Comparison of the Bohr and Quantum Mechanical
... To satisfy the Pauli Exclusion Principle that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers, a fourth quantum number, the spin quantum number (ms), was added. 2. In the Bohr model, the energy of the electron is described in terms of a definite orbit of definite energy. In the quantum m ...
... To satisfy the Pauli Exclusion Principle that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers, a fourth quantum number, the spin quantum number (ms), was added. 2. In the Bohr model, the energy of the electron is described in terms of a definite orbit of definite energy. In the quantum m ...
Electron Configuration Notes File
... Pauli Exclusion Principle No two electrons in an atom can have the same 4 quantum numbers. Each e- has a unique “address”: 1. Principal # 2. Ang. Mom. # 3. Magnetic # 4. Spin # ...
... Pauli Exclusion Principle No two electrons in an atom can have the same 4 quantum numbers. Each e- has a unique “address”: 1. Principal # 2. Ang. Mom. # 3. Magnetic # 4. Spin # ...
Electrons
... determine the charge-to-mass ratio e is charge on electron in Coulombs, (C) and m is its mass. The interaction between charged objects is a noncontact force that acts over some distance of separation. Charge, charge and distance e/m =-1.76 x 108 C/g e is charge on electron in Coulombs, (C) and ...
... determine the charge-to-mass ratio e is charge on electron in Coulombs, (C) and m is its mass. The interaction between charged objects is a noncontact force that acts over some distance of separation. Charge, charge and distance e/m =-1.76 x 108 C/g e is charge on electron in Coulombs, (C) and ...
Lecture 1 - UW Canvas
... In 1927, C. J. Davisson and L. H. Germer first observed the diffraction of electron waves using electrons scattered from a ...
... In 1927, C. J. Davisson and L. H. Germer first observed the diffraction of electron waves using electrons scattered from a ...
Chapter 4 - Rothschild Science
... energy and because of this cannot lose energy and fall into the nucleus Energy Level of an electron is the region around the nucleus where the electron is likely to be moving ...
... energy and because of this cannot lose energy and fall into the nucleus Energy Level of an electron is the region around the nucleus where the electron is likely to be moving ...
ch28_lecture
... In an analysis relating Bohr's theory to the de Broglie wavelength of electrons, when an electron moves from the n = 1 level to the n = 3 level, the circumference of its orbit becomes 9 times greater. This occurs because (a) there are 3 times as many wavelengths in the new orbit, (b) there are 3 tim ...
... In an analysis relating Bohr's theory to the de Broglie wavelength of electrons, when an electron moves from the n = 1 level to the n = 3 level, the circumference of its orbit becomes 9 times greater. This occurs because (a) there are 3 times as many wavelengths in the new orbit, (b) there are 3 tim ...
Chapter 28
... In an analysis relating Bohr's theory to the de Broglie wavelength of electrons, when an electron moves from the n = 1 level to the n = 3 level, the circumference of its orbit becomes 9 times greater. This occurs because (a) there are 3 times as many wavelengths in the new orbit, (b) there are 3 tim ...
... In an analysis relating Bohr's theory to the de Broglie wavelength of electrons, when an electron moves from the n = 1 level to the n = 3 level, the circumference of its orbit becomes 9 times greater. This occurs because (a) there are 3 times as many wavelengths in the new orbit, (b) there are 3 tim ...
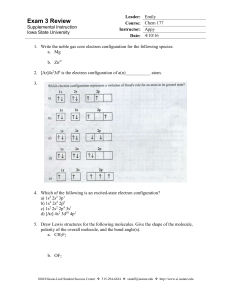
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... 9. Which has the largest 2nd Ionization energy between K and Ca? a. K b. Ca c. Both K and Ca have the same second Ionization energy d. It’s impossible to tell 10. In terms of electronegativity, determine whether the following compounds contain nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic bonds. a. I— ...
