Hwk Set #14 - Publisher`s solutions
... know the emitted photon has energy Ephoton = hf photon = ΔE. Combine these to get ωe = 2π λc . Solve: ...
... know the emitted photon has energy Ephoton = hf photon = ΔE. Combine these to get ωe = 2π λc . Solve: ...
4.2_The_Quantum_Model_of_the_Atom1
... • Quantum numbers specify the properties of atomic orbitals and the properties of electrons in orbitals. • The principal quantum number, symbolized by n, indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron. • The angular momentum quantum number, symbolized by l, indicates the shape of the orbit ...
... • Quantum numbers specify the properties of atomic orbitals and the properties of electrons in orbitals. • The principal quantum number, symbolized by n, indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron. • The angular momentum quantum number, symbolized by l, indicates the shape of the orbit ...
Atoms: Some Basics
... provided the major impetus for developing quantum mechanics. Balmer’s empirical formula of 1885 had reproduced Angstrom’s observations of spectral lines in hydrogen to 0.1 Åaccuracy, but it was not until 1913 that Bohr gave an explanation for this based on a quantized mechanical model of the atom. ...
... provided the major impetus for developing quantum mechanics. Balmer’s empirical formula of 1885 had reproduced Angstrom’s observations of spectral lines in hydrogen to 0.1 Åaccuracy, but it was not until 1913 that Bohr gave an explanation for this based on a quantized mechanical model of the atom. ...
Mr. Knittel`s Final Review Sheet I Answers
... occurred when the alpha particles were hitting some very dense matter. This dense region must be very small since only about 1 in 8000 particles were deflected in this way. In the end, Rutherford concluded that atoms contained a nucleus—a small, dense, positively charged are in the center of the ato ...
... occurred when the alpha particles were hitting some very dense matter. This dense region must be very small since only about 1 in 8000 particles were deflected in this way. In the end, Rutherford concluded that atoms contained a nucleus—a small, dense, positively charged are in the center of the ato ...
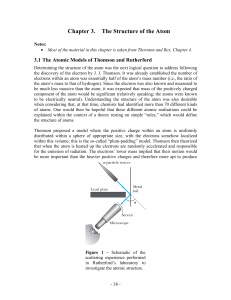
Chapter 3. The Structure of the Atom
... could see through the challenges classical physics faced and came up with imaginative solutions based on the nascent quantum theory. When considering the failure of the atomic classical model Bohr proposed four general assumptions or postulates, which he could then use to explain much of the experim ...
... could see through the challenges classical physics faced and came up with imaginative solutions based on the nascent quantum theory. When considering the failure of the atomic classical model Bohr proposed four general assumptions or postulates, which he could then use to explain much of the experim ...
Statistical complexity, Fisher-Shannon information, and Bohr orbits
... The atom can be considered a complex system. Its structure can be determined through the well established equations of Quantum Mechanics [1,2]. Depending on the set of quantum numbers defining the state of the atom, different conformations are avalaible to it. As a consequence, if the wave function ...
... The atom can be considered a complex system. Its structure can be determined through the well established equations of Quantum Mechanics [1,2]. Depending on the set of quantum numbers defining the state of the atom, different conformations are avalaible to it. As a consequence, if the wave function ...
Bohr model
... • With the increase of grid potential, more electrons move to the plate and the current rises accordingly. • For mercury atoms, when V=4.9V, the electrons make inelastic collision and leave the atom jump to a high orbit (n=2). The original electrons move off with little energy and could not reach th ...
... • With the increase of grid potential, more electrons move to the plate and the current rises accordingly. • For mercury atoms, when V=4.9V, the electrons make inelastic collision and leave the atom jump to a high orbit (n=2). The original electrons move off with little energy and could not reach th ...
The energy
... » e- arrangement is dependent upon the energy condition of the atom. (Energy of the e- is quantized) ...
... » e- arrangement is dependent upon the energy condition of the atom. (Energy of the e- is quantized) ...
Chem 121 QU 78 Due in lecture
... What are valence electrons?↑ →_________________________________________________________________ 34a Compare cation and atomic radii. ↑ →__________________________________________________________________ 36 What is the general trend of ionization energy going down a column ? ↑ →______________________ ...
