Energy, Heat, and Work* Oh My*
... Determine your wavelength if you are walking at a pace of 2.68 m/s. (1 kg = 2.20 lb) ...
... Determine your wavelength if you are walking at a pace of 2.68 m/s. (1 kg = 2.20 lb) ...
Outline of section 4
... In general we get an uncertainty relation for any two incompatible observables, i.e. whose corresponding operators do not commute ...
... In general we get an uncertainty relation for any two incompatible observables, i.e. whose corresponding operators do not commute ...
Algebra 2
... Find the value of the discriminant “D”, and then tell how many solutions equation has and what type of solutions (rational, irrational, or imaginary) 13. 2x2 – 8x + 9 = 0 ...
... Find the value of the discriminant “D”, and then tell how many solutions equation has and what type of solutions (rational, irrational, or imaginary) 13. 2x2 – 8x + 9 = 0 ...
Section 11.1 Assessment How many mole ratios can be written for
... equation, how many of each (formula units, molecules and/or atoms)? Moles: from the balanced equation, how many of each? Mass: from the balanced equation, convert known mole quantities to mass of products total & compare to mass of reactants total, should be equal. ...
... equation, how many of each (formula units, molecules and/or atoms)? Moles: from the balanced equation, how many of each? Mass: from the balanced equation, convert known mole quantities to mass of products total & compare to mass of reactants total, should be equal. ...
The Spin-Statistics Relation and Noncommutative Quantum
... Hamiltonian, essentially setting a lower limit on the binding energy of an atom HN ≥ CN. Lieb and Thirring further advanced this model in [6, 9] by using Thomas-Fermi theory to find a realistic value for the constant C. The important requirement is that an assembly of N electrons has a binding energ ...
... Hamiltonian, essentially setting a lower limit on the binding energy of an atom HN ≥ CN. Lieb and Thirring further advanced this model in [6, 9] by using Thomas-Fermi theory to find a realistic value for the constant C. The important requirement is that an assembly of N electrons has a binding energ ...
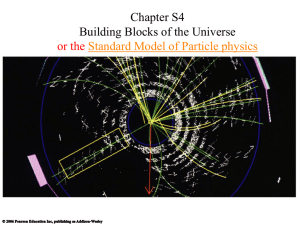
chapterS4BuildingBlo..
... • Smashing together high-energy particles produces showers of new particles ...
... • Smashing together high-energy particles produces showers of new particles ...
Just enough on Dirac Notation
... rather like the difference between a physical vector (eg the velocity of a particle) and the list of its components in a particular basis. The latter is a particular representation of the former, and so it is with quantum states and wavefunctions. To see the connection more rigorously, consider a ra ...
... rather like the difference between a physical vector (eg the velocity of a particle) and the list of its components in a particular basis. The latter is a particular representation of the former, and so it is with quantum states and wavefunctions. To see the connection more rigorously, consider a ra ...
Statistical Mechanics
... Here we deal with ideal particles whose wave functions overlap. We introduce quantum physics because of this overlap. Remember: ...
... Here we deal with ideal particles whose wave functions overlap. We introduce quantum physics because of this overlap. Remember: ...
moodle unit 2
... A positively charge sub atomic particle. proton A negatively charged sub atomic particle. electron An uncharged sub atomic particle. neutron The central part of an atom which contains one or more protons and perhaps some neutrons as well. nucleus 5. A proton or neutron. nucleon 6. A classical closed ...
... A positively charge sub atomic particle. proton A negatively charged sub atomic particle. electron An uncharged sub atomic particle. neutron The central part of an atom which contains one or more protons and perhaps some neutrons as well. nucleus 5. A proton or neutron. nucleon 6. A classical closed ...