... 9. Which has the largest 2nd Ionization energy between K and Ca? a. K b. Ca c. Both K and Ca have the same second Ionization energy d. It’s impossible to tell 10. In terms of electronegativity, determine whether the following compounds contain nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic bonds. a. I— ...
Ph.D Projects – New Quantum Phenomena in Semiconductor
... (quantum dot), systems are of importance and there will be a number of Ph.D projects aimed at investigations using these unique structures. It is intended to form integrated quantum circuits which combine different quantum effects for new functions, this follows the philosophy that “complexity bring ...
... (quantum dot), systems are of importance and there will be a number of Ph.D projects aimed at investigations using these unique structures. It is intended to form integrated quantum circuits which combine different quantum effects for new functions, this follows the philosophy that “complexity bring ...
SOME ELEMENTS OF ATOMIC STRUCTURE THEORY
... orbital angular momenta of the individual electrons into a total orbital angular momentum L = l1 + l2 + · · ·, and also combining all the spin angular momenta of the individual electrons into a total spin angular momentum S = s1 + s2 + · · ·. Only after that are these two added together to get the ...
... orbital angular momenta of the individual electrons into a total orbital angular momentum L = l1 + l2 + · · ·, and also combining all the spin angular momenta of the individual electrons into a total spin angular momentum S = s1 + s2 + · · ·. Only after that are these two added together to get the ...
Fine Structure of the Spectral Lines of Hydrogen - Labs
... Where, + is the total or principal quantum number, which is an integer and positive. We can look at the principal quantum number for an atom free from externally applied fields as being a generalized angular momentum composed of multiple components, including one due to the linear momentum parallel ...
... Where, + is the total or principal quantum number, which is an integer and positive. We can look at the principal quantum number for an atom free from externally applied fields as being a generalized angular momentum composed of multiple components, including one due to the linear momentum parallel ...
CHEM 347 Quantum Chemistry
... Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom The classical mechanical picture of an electron and proton cannot explain the discrete emission spectra of the hydrogen atom. Bohr (1913) comes close with the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom. Bohr assumed that the angular momentum of the electron in hydrogen is quant ...
... Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom The classical mechanical picture of an electron and proton cannot explain the discrete emission spectra of the hydrogen atom. Bohr (1913) comes close with the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom. Bohr assumed that the angular momentum of the electron in hydrogen is quant ...
Trends in the periodic table - Brigham Young University
... • Shielding effect of core electrons (S) • Nuclear effective charge, Zeff • Zeff = Z – S – What is Z? What is S? ...
... • Shielding effect of core electrons (S) • Nuclear effective charge, Zeff • Zeff = Z – S – What is Z? What is S? ...
AtomsFirst2e_day6_sec3.7
... values for each of the 4 quantum numbers •Be able to describe an experiment that could be used to show that half of the electrons in an atom have a spin = ½ and the other half have a spin = -½. •Be able to draw a figure that shows the shape and location of nodes in any orbital in the 1st, 2nd, or 3r ...
... values for each of the 4 quantum numbers •Be able to describe an experiment that could be used to show that half of the electrons in an atom have a spin = ½ and the other half have a spin = -½. •Be able to draw a figure that shows the shape and location of nodes in any orbital in the 1st, 2nd, or 3r ...
Advances in Atomic Theory
... of ___________ but the number of _____________ may vary. Isotopes - Atoms of the ________ element that have different numbers of __________________. Isotopes can be written two ways: 1. The name of the element followed by the mass number. Ex. Carbon - 12 2. The chemical symbol with the mass number a ...
... of ___________ but the number of _____________ may vary. Isotopes - Atoms of the ________ element that have different numbers of __________________. Isotopes can be written two ways: 1. The name of the element followed by the mass number. Ex. Carbon - 12 2. The chemical symbol with the mass number a ...
Chapter 5
... • Atomic spectra: Result from excited atoms emitting light. – Line spectra: Result from electron transitions between specific energy levels. ...
... • Atomic spectra: Result from excited atoms emitting light. – Line spectra: Result from electron transitions between specific energy levels. ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).