Solutions to the exam itself are now available.
... The ionization energies are, in turn, one small amount, two larger but close to the same, and one last one quite large. This trend reveals the electron configuration shell sequence: the first electron to go is the Al 3p electron, then come two 3s electrons, and finally a 2p electron, requiring quite ...
... The ionization energies are, in turn, one small amount, two larger but close to the same, and one last one quite large. This trend reveals the electron configuration shell sequence: the first electron to go is the Al 3p electron, then come two 3s electrons, and finally a 2p electron, requiring quite ...
Degeneracy vs. Energy Level Scaling for Hydrogen
... of Hydrogen are further away from the proton. Increasing the amount of orbiting electron charge by n2 would cancel this e↵ect and give the same potential energy for each ...
... of Hydrogen are further away from the proton. Increasing the amount of orbiting electron charge by n2 would cancel this e↵ect and give the same potential energy for each ...
CHAPTER 2: STRUCTURE OF ATOM
... The threshold frequency ال0 for a metal is 6.0 X 1013 s-1. Calculate the kinetic energy of an electron when the radiation of frequency = ال1.0 X 1014 s-1 hits the ...
... The threshold frequency ال0 for a metal is 6.0 X 1013 s-1. Calculate the kinetic energy of an electron when the radiation of frequency = ال1.0 X 1014 s-1 hits the ...
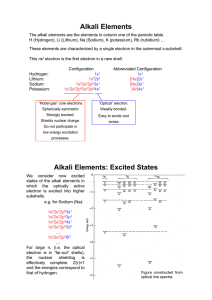
Alkali Elements Alkali Elements: Excited States
... i.e. atoms with several electrons in partially filled subshells. e.g. carbon (ground state): e.g. nitrogen (ground state): e.g. beryllium (excited state): e.g. uranium (ground state): ...
... i.e. atoms with several electrons in partially filled subshells. e.g. carbon (ground state): e.g. nitrogen (ground state): e.g. beryllium (excited state): e.g. uranium (ground state): ...
1 The Photoelectric Effect 2 Line Spectra and Energy Levels
... Geiger counter : a device commonly used to detect radiation. nucleus: positively charged, dense core of the atom consisting of neutrons (neutral) and protons (positive). Bohr model : a mechanical model of the hydrogen atom proposed by Bohr using the relationship between spectral wavelengths and ener ...
... Geiger counter : a device commonly used to detect radiation. nucleus: positively charged, dense core of the atom consisting of neutrons (neutral) and protons (positive). Bohr model : a mechanical model of the hydrogen atom proposed by Bohr using the relationship between spectral wavelengths and ener ...
Chapter 28 notes
... Geiger counter : a device commonly used to detect radiation. nucleus: positively charged, dense core of the atom consisting of neutrons (neutral) and protons (positive). Bohr model : a mechanical model of the hydrogen atom proposed by Bohr using the relationship between spectral wavelengths and ener ...
... Geiger counter : a device commonly used to detect radiation. nucleus: positively charged, dense core of the atom consisting of neutrons (neutral) and protons (positive). Bohr model : a mechanical model of the hydrogen atom proposed by Bohr using the relationship between spectral wavelengths and ener ...
32__atom_quantum____..
... D) one half as large. E) one quarter as large. 12) A new theory conforms to the correspondence principle when it A) ties two or more theories together. B) corresponds to all theories in nature. C) updates the essence of the old theory. D) accounts for verified results of the old theory. E) none of t ...
... D) one half as large. E) one quarter as large. 12) A new theory conforms to the correspondence principle when it A) ties two or more theories together. B) corresponds to all theories in nature. C) updates the essence of the old theory. D) accounts for verified results of the old theory. E) none of t ...
Chapter 7(Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Introduction to Atomic
... Some of the electronic “transitions” for a hydrogen atom .. the Bohr model The length of each of the arrows is proportional to the transition energy … regardless of whether the transition is an absorption or an emission Rank of transition energies: (a) > (b) > (d) > (c) Rank of wavelengths: l ∝ 1/∆E ...
... Some of the electronic “transitions” for a hydrogen atom .. the Bohr model The length of each of the arrows is proportional to the transition energy … regardless of whether the transition is an absorption or an emission Rank of transition energies: (a) > (b) > (d) > (c) Rank of wavelengths: l ∝ 1/∆E ...
