutrons Neutrons are uncharged particles found in the atomic nucleus. They have a mass of 1 amu ...
... Neutrons Neutrons are uncharged particles found in the atomic nucleus. They have a mass of 1 amu ...
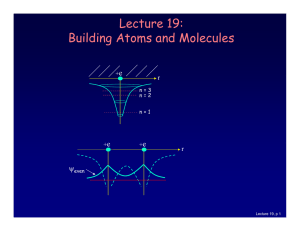
lecture 17
... the Schrodinger equation and solving for the energy. •We know that the particle’s position cannot be determined precisely, but that the probability of a particle being found at a particular point can be calculated from the wave-function. •Okay, we can’t calculate the position (or other position depe ...
... the Schrodinger equation and solving for the energy. •We know that the particle’s position cannot be determined precisely, but that the probability of a particle being found at a particular point can be calculated from the wave-function. •Okay, we can’t calculate the position (or other position depe ...
slides
... prevent its electrons from being squeezed into a smaller space • Neutron degeneracy pressure is what supports neutron stars against gravity—quantum laws prevent its neutrons from being squeezed into a smaller space ...
... prevent its electrons from being squeezed into a smaller space • Neutron degeneracy pressure is what supports neutron stars against gravity—quantum laws prevent its neutrons from being squeezed into a smaller space ...
Physically Based Modeling
... a finite amount – Another use: angular springs on polygon corners to prevent self-penetration – Numerical integration for animation ...
... a finite amount – Another use: angular springs on polygon corners to prevent self-penetration – Numerical integration for animation ...
here - University of Kent
... In the figure above we display how the energy of various types of Skyrmions is distributed in space. Each Skyrmion can be labelled by an integer B. The number B cannot be changed by deforming the Skyrmion. B is identified with the mass number (the total number of protons and neutrons in an ...
... In the figure above we display how the energy of various types of Skyrmions is distributed in space. Each Skyrmion can be labelled by an integer B. The number B cannot be changed by deforming the Skyrmion. B is identified with the mass number (the total number of protons and neutrons in an ...
Aalborg Universitet CERN Experiment and Violation of Newton’s Second Law
... Where n1 and n 2 are integers. With increasing in a photon’s energy (as in gravitational blue shift), its frequency also increases. Thus there should be a logical explanation between energy increases and frequency increases. Therefore, based on SQE definition and relation (2) could relate the relati ...
... Where n1 and n 2 are integers. With increasing in a photon’s energy (as in gravitational blue shift), its frequency also increases. Thus there should be a logical explanation between energy increases and frequency increases. Therefore, based on SQE definition and relation (2) could relate the relati ...
Chem 1a Review
... A: Ionization energies are very high at the noble gases because they have the highest number of protons (positive charge) for that quantum number n. B: Exception to general trend of increase Iz with increase Z. Due to going from filling 1s shell to 1p shell and since p penetrates less well then s it ...
... A: Ionization energies are very high at the noble gases because they have the highest number of protons (positive charge) for that quantum number n. B: Exception to general trend of increase Iz with increase Z. Due to going from filling 1s shell to 1p shell and since p penetrates less well then s it ...
Phys 518 Homework Set I, Jan
... Phys 518 Homework Set I, Jan., 18, 2006 (Due Feb., 1, 2006) Prob. 1 1) The BCS wavefunction usually involves states with different numbers of particles. Given the coherence factor (u,v) for each k, calculate explicitly the average number of particles and fluctuations for a given chemical potential. ...
... Phys 518 Homework Set I, Jan., 18, 2006 (Due Feb., 1, 2006) Prob. 1 1) The BCS wavefunction usually involves states with different numbers of particles. Given the coherence factor (u,v) for each k, calculate explicitly the average number of particles and fluctuations for a given chemical potential. ...
Test #1 solutions
... particle anywhere on the ring. This is a manifestation of its wavelike nature. If we measure its location it will collapse to a single value (as in part d) but we can’t predict which value we will obtain. This is a manifestation of the inherent uncertainty in quantum mechanics, and the interpretati ...