... What are valence electrons?↑ →_________________________________________________________________ 34a Compare cation and atomic radii. ↑ →__________________________________________________________________ 36 What is the general trend of ionization energy going down a column ? ↑ →______________________ ...
ENT145/3 Materials Engineering Tutorial 1 (Answer) 1. Why is it
... (b) Two important quantum-mechanical concepts associated with the Bohr model of the atom are (1) that electrons are particles moving in discrete orbitals, and (2) electron energy is quantized into shells. (c) Two important refinements resulting from the wave-mechanical atomic model are (1) that ele ...
... (b) Two important quantum-mechanical concepts associated with the Bohr model of the atom are (1) that electrons are particles moving in discrete orbitals, and (2) electron energy is quantized into shells. (c) Two important refinements resulting from the wave-mechanical atomic model are (1) that ele ...
explo3
... Where, En are the energy eigen values without any corrections. 2) The above equation gives the energy levels with fine structure corrections. a) Show that the correction term does not vanish for any possible combination of n and j, but always reduces the value of uncorrected energy. b) In how many e ...
... Where, En are the energy eigen values without any corrections. 2) The above equation gives the energy levels with fine structure corrections. a) Show that the correction term does not vanish for any possible combination of n and j, but always reduces the value of uncorrected energy. b) In how many e ...
Lecture 8 - Pauli exclusion principle, particle in a box, Heisenberg
... We classify particles into two types: bosons and fermions. Bosons: particles such as photons and mesons, these have integer spin and use the plus sign. Fermions: particles such as electrons and protons, these have half-integer spin and take the minus sign. Suppose we have two electrons with wavefunc ...
... We classify particles into two types: bosons and fermions. Bosons: particles such as photons and mesons, these have integer spin and use the plus sign. Fermions: particles such as electrons and protons, these have half-integer spin and take the minus sign. Suppose we have two electrons with wavefunc ...
WBL6_Lecture_Ch27
... Thermal radiation depends only on the temperature of the radiating body. The peak wavelength increases with temperature. Classical theory could not predict the thermal radiation spectrum; Planck did so by assuming that the energies of the atoms in the material were quantized. ...
... Thermal radiation depends only on the temperature of the radiating body. The peak wavelength increases with temperature. Classical theory could not predict the thermal radiation spectrum; Planck did so by assuming that the energies of the atoms in the material were quantized. ...
Quantum Mechanics
... fields of physics and chemistry, including condensed matter physics, atomic physics, molecular physics, computational chemistry, quantum chemistry, particle physics, and nuclear physics. It is a pillar of modern physics, together with general relativity. ...
... fields of physics and chemistry, including condensed matter physics, atomic physics, molecular physics, computational chemistry, quantum chemistry, particle physics, and nuclear physics. It is a pillar of modern physics, together with general relativity. ...
Physics 411: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
... Prerequisites: PHY 240 or, equivalently MATH 435 Brief course description: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics is a two-semester course (411 and 412) and is mandatory for all physics majors pursuing the Academic Physics Concentration. Roughly, 411 deals with the foundations and development of quantum ...
... Prerequisites: PHY 240 or, equivalently MATH 435 Brief course description: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics is a two-semester course (411 and 412) and is mandatory for all physics majors pursuing the Academic Physics Concentration. Roughly, 411 deals with the foundations and development of quantum ...
Modern Physics-Syll
... focuses on two failings of classical physics - the realm of the very fast and the realm of the very small. We will make inquiries into the nature of light and the nature of matter, taking a historical approach. Students are expected to master the basic tenets of the theory of special relativity: the ...
... focuses on two failings of classical physics - the realm of the very fast and the realm of the very small. We will make inquiries into the nature of light and the nature of matter, taking a historical approach. Students are expected to master the basic tenets of the theory of special relativity: the ...
Photon model of light - High Point University
... 3. A beam of photons, each with energy, 12.09 eV is incident on a container of atomic hydrogen. To what state will a particular atom be excited? 4. A beam of photons, each with energy, 11 eV is incident on a container of atomic hydrogen. To what state will a particular atom be excited? 5. What is t ...
... 3. A beam of photons, each with energy, 12.09 eV is incident on a container of atomic hydrogen. To what state will a particular atom be excited? 4. A beam of photons, each with energy, 11 eV is incident on a container of atomic hydrogen. To what state will a particular atom be excited? 5. What is t ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).