Lectures 3-5 - University of Lethbridge
... quantized (i.e. has a fixed set of allowed values). Only orbitals whose angular momentum is an integer multiple of h/2p are “allowed”. These orbitals are called stationary states. The emission or absorption of light occurs when electrons ‘jump’ from one orbital to another. ...
... quantized (i.e. has a fixed set of allowed values). Only orbitals whose angular momentum is an integer multiple of h/2p are “allowed”. These orbitals are called stationary states. The emission or absorption of light occurs when electrons ‘jump’ from one orbital to another. ...
quantum mechanical model
... the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, the position of an electron cannot be precisely known. Instead, electrons occupy orbitals, regions of space where the electrons have the highest probability of existing. To understand the properties of an atom, there are four quantum numbers that describe an ele ...
... the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, the position of an electron cannot be precisely known. Instead, electrons occupy orbitals, regions of space where the electrons have the highest probability of existing. To understand the properties of an atom, there are four quantum numbers that describe an ele ...
112 unit II Atom Stru
... According to classical physics the radiant energy emitted by a solid could have an energy value within a continuous range. Scientists could not explain the dependence of emitted radiation on the wavelength, . According to Planck’s quantum theory, radiant energy could not have any arbitrary value; in ...
... According to classical physics the radiant energy emitted by a solid could have an energy value within a continuous range. Scientists could not explain the dependence of emitted radiation on the wavelength, . According to Planck’s quantum theory, radiant energy could not have any arbitrary value; in ...
3D Schrödinger Eq.
... What’s different for these cases? Potential energy (V) changes! (Now more protons AND other electrons) V (for q1) = kqnucleusq1/rn-1 + kq2q1/r2-1 + kq3q1/r3-1 + …. Need to account for all the interactions among the electrons Must solve for all electrons at once! (use matrices) Gets very difficult to ...
... What’s different for these cases? Potential energy (V) changes! (Now more protons AND other electrons) V (for q1) = kqnucleusq1/rn-1 + kq2q1/r2-1 + kq3q1/r3-1 + …. Need to account for all the interactions among the electrons Must solve for all electrons at once! (use matrices) Gets very difficult to ...
PHYS 221: Homework Assignment 3 This homework due just prior
... b) [2 points] Now suppose that the electron is replaced by a photon having the same wavelength as the electron had. Will it in general be Bragg reflected or not? If not, why not? c) [2 points] Now suppose that the electron is replaced by a photon having the same momentum as the electron had. Will it ...
... b) [2 points] Now suppose that the electron is replaced by a photon having the same wavelength as the electron had. Will it in general be Bragg reflected or not? If not, why not? c) [2 points] Now suppose that the electron is replaced by a photon having the same momentum as the electron had. Will it ...
Elementary my dear Watson review
... Protons are found in the nucleus The number under the chemical symbol is the atomic mass (the mass of one atom of that element) ...
... Protons are found in the nucleus The number under the chemical symbol is the atomic mass (the mass of one atom of that element) ...
Lectures 7-9 - U of L Class Index
... (i.e. has a fixed set of allowed values). Only orbitals whose angular momentum is an integer multiple of h/2p are “allowed”. These orbitals are called stationary states. The emission or absorption of light occurs when electrons ‘jump’ from one orbital to another. ...
... (i.e. has a fixed set of allowed values). Only orbitals whose angular momentum is an integer multiple of h/2p are “allowed”. These orbitals are called stationary states. The emission or absorption of light occurs when electrons ‘jump’ from one orbital to another. ...
Lectures 7-9
... (i.e. has a fixed set of allowed values). Only orbitals whose angular momentum is an integer multiple of h/2p are “allowed”. These orbitals are called stationary states. The emission or absorption of light occurs when electrons ‘jump’ from one orbital to another. ...
... (i.e. has a fixed set of allowed values). Only orbitals whose angular momentum is an integer multiple of h/2p are “allowed”. These orbitals are called stationary states. The emission or absorption of light occurs when electrons ‘jump’ from one orbital to another. ...
Atomic 1
... Where B is the fundamental unit of magnetic moment, called the Bohr Magneton e μ B 2m e We can now explain the result of the S-G experiment. If the atom was in a state with l = 0, there would be now splitting due to mL. However there is still space quantisation due to the intrinsic spin of the ...
... Where B is the fundamental unit of magnetic moment, called the Bohr Magneton e μ B 2m e We can now explain the result of the S-G experiment. If the atom was in a state with l = 0, there would be now splitting due to mL. However there is still space quantisation due to the intrinsic spin of the ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).