DeBroglie Hypothesis
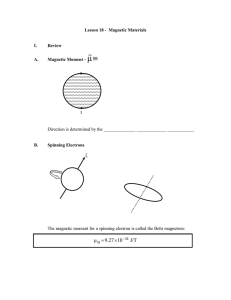
... The fourth quantum number, ms, does not have a classical explanation - it is a relativistic quantum phenomenon. It is related to magnetic behavior, and hence has the m name. The closest thing classically we can relate it to is to the case of the electron “spinning”, so that its spinning charge creat ...
... The fourth quantum number, ms, does not have a classical explanation - it is a relativistic quantum phenomenon. It is related to magnetic behavior, and hence has the m name. The closest thing classically we can relate it to is to the case of the electron “spinning”, so that its spinning charge creat ...
PHYS2042 Quantum Mechanics (Part II)
... the special property that the energy levels are equally spaced by ∆E = h̄ω. This result is different from a particle in a box, where the energy levels get increasingly further apart. Also note that the wave functions, like those of the finite potential well, extend well beyond the turning points int ...
... the special property that the energy levels are equally spaced by ∆E = h̄ω. This result is different from a particle in a box, where the energy levels get increasingly further apart. Also note that the wave functions, like those of the finite potential well, extend well beyond the turning points int ...
Density Matrix
... in which case ρ = |ψ >< ψ| if the state vector is normalized to unity. In summary, by the term “state of a system” we will understand as a state of a micro or macroscopic system defined by its complete density matrix. With that understanding, not all states are characterized by a state vector. Only ...
... in which case ρ = |ψ >< ψ| if the state vector is normalized to unity. In summary, by the term “state of a system” we will understand as a state of a micro or macroscopic system defined by its complete density matrix. With that understanding, not all states are characterized by a state vector. Only ...
Document
... • Knowing that light has a particle nature, it seems reasonable to ask if matter has a wave nature. • Using Einstein’s and Planck’s equations, de Broglie h showed: l mv • The momentum, mv, is a particle property, whereas l is a wave property. • de Broglie summarized the concepts of waves and partic ...
... • Knowing that light has a particle nature, it seems reasonable to ask if matter has a wave nature. • Using Einstein’s and Planck’s equations, de Broglie h showed: l mv • The momentum, mv, is a particle property, whereas l is a wave property. • de Broglie summarized the concepts of waves and partic ...
ppt
... and B) don't commute leads to a problem. A and B represent momentum and position respectively (uncertainty principle) this means knowing the momentum of the particle means its coordinate has no physical reality. ...
... and B) don't commute leads to a problem. A and B represent momentum and position respectively (uncertainty principle) this means knowing the momentum of the particle means its coordinate has no physical reality. ...
Quantum Spin Hall Effect
... g being the magnitude of the strain gradient C3/h is 8×105 m/S for GaAs by experiment For a gap of 1 mK, we hence need a strain gradient or 1% over 60 μm. ...
... g being the magnitude of the strain gradient C3/h is 8×105 m/S for GaAs by experiment For a gap of 1 mK, we hence need a strain gradient or 1% over 60 μm. ...
Problem Set 8 8.1 Chemical Equilibrium 8.2 Partial Pressure 8.3
... (a) Calculate the “canonical partition function” Zn (T ) for a harmonic oscillator with n oscillation quanta. (b) Calculate the “grand canonical partition function” Ξ(T, µ), where µ is the “chemical potential” for the oscillation quanta. [You’ll fix the value of µ in part (d) below.] (c) Use your an ...
... (a) Calculate the “canonical partition function” Zn (T ) for a harmonic oscillator with n oscillation quanta. (b) Calculate the “grand canonical partition function” Ξ(T, µ), where µ is the “chemical potential” for the oscillation quanta. [You’ll fix the value of µ in part (d) below.] (c) Use your an ...
Lecture 8 Relevant sections in text: §1.6 Momentum
... So, moving the system to the right by an amount a shifts the argument of the wave function to the left. To see that this makes sense, consider for example a particle with a Gaussian wave function (exercise). The unitarity of Ta is expressed in the position wave function representation via (exercise) ...
... So, moving the system to the right by an amount a shifts the argument of the wave function to the left. To see that this makes sense, consider for example a particle with a Gaussian wave function (exercise). The unitarity of Ta is expressed in the position wave function representation via (exercise) ...
ESR Theory - Personal WWW Pages
... used for about the last 50 years to study species which contain unpaired electrons (paramagnetic). Such species can include organic and main group radicals and transition metal compounds with unpaired electrons. ESR can be thought of as broadly complementary to NMR spectroscopy in that ESR deals wit ...
... used for about the last 50 years to study species which contain unpaired electrons (paramagnetic). Such species can include organic and main group radicals and transition metal compounds with unpaired electrons. ESR can be thought of as broadly complementary to NMR spectroscopy in that ESR deals wit ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
... which emits electrons, a nearby positive anode attracts these electrons which pass through a hole in the anode to form a beam. This is called Thermionic emission. The potential difference between the anode and cathode controls the speed of the electrons. ...
... which emits electrons, a nearby positive anode attracts these electrons which pass through a hole in the anode to form a beam. This is called Thermionic emission. The potential difference between the anode and cathode controls the speed of the electrons. ...