... particle anywhere on the ring. This is a manifestation of its wavelike nature. If we measure its location it will collapse to a single value (as in part d) but we can’t predict which value we will obtain. This is a manifestation of the inherent uncertainty in quantum mechanics, and the interpretati ...
chapter 14 - UniMAP Portal
... When the particle is attach to a spring, then the force Fs exerted on the particle is opposite to that exerted on the spring. The force will do negative work on the particle when the particle is moving so as a further elongate ( or compress ) the spring. U1-2 = - ( 1 ks22 1 ks12 ). ...
... When the particle is attach to a spring, then the force Fs exerted on the particle is opposite to that exerted on the spring. The force will do negative work on the particle when the particle is moving so as a further elongate ( or compress ) the spring. U1-2 = - ( 1 ks22 1 ks12 ). ...
chapter1-answers - Westmount High School
... a) The cathode rays cause a small propeller inside the tube to turn. The rays are made up of particles of matter. b) The rays are identical regardless of the metal used to make the cathode. The rays are common to all elements. c) The cathode rays are attracted to the positive pole of an electrical f ...
... a) The cathode rays cause a small propeller inside the tube to turn. The rays are made up of particles of matter. b) The rays are identical regardless of the metal used to make the cathode. The rays are common to all elements. c) The cathode rays are attracted to the positive pole of an electrical f ...
Changing State Level Ladder File
... Draw particle arrangements accurately using diagrams. Describe some differences between particle arrangement of each state. Explain why the ice cube melts and evaporates. Use most of the key words accurately. ...
... Draw particle arrangements accurately using diagrams. Describe some differences between particle arrangement of each state. Explain why the ice cube melts and evaporates. Use most of the key words accurately. ...
Unit 2: Atom - newshamchemistry
... What original statements of Dalton’s Atomic Theory are no longer valid? ( star them in your notes) Atom & its two main regions Joseph Thomson a. Plum pudding model/ seeds in a watermelon b. electron Robert Millikan a. electron What two inferences were made about the atomic structure at the end of th ...
... What original statements of Dalton’s Atomic Theory are no longer valid? ( star them in your notes) Atom & its two main regions Joseph Thomson a. Plum pudding model/ seeds in a watermelon b. electron Robert Millikan a. electron What two inferences were made about the atomic structure at the end of th ...
Lecture 20 The Redox Sequence
... Ox1 + Red2 = Red1 + Ox2 In this case Red2 is the electron donor, passing electrons to Ox1 which is the electron acceptor. Thus Red2 is oxidized to Ox2 and Ox1 is reduced to Red1. The equilibrium constant for an oxidation-reduction reaction can be determined by combining the constants from Table 1 as ...
... Ox1 + Red2 = Red1 + Ox2 In this case Red2 is the electron donor, passing electrons to Ox1 which is the electron acceptor. Thus Red2 is oxidized to Ox2 and Ox1 is reduced to Red1. The equilibrium constant for an oxidation-reduction reaction can be determined by combining the constants from Table 1 as ...
atomic physics
... 1. Electrons in atoms orbit the nucleus. 2. The electrons can only orbit stably, without radiating, in certain orbits (called the "stationary orbits”) at a certain discrete set of distances from the nucleus. These orbits are associated with definite energies and are also called energy shells or ener ...
... 1. Electrons in atoms orbit the nucleus. 2. The electrons can only orbit stably, without radiating, in certain orbits (called the "stationary orbits”) at a certain discrete set of distances from the nucleus. These orbits are associated with definite energies and are also called energy shells or ener ...
Photoelectric Effect and Einstein`s hypothesis
... A potential slightly more positive than –VS will not be able to repel all electrons and a small current will be measured. As the applied voltage increases in a positive sense the current will increase until most of the electrons will be collected and the current will be at a maximum. If the light in ...
... A potential slightly more positive than –VS will not be able to repel all electrons and a small current will be measured. As the applied voltage increases in a positive sense the current will increase until most of the electrons will be collected and the current will be at a maximum. If the light in